Investments can earn compound interest, which is when the interest you earn on savings or investments accumulates interest on itself. This is in contrast to simple interest, where interest payments are based only on the principal. Compound interest can be applied to various investment types, including stocks, mutual funds, and money market accounts. It is important to understand how compounding works, as it can also apply to interest added to credit card balances, making them harder to pay back.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Compound interest is when the interest you earn on savings or investments accumulates interest on itself. |
| Calculation | Interest is calculated on the principal investment in an account, as well as on any returns earned over time. |
| Comparison to simple interest | Simple interest is when interest payments are based only on the principal. |
| Types of investment | Compound interest is earned on certain types of investments, such as certificates of deposit, fixed annuities, money market accounts, and zero-coupon bonds. |
| Other types of returns | Compound returns is a broader concept that includes compound interest, but also extends to other types of investment returns, such as dividends and capital gains. |

Certificates of deposit
CDs are considered a low-risk investment option as they are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) up to $250,000, meaning that your initial deposit is guaranteed to be returned to you at the end of the term, along with any interest earned. This makes CDs a popular choice for those looking to grow their savings without taking on too much risk.
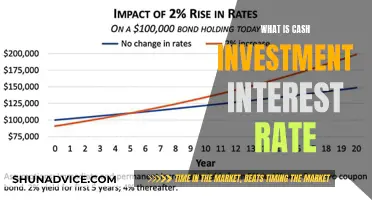
The compound interest earned on CDs can add up significantly over time, especially if you choose a longer-term CD with a higher interest rate. For example, let's say you invest $10,000 in a 5-year CD with an annual interest rate of 2%. At the end of the 5-year term, you would have earned approximately $1,040 in interest, assuming the interest is compounded annually.
It's important to note that CDs typically have early withdrawal penalties, so it's crucial to ensure you can commit to the full term before investing. Additionally, while compound interest can boost your earnings, it's also essential to consider the impact of inflation on your returns. Nevertheless, CDs remain a popular choice for those seeking a relatively safe and straightforward way to grow their savings over time.
Higher Interest Rates: Investing Incentive or Hindrance?
You may want to see also

Fixed annuities
Compound interest is when the interest you earn on savings or investments accumulates interest on itself. In other words, you earn interest on both your initial balance, called the principal, and the interest that's added to the balance over time. This is in contrast to simple interest, where interest payments are based only on the principal.
Investors can buy a fixed annuity with either a lump sum of money or a series of payments over time. Clients can take a payout immediately or defer the payment until later.
Interest Groups: Investing in Candidates?
You may want to see also

Money market accounts
Compound interest is one of the most important concepts for building long-term wealth. This is because, over time, the interest on interest adds up. For example, let's say you have a $6,000 balance that earns a 3.5% interest rate. If this was simple interest, you would only earn interest on the original $6,000. However, with compound interest, you earn interest on both your initial balance and the interest that's added to the balance over time.
When considering a money market account, it's important to shop around for the best interest rates and to understand the fees and risks associated with the account. It's also a good idea to use a compound interest calculator to check the potential value of your investment over the long term. This can help you make an informed decision about whether a money market account is the right choice for your financial goals.
Unlocking Compound Interest: Smart Investments for Long-Term Growth
You may want to see also

Dividends
Compound interest is when the interest you earn on savings or investments accumulates interest on itself. In other words, you earn interest on both your initial balance (called the principal) and the interest that's added to the balance over time. This is in contrast to simple interest, where interest payments are based only on the principal.
Compound returns are a broader concept that includes compound interest, but also extends to other types of investment returns, such as dividends and capital gains. This is commonly used in the context of stocks, mutual funds, and other types of investment vehicles.
When a company pays dividends, it typically does so on a quarterly or annual basis. The amount of the dividend is usually determined by the company's board of directors and is based on the company's financial performance and future outlook. Dividends can provide a steady stream of income for investors, especially those who are retired or living on a fixed income.
Reinvested dividends can also have a compounding effect, as they are added to the investment value, and that money also earns dividends. This can lead to even greater returns over time, as the dividends are essentially earning interest on themselves. This is why compound interest is often referred to as "the eighth wonder of the world," as it can lead to exponential growth in wealth over time.
It is important to note that compound interest can also work against you in certain circumstances, such as with high-interest debt. Therefore, it is crucial to understand how compounding works and to make informed investment decisions accordingly.
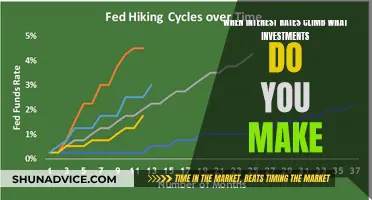
Interest Rates: Impact on Investment Decisions
You may want to see also

Capital gains
For example, if you buy shares in a company for £1000, and the value of those shares increases to £1500, you have made a capital gain of £500. If you then reinvest that £500 into another investment that earns compound interest, you will earn interest on the full £1500, rather than just the original £1000.
Compound returns can also apply to other types of investment returns, such as dividends. This is when the reinvested dividends are added to your investment value, and that money also earns dividends. For example, if you own shares in a company that pays dividends, you can choose to reinvest those dividends to buy more shares. Those new shares will also pay dividends, which can then be reinvested to buy even more shares, and so on.
It is important to note that compound returns can work against you in certain circumstances. For example, compound interest often applies to interest added to credit card balances, which can make them harder to pay back. Therefore, it is important to understand how compounding works and to manage your investments carefully.
Investing Strategies for Rising Interest Rates: Where to Focus
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Compound interest is when the interest you earn on savings or investments accumulates interest on itself. This is in contrast to simple interest, where interest payments are based only on the principal.
Compound interest is calculated on the principal investment in an account, as well as on any returns earned over time. This means that the interest you earn on the investment also earns interest.
Some investments that earn compound interest include money market accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and zero-coupon bonds.
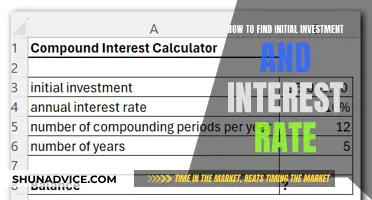
You can use a compound interest calculator to check the potential value of your investments over the long term.