Buying a home is a huge financial decision, so it's important to understand how much you can afford to pay. There are many factors to consider when calculating your estimated mortgage payment, such as your income, monthly expenses, and credit score. You can use a mortgage calculator to estimate your monthly mortgage payments, but it's also possible to calculate them manually. To do this, you'll need to know the market value of the home you want to buy and your monthly income. You'll also need to consider property taxes, insurance, and other associated costs. By calculating your estimated mortgage payment, you can determine whether you can afford the home you're interested in and plan your financial future.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To determine how much house you can afford and whether you can afford the home you're looking to buy |
| Factors | Income, debt, assets, liabilities, down payment, monthly expenses, credit history, interest rate, loan term, property taxes, insurance, HOA fees, closing costs |
| Tools | Online mortgage calculators, DTI calculator, affordability calculator, refinance calculator, pre-qualification by a lender |
| Considerations | Income stability, consumption choices, loan affordability, budget, financial goals, other financial obligations |
What You'll Learn

How to calculate your estimated mortgage payment
Calculating your estimated mortgage payment is a crucial step in the process of buying a home. It gives you an idea of how much house you can comfortably afford and ensures that you don't overextend yourself financially. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to calculate your estimated mortgage payment:
Determine your monthly income:
Start by figuring out your monthly income. If you have a budget, you already know this number. If not, create a budget to make the calculations easier. Check your pay stubs from the past few months and calculate your monthly income by adding up your paychecks.
Assess your financial obligations and goals:
Consider your other financial commitments and goals. Calculate your monthly expenses, including bills, savings targets for retirement and emergency funds, and any other debts. Ensure that your estimated mortgage payment fits comfortably within your budget without compromising these other financial obligations.
Understand the components of a mortgage payment:
A typical mortgage payment consists of two main parts: the principal and the interest. The principal is the amount you borrowed from the lender, which is effectively the home's price minus the down payment. The interest is the fee charged by the lender for borrowing their money, expressed as an annual percentage rate.
Gather property information:
You'll need to know the market value or sale price of the property you're interested in purchasing. Additionally, gather information on annual property taxes, annual hazard insurance, and monthly private mortgage insurance. You can opt to use online tools that estimate these values for you.
Use a mortgage calculator:
Utilize online mortgage calculators provided by websites like Bankrate, NerdWallet, or Zillow. Input the information you've gathered, including the property price, down payment, loan term length, interest rate, property taxes, and insurance. These calculators will provide you with an estimated monthly payment and help you understand if the house fits within your budget.
Consider pre-approval and refinancing options:
Get pre-qualified or pre-approved by a lender to receive a more accurate estimate of your monthly mortgage payment. Additionally, consider using a refinance calculator to determine if refinancing your existing mortgage is a suitable option.
Remember, it's essential to calculate your estimated mortgage payment to make an informed decision about purchasing a home. This process will help you understand your financial capabilities and ensure that your monthly payments are manageable within your budget.
Unlocking Home Equity: Borrowing Against Your Mortgage
You may want to see also

What factors determine the affordability of a mortgage
When it comes to determining the affordability of a mortgage, there are several factors to consider. These include your income, debts, assets, and liabilities. Lenders will want to know how much income you make, how many demands there are on that income, and the potential for income in the future. This includes your monthly income, which can be calculated by checking your pay stubs from the past few months and adding up your paychecks.
Your income, down payment, and monthly expenses are generally base qualifiers for financing. The larger your down payment, the less you'll need to borrow and pay back in interest. A down payment of 20% or more can also help you avoid paying private mortgage insurance. Your monthly expenses include credit card payments, car payments, student loans, alimony, child support, rental property maintenance, and other personal loans with periodic payments.
Your credit history and score will also determine the rate of interest on the financing. A higher credit score indicates better creditworthiness and can lead to better interest rates. Interest rates play a pivotal role in determining mortgage affordability, as they directly impact the total amount you'll pay for your home over the loan's life. Lower interest rates mean lower monthly payments, allowing you to borrow more.
Additionally, it's important to consider the debt-to-income ratio (DTI), which is the percentage of your annual gross income that goes towards paying your mortgage and debts. Lenders typically recommend that your monthly housing payment should not exceed 28% of your gross monthly income, ensuring that you have enough money for other expenses.
Other factors that can impact mortgage affordability include property taxes, homeowners insurance, and homeowners association fees. These additional costs can add up, so it's essential to consider them when planning your budget.
Consolidating Debt: Adding to Your Mortgage?
You may want to see also

How to calculate the cost of Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)
To calculate the cost of Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI), you need to consider several factors. Firstly, PMI is only required if you take out a conventional mortgage and make a down payment of less than 20%. In this case, PMI protects the lender if you default on your mortgage.
The cost of PMI depends on several factors, including the size of your loan, your down payment amount, debt-to-income ratio, and credit score. The larger your down payment, the less your PMI will cost. The average cost of PMI for a conventional home loan is between 0.46% and 1.50% of the original loan amount per year, according to the Urban Institute's Housing Finance Policy Center. For example, PMI on a $300,000 mortgage would cost $1,380 to $4,500 per year, or $115 to $375 per month.
Your credit score also affects your PMI rate. A higher credit score will generally lead to a lower PMI cost. Additionally, the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio, which measures the percentage of the home's purchase price you're financing against its value, impacts your PMI rate. A higher LTV ratio results in a higher PMI payment.
There are different ways to make PMI payments. The most common method is to pay PMI premiums monthly along with your mortgage payment. This increases your monthly bill but allows you to spread out the premiums. Another option is to make an upfront PMI payment, paying the full premium amount for the year in one go.
You can use online calculators to estimate your PMI costs, helping you determine how much home you can afford and whether you're stretching your budget too far. These calculators consider factors such as your down payment, loan term, interest rate, and property taxes to provide an estimate of your monthly payments, including PMI.
Becoming a Mortgage Advisor: Steps to Independence
You may want to see also

How to compare different loan terms
When comparing different loan terms, it's important to do your research and shop around for the best deal. Here are some key factors to consider:
Type of Mortgage
Firstly, you need to decide on the type of mortgage you want. There are several options, including conventional loans, government-backed FHA loans, and VA loans. Each has its pros and cons. For example, FHA loans may be easier to qualify for, but they could require mortgage insurance and cost more overall. VA loans may not require a down payment, but putting at least 20% down on a conventional loan could help you secure a lower interest rate.
Interest Rates
Interest rates are a crucial factor in any loan. You'll want to compare the rates offered by different lenders and understand how they will impact your monthly payments. Fixed-rate mortgages offer stability, with the same interest rate for the entire term. Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) typically offer a lower initial rate that adjusts after a set period, which can result in higher monthly payments over time.
Loan Term
The loan term is the number of years it will take to pay off the mortgage. Common fixed-rate loan terms include 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 years. Shorter-term loans usually have lower interest rates, but the trade-off is higher monthly payments. A longer-term loan, such as 30 years, will have lower monthly payments but may result in paying more interest over time.
Down Payment
Consider how much you can afford for a down payment. Different loans have varying requirements. For example, a conventional loan may require a 20% down payment to qualify for a lower interest rate and avoid private mortgage insurance. On the other hand, VA and USDA loans may not require any down payment at all.
Fees and Closing Costs
Pay attention to all the loan terms, not just the interest rate. Some lenders may charge excessive fees and closing costs, which can add up significantly. Understand all the associated costs, including origination charges, discount points, and any other upfront fees. These can impact the overall affordability of the loan.
Your Financial Goals
Consider your short-term and long-term financial goals. If you plan to stay in the home long-term, a fixed-rate mortgage may be more suitable. If you anticipate selling within a few years, an adjustable-rate mortgage with a lower initial rate could be a more attractive option.
By carefully considering these factors and comparing loan estimates from multiple lenders, you can make an informed decision about which loan terms best fit your financial needs and goals.
Adding Your Adult Son to Your Mortgage: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

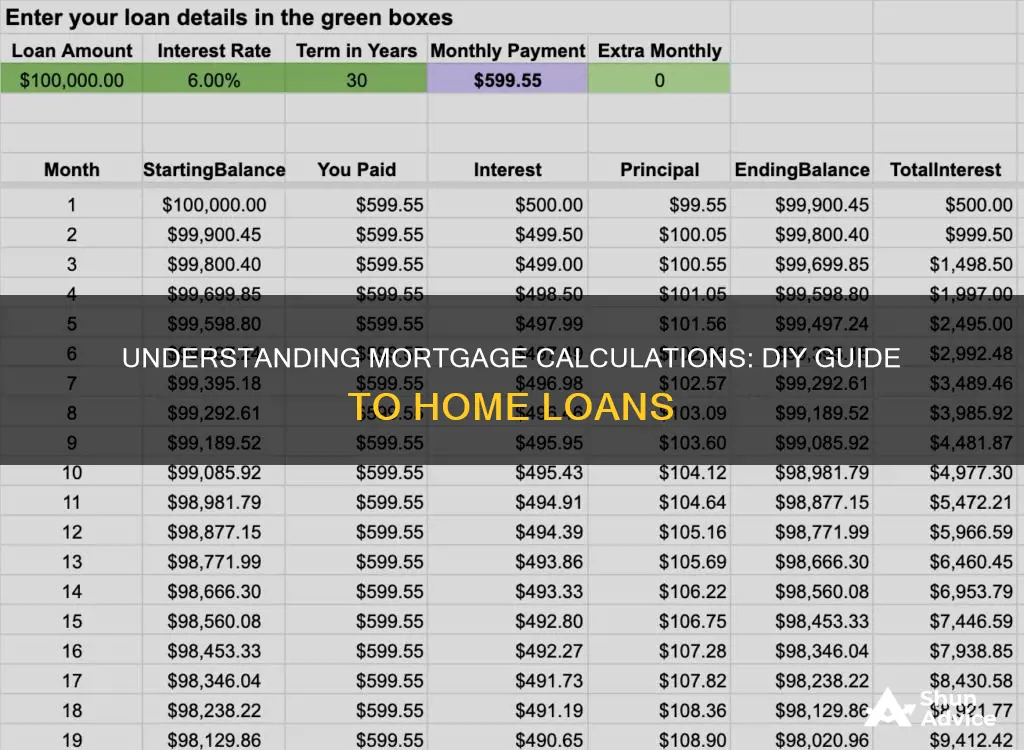
How to calculate your monthly mortgage payment
It is essential to calculate your monthly mortgage payment to ensure that you can afford the home you want to buy. It will also help you plan your financial future and determine how much money you can allocate to other expenses.
To calculate your monthly mortgage payment, you need to know the variables that go into it. These include the loan amount, interest rate, loan term length, and mortgage insurance.
The loan amount is the asking price of the house minus your down payment. The interest rate is what the lender charges you to borrow the principal or loan amount, and it is expressed as an annual percentage. The loan term length is how long you have to pay off the loan, usually 30 years but can be shorter. A longer-term loan will result in smaller monthly payments but more interest paid overall, while a shorter-term loan will have higher monthly payments but less interest paid overall. Mortgage insurance is required if your down payment is less than 20% of the home's purchase price, and this is added to your monthly payment.
You can calculate your monthly mortgage payment manually using a formula or use a mortgage calculator available online. The formula will help you calculate your mortgage payment based on the loan principal, interest, property taxes, homeowners insurance, and homeowners association (HOA) fees. HOA fees are typically not included in your monthly mortgage payment but should be considered part of your overall housing costs.
Additionally, when calculating your payment, consider using the base mortgage rate instead of the annual percentage rate (APR) since your interest rate may not include closing costs.
Carrying a Mortgage for Another: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
To figure out your mortgage, you will need to know the market value of the home you want to purchase. You can then use a mortgage calculator to estimate your monthly mortgage payments. You will need to input the amount of your down payment, the length of your loan, the interest rate, and your zip code.
Your monthly mortgage payment consists of principal, interest, taxes, and insurance (PITI).
Your income, along with your debt, assets, and liabilities, will determine your mortgage lender's decision on homebuyer affordability. A general guideline for an affordable mortgage is one that is equal to roughly 200% to 250% of your gross annual income.
The higher your down payment, the lower your monthly payment and the more favorable your interest rate will be. Most home loans require at least 3% of the price of the home as a down payment, but some loans allow for 0% down.







