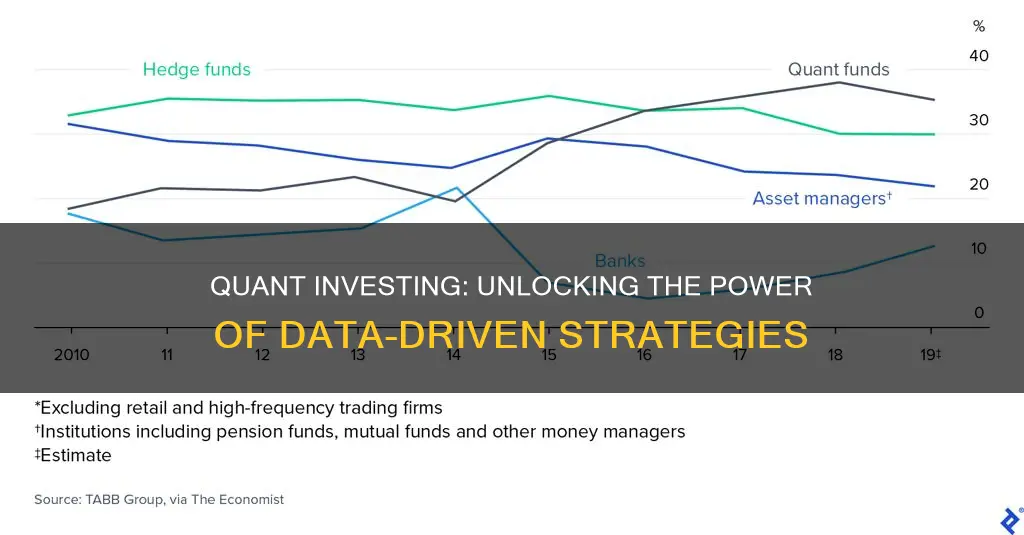
Quantitative investing, or quant investing, is a strategy that relies on mathematical models and statistical analysis to identify and select investment opportunities. It involves using advanced algorithms and data-driven techniques to make investment decisions, aiming to outperform traditional active management by leveraging historical data and market trends. This approach has gained popularity in recent years, but its effectiveness and long-term success are still subjects of debate among investors and financial experts. This paragraph will explore the concept of quant investing, its underlying principles, and the arguments for and against its effectiveness, providing insights into whether this strategy can consistently deliver positive results.
What You'll Learn
- Historical Performance: Past success of quantitative strategies varies, with some outperforming others
- Market Conditions: Quant models perform differently in volatile vs. stable markets
- Data Quality: Accuracy of predictions relies on high-quality, relevant data
- Model Complexity: Simpler models may be more robust and reliable
- Backtesting: Historical performance data helps validate the effectiveness of quant strategies

Historical Performance: Past success of quantitative strategies varies, with some outperforming others
The historical performance of quantitative investing strategies has been a subject of much debate and analysis within the financial industry. Quantitative investing, which relies on mathematical models and statistical techniques to identify investment opportunities, has gained popularity in recent decades. However, the effectiveness of these strategies is not universally accepted, and past performance can vary significantly.
One of the key challenges in assessing the success of quantitative strategies is the diverse range of approaches and the varying time periods over which they have been employed. Some quantitative models have consistently demonstrated superior performance, particularly in the realm of algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading. These models often utilize complex algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and execute trades at lightning speeds. For instance, quantitative strategies have been credited with outperforming traditional active management in certain market conditions, especially during periods of market volatility or when specific market inefficiencies are exploited.
On the other hand, critics argue that the success of quantitative investing is often overstated or attributed to luck rather than the underlying models' capabilities. The performance of these strategies can be highly dependent on market conditions and may not be sustainable over extended periods. During market trends that favor fundamental analysis and active management, quantitative strategies might struggle to keep up with the performance of traditional investment approaches. Moreover, the backtesting of quantitative models, which involves evaluating their historical performance, can sometimes lead to overfitting, where the model performs exceptionally well on historical data but fails to generalize to new, unseen data.
A comprehensive review of historical performance reveals that the success of quantitative strategies is not a one-size-fits-all concept. Some quantitative funds and hedge funds have consistently beaten market benchmarks, attracting significant investor interest. These successful strategies often involve innovative approaches, such as machine learning algorithms, factor investing, or the utilization of alternative data sources. However, many other quantitative funds have underperformed, sometimes significantly, leading to questions about the consistency and reliability of these strategies.
In conclusion, the past success of quantitative investing strategies is varied and often depends on the specific approach, market conditions, and the skill of the investors implementing these strategies. While some quantitative models have demonstrated impressive performance, others have fallen short. Investors should approach quantitative investing with a critical eye, considering the potential risks and the need for ongoing adaptation to changing market dynamics. As with any investment strategy, a thorough understanding of the underlying principles and a long-term perspective are essential to navigating the complexities of quantitative investing.
The Power of Sustainability: Reshaping Investment Strategies
You may want to see also

Market Conditions: Quant models perform differently in volatile vs. stable markets
The performance of quantitative (quant) models in financial markets is closely tied to market conditions, particularly the level of volatility and market stability. In volatile markets, characterized by rapid and significant price fluctuations, quant models often face challenges. These models typically rely on historical data and statistical patterns to make trading decisions, but during periods of high volatility, the underlying data may not accurately represent the current market dynamics. As a result, quant strategies that heavily depend on historical trends and correlations might struggle to adapt to the rapidly changing environment, leading to suboptimal performance.
In contrast, stable markets, where prices tend to move in a more predictable manner, can provide a more favorable environment for quant models. In these conditions, the models can more effectively identify and exploit consistent patterns and trends. For instance, a quant strategy that identifies mean-reversion opportunities in stable markets is more likely to generate positive returns consistently. Mean-reversion strategies assume that extreme price movements will eventually revert to the average or mean price, allowing investors to profit from short-term deviations from the norm.
The key difference in performance lies in the ability of quant models to adapt to changing market conditions. Volatile markets demand more sophisticated and dynamic models that can quickly adjust to new information and market shifts. These models might incorporate real-time data, news sentiment analysis, or alternative data sources to make more informed decisions. On the other hand, stable markets allow for simpler, more traditional quant models that focus on historical patterns and statistical relationships.
Additionally, the choice of trading strategy within a quant framework can significantly impact performance. In volatile markets, strategies that focus on risk management and hedging might be more effective, as they aim to protect capital rather than maximize gains. In contrast, during stable periods, strategies that prioritize capital appreciation and long-term growth may outperform. The flexibility and adaptability of quant models are crucial in navigating these market condition differences.
Understanding the market conditions and their impact on quant model performance is essential for investors and traders. By recognizing the strengths and limitations of quant strategies in volatile versus stable markets, investors can make more informed decisions, adjust their strategies accordingly, and potentially improve their overall investment outcomes. This awareness also highlights the importance of regularly reviewing and optimizing quant models to ensure they remain effective across various market environments.
Retirement Planning: Navigating Your Investment Journey
You may want to see also

Data Quality: Accuracy of predictions relies on high-quality, relevant data
The accuracy and reliability of quantitative investing strategies heavily depend on the quality of the data used for analysis and prediction. In the realm of quantitative finance, data is the raw material that fuels the entire process, and its quality is paramount. High-quality data is essential because it directly impacts the performance and effectiveness of quantitative models, which are designed to make investment decisions based on mathematical and statistical principles.
When it comes to quant investing, the old adage "garbage in, garbage out" holds true. This means that if the input data is inaccurate, incomplete, or irrelevant, the output predictions will also be flawed. For instance, if a quantitative model is trained on historical market data with numerous errors or biases, the model's predictions might not reflect the true market behavior, leading to poor investment outcomes. Therefore, ensuring data quality is a critical step in the development and implementation of successful quant investing strategies.
Relevance is another key aspect of data quality. Quantitative investors need data that is specific to the assets and markets they are analyzing. For example, if a strategy involves trading options, historical data on option prices, volatility, and underlying asset prices would be highly relevant. Using data that is not specific to the investment context can lead to inaccurate models and potentially costly mistakes. The data should be carefully curated and tailored to the specific needs of the investment strategy.
Moreover, data quality also encompasses the consistency and reliability of the information. Consistent data ensures that the models can learn and make predictions without confusion. Inconsistent or noisy data can introduce biases and errors, affecting the overall performance of the quantitative model. Investors should employ data cleaning techniques to remove outliers, handle missing values, and ensure data integrity. This process is crucial to building a robust and accurate predictive model.
In summary, the accuracy of predictions in quant investing is intrinsically linked to the quality of the data. High-quality, relevant data is the foundation upon which successful quantitative strategies are built. Investors must pay close attention to data collection, cleaning, and selection processes to ensure that their models are trained on the most reliable and pertinent information. By doing so, they can increase the chances of making informed investment decisions and potentially improve the overall performance of their quant investing endeavors.
Retirement Reinvented: Navigating Post-Retirement Investment Strategies
You may want to see also

Model Complexity: Simpler models may be more robust and reliable
In the realm of quantitative investing, the concept of model complexity is a critical aspect that often sparks debate among professionals. While more complex models might offer advanced capabilities, there is a growing body of evidence and practical experience suggesting that simpler models can be equally, if not more, effective and reliable. This idea challenges the conventional wisdom that more intricate models always lead to better performance.
The argument for simpler models is rooted in the idea of robustness. In quantitative finance, a robust model is one that can withstand various market conditions and still provide accurate predictions or insights. Simpler models often exhibit this robustness due to their fewer parameters and assumptions. With fewer variables to consider, these models are less prone to overfitting, which occurs when a model captures the noise in the training data instead of the underlying patterns. Overfitting can lead to poor out-of-sample performance, meaning the model fails to generalize to new, unseen data. By keeping the model simple, investors can ensure that it captures the essential relationships in the data without being swayed by minor fluctuations or outliers.
Moreover, simpler models can be more interpretable, a crucial aspect of model validation and risk management. Interpretability allows investors to understand the underlying drivers of the model's predictions, which is essential for building trust and confidence in the model. Complex models with numerous parameters can be challenging to interpret, making it difficult to identify potential issues or biases. In contrast, simpler models provide a clearer picture of the relationships between variables, enabling investors to make more informed decisions and quickly identify any discrepancies or anomalies in the data.
The reliability of a model is another critical factor, and simpler models often excel in this regard. Reliability refers to the consistency and stability of the model's performance over time. More complex models might offer higher accuracy in certain periods but may struggle to maintain this performance during market shifts or changes in market dynamics. Simpler models, with their fewer parameters, are less likely to be affected by short-term market fluctuations, ensuring more consistent and reliable results. This consistency is particularly valuable for long-term investment strategies, where stability and predictability are essential.
In conclusion, while more complex models have their advantages, the argument for simpler models in quantitative investing is compelling. Simpler models offer robustness, interpretability, and reliability, ensuring that investors can make informed decisions based on accurate and consistent insights. By embracing simplicity, investors can build more effective and trustworthy quantitative investment strategies, demonstrating that sometimes, less is indeed more in the world of quantitative finance.
Ally Invest Dividends: Unlocking the Power of Passive Income
You may want to see also

Backtesting: Historical performance data helps validate the effectiveness of quant strategies
Backtesting is a critical process in quantitative investing, serving as a rigorous method to evaluate the historical performance of quantitative trading strategies. It involves simulating the performance of a trading strategy using historical market data to assess its profitability, risk, and effectiveness over a specific period. This practice is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it provides a quantitative measure of a strategy's past performance, allowing investors to understand its potential for future success. By analyzing historical data, investors can identify patterns, trends, and market conditions that the strategy has successfully navigated, providing valuable insights into its potential adaptability.
The process of backtesting typically involves several key steps. Firstly, historical market data, including asset prices, trading volumes, and relevant economic indicators, is gathered. This data is then used to reconstruct the trading environment, ensuring that the backtest accurately reflects the conditions under which the strategy was intended to be implemented. The next step is to apply the quantitative strategy to this historical data, executing trades according to the defined rules and parameters. This simulation allows for the calculation of various performance metrics, such as return, risk exposure, drawdown, and Sharpe ratio, which provide a comprehensive assessment of the strategy's historical performance.
One of the primary benefits of backtesting is its ability to validate the effectiveness of quantitative strategies. By analyzing the results, investors can assess whether the strategy has consistently generated profits, controlled risk, and outperformed relevant benchmarks. For example, a backtest might reveal that a strategy has consistently achieved positive returns over a 10-year period, with a low volatility profile, indicating its potential for long-term success. Additionally, backtesting can help identify any flaws or limitations in the strategy, such as underperformance during specific market conditions or the presence of significant drawdowns, allowing for necessary adjustments and improvements.
Furthermore, backtesting provides a means to compare different quantitative strategies or variations of the same strategy. By running multiple backtests, investors can evaluate the performance of different parameters, entry/exit rules, or risk management techniques. This comparative analysis enables the identification of the most effective strategy or the optimal set of parameters, increasing the likelihood of successful implementation in live trading.
In summary, backtesting is an indispensable tool for quantitative investors, offering a comprehensive evaluation of historical performance. It provides a quantitative framework to assess the effectiveness of strategies, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions. Through backtesting, investors can increase their confidence in the chosen strategies, ensuring that the quantitative approach is well-validated and prepared for real-world application. This process is a critical step in the development and refinement of quantitative investing strategies, ultimately contributing to more robust and successful investment outcomes.
Paying Salaries: A Strategic Investment or a Necessary Expense?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Quantitative investing, also known as quant investing, is an investment strategy that relies on mathematical and statistical models to identify and analyze investment opportunities. It involves using data-driven techniques to build investment portfolios, often focusing on factors like price, volume, and financial ratios.
Traditional active management involves human analysts making investment decisions based on their expertise and judgment. In contrast, quant investing automates this process by using algorithms and models to identify patterns and make trading decisions. It aims to eliminate emotional biases and provide a more systematic approach.
While quant investing has shown promise in various market conditions, it may not be equally effective in all environments. During periods of market volatility or rapid changes in market dynamics, quantitative models might struggle to adapt quickly. However, many quant investors believe that a well-designed strategy can still generate consistent returns over the long term.
One of the key advantages is the ability to process vast amounts of data quickly and make rapid trading decisions. Quantitative models can identify patterns and correlations that might be difficult for humans to detect. Additionally, quant investing can help reduce emotional decision-making, leading to more disciplined and consistent trading.
Absolutely. Many investors adopt a multi-strategy approach, combining quantitative models with fundamental analysis or other qualitative insights. This hybrid approach allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of investment opportunities. By integrating different strategies, investors can potentially enhance risk-adjusted returns and better navigate various market conditions.