Bitcoin is a highly volatile cryptocurrency, making it a challenging investment for long-term investors and an even more complex prospect for traders. One way to increase profits when investing in Bitcoin is through margin trading, also known as leveraged trading. This strategy involves borrowing capital at high-interest rates to increase leverage and, consequently, potential profits. However, it also accelerates losses when trades are unsuccessful. To calculate the profit or loss on a Bitcoin investment, investors can use online tools or a formula that considers the initial investment amount, fees, and the difference between the buying and selling price.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Volatility | High |
| Profit Calculation | Subtract the buy amount from the selling price |
| Profit Calculation Formula | profitloss = (current_BTC_price - averagecost) x total_BTC |
| Profit Calculation Example | If you bought 1 BTC for $10,000 and sold it for $15,000, you made a 50% profit ($5,000) |
| Taxes | In the US, you must pay capital gains taxes when you sell Bitcoin for a profit |
| Risk | Margin trading is risky and increases losses when unsuccessful |
What You'll Learn

Calculating profit and loss
There are several ways to calculate profit and loss on Bitcoin investments. One simple method is to subtract the initial purchase price from the eventual selling price. For example, if you bought 1 BTC for $10,000 and sold it for $15,000, you made a profit of $5,000. This can also be expressed as a percentage, in this case, a 50% profit.
Another way to calculate profit and loss is to use an average cost basis. This method is useful if you have bought Bitcoin at different prices over time. To do this, you calculate the average cost of all your Bitcoin purchases and then subtract that from the current market price. This will give you your profit or loss per Bitcoin.
For example, let's say you bought 1 BTC for $10,000, then bought another 0.5 BTC for $5,000 when the price dropped to $8,000. Your average cost per Bitcoin would be $8,666.67 [((1x$10,000)+(0.5x$8,000))/1.5]. If you then sold 1 BTC for $15,000, your profit would be $6,333.33 ($15,000 - $8,666.67).
It is also important to consider fees and taxes when calculating profit and loss. Some exchanges may charge transaction fees, deposit fees, or withdrawal fees, which can impact your overall profit or loss. Additionally, in some countries, you may be required to pay capital gains taxes on any profits made from Bitcoin investments.
Finally, it is worth noting that while calculating profit and loss can be straightforward, the decision of when to buy or sell Bitcoin is much more complex. The extreme volatility of the cryptocurrency market means that the potential for large profits is accompanied by the risk of significant losses. As such, it is crucial to understand the risks involved and to only invest what you can afford to lose.
UK Guide: Getting Started with Bitcoin Investments
You may want to see also

The impact of fees
When investing in Bitcoin, fees can have a significant impact on your overall profitability. Even a small fee of 0.1% can add up quickly, especially for active traders. For instance, if you're trading $10,000 per day, a 0.1% fee would amount to a $10 loss per trade. Multiply that by the number of trades you execute daily, and you could be losing a substantial sum.
The issue of fees becomes even more critical for high-frequency traders who might execute dozens of trades in a single day. In such cases, the fees can accumulate to a point where they eat into a significant portion of the profits. Therefore, choosing a crypto exchange with low fees can be strategic in maximising your profitability.
Trading fees don't just eat into your profits; they can also severely limit your trading strategies. For example, day traders buy and sell assets within the same day, often executing multiple trades in a single session. However, each of these trades incurs a fee, limiting the range of strategies a day trader can employ.
Another strategy, scalping, involves making a large number of small trades to profit off minor price changes. This approach is even more sensitive to trading fees, as the profit margins are often razor-thin. A high fee structure can make scalping virtually impossible, as the costs could easily exceed the profits.
The psychological impact of trading fees is another often-overlooked aspect. Knowing that you'll incur a fee with every trade can make you hesitant to execute trades that you would otherwise consider low-risk and profitable. This hesitation can lead to missed opportunities, further emphasizing the importance of low fees in crypto trading.
Over the long term, the impact of fees compounds. Each dollar paid in fees is a dollar less that you have to invest. Over time, this can result in a significantly smaller portfolio, especially considering the potential returns that those lost dollars could have earned if they were invested.
When it comes to fees, it's important to consider not only the cost of trading but also the cost of depositing and withdrawing funds. Some platforms charge a fixed amount or a percentage for withdrawals, while others may have lower fees for certain cryptocurrencies.
Additionally, transaction fees, also known as mining fees, are paid by Bitcoin owners whenever they transfer funds to another Bitcoin address. These fees allow users to prioritise their transactions and get them included faster into the blockchain. Miners will prioritise transactions with higher fees attached, so if you want your transaction confirmed faster, you may need to submit it with a larger fee.
In summary, fees play a crucial role in determining the profitability of Bitcoin investments. They can impact your overall earnings, limit your trading strategies, affect your decision-making, and compound over time. By choosing platforms with lower fees and being mindful of transaction fees, you can maximise your potential profits when investing in Bitcoin.
The Ultimate Guide: Getting Started with Bitcoin
You may want to see also

The volatility of Bitcoin
Bitcoin is considered a highly volatile asset. Volatility is a measure of how much the price of a financial asset varies over time. The volatility of Bitcoin is measured by how much its price fluctuates relative to its average price over a period of time.
Volatility means that an asset is risky to hold, as its value may substantially increase or decrease on any given day. The more volatile an asset is, the more people will want to limit their exposure to it, either by not holding it or by hedging. Volatility also increases the cost of hedging, a major contributor to the price of merchant services. If Bitcoin volatility decreases, the cost of converting into and out of Bitcoin will also decrease.
Bitcoin's volatility is influenced by the speculative nature of the cryptocurrency industry. Crypto investors bet on Bitcoin's price going up or down to make profits, causing sudden price increases or decreases, leading to volatility.
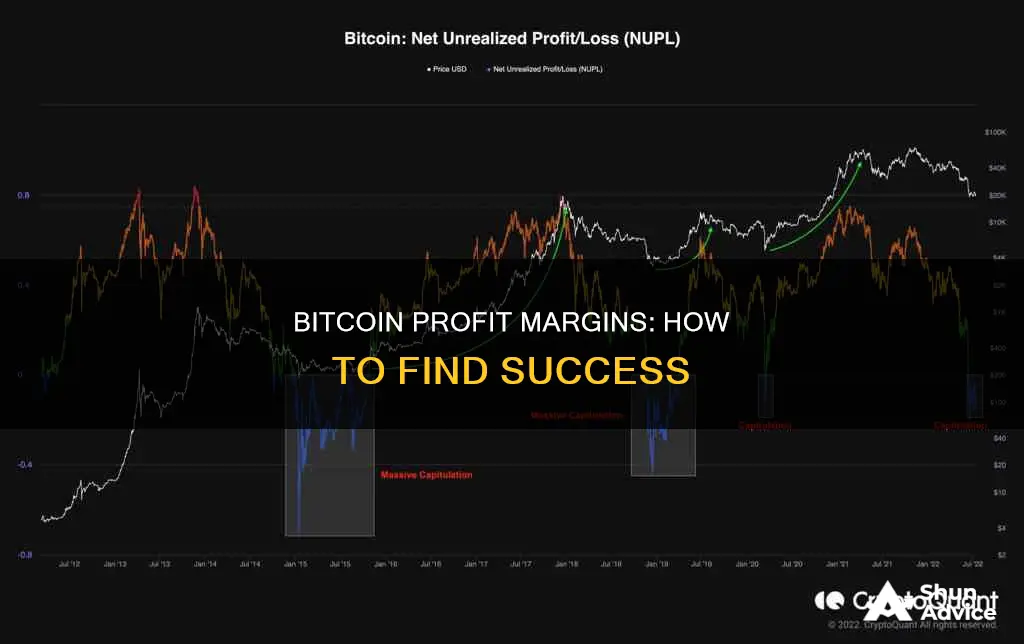
Bitcoin's price swings increased substantially in November 2022, recording a 10-day volatility of more than 100%. Despite the rise of several cryptocurrencies since 2021, Bitcoin maintained the highest market share ("dominance") of all cryptocurrencies in 2022.
The potential for high volatility in Bitcoin's price means that investors need to keep a close eye on their profits. For example, Bitcoin hit an all-time high of just under $69,000 in November 2021, but as of June 2024, its price was around $24,000. This would have resulted in a significant loss for those who bought at the peak. However, for those who bought in January 2021 and sold at its peak, there would have been a 115% gain.
The extreme volatility of Bitcoin makes it a challenge for long-term investors and an even more complex prospect for short-term traders. Drops and gains of 10% to 20% in a single day are not uncommon.
The Ultimate Guide to Investing in Bitcoin Code
You may want to see also

The risks of margin trading
Margin trading is a risky business, and it is important to understand the mechanics, risks, and rewards before engaging in it. Here are some of the key risks associated with margin trading:
- Magnified Losses: While margin trading can amplify gains, it can also amplify losses. If the market moves against your position, you may lose more than your initial investment. In some cases, you may even lose more than your entire account balance.
- Interest Payments: Margin trading involves borrowing funds, which come with interest payments. These interest rates can be high, especially for digital asset investments, and can quickly add up if you hold the position for an extended period.
- Margin Calls: If your margin position moves against you and you don't have enough funds in your account to cover the loss, you will receive a margin call. This means you will be required to deposit additional funds to maintain your position. If you are unable to do so, the exchange may forcibly liquidate your position, selling your assets to cover the loss.
- Liquidation: If you cannot meet the margin requirements for your leveraged position, the exchange may forcibly liquidate your assets to meet the minimum margin requirements. This is an automatic process, and assets not associated with the trade may also be sold to repay borrowed funds.
- High Volatility: Crypto is a highly volatile market, and prices can fluctuate significantly in a short period. This makes it difficult to predict market movements and increases the risk of losses.
- Complex Nature: Margin trading is more complex than regular trading, with additional jargon and concepts to understand, such as long and short positions, isolated and cross-margin trading, and margin calls and liquidation.
- Emotional Factor: Margin trading can be emotionally challenging, as it involves borrowing money and taking on more risk. It is important to set strict risk management rules and not let emotions dictate your trading decisions.
- Suitable for Experts: Margin trading is generally not recommended for beginners or occasional speculators. It is best suited for experienced traders who are familiar with the fundamentals and have the expertise to manage the risks effectively.
- Additional Costs: Aside from interest payments, there may be other additional costs associated with margin trading, such as trading fees, rollover fees, and maintenance fees. These costs can eat into your profits.
- Limited to Specific Exchanges: Not all crypto exchanges offer margin trading, and those that do may have different fee structures, leverage amounts, and requirements. It is important to carefully research and compare different exchanges before choosing one.
In conclusion, margin trading in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies can be a lucrative opportunity for investors to magnify their gains. However, it comes with significant risks that should not be taken lightly. It is crucial to understand the mechanics, risks, and rewards of margin trading before engaging in it and to only invest what you can afford to lose.
Best Apps to Invest in Dogecoin
You may want to see also

Taxation on Bitcoin profits
Taxation Rules:
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States treats Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as property, specifically a capital asset, rather than a currency. This classification has significant tax implications. When you buy, sell, trade, or use Bitcoin to pay for goods and services, it triggers tax consequences similar to those of stocks or exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Timing of Taxation:
You are taxed on Bitcoin profits when you sell or trade your holdings. If you simply hold Bitcoin without selling or trading, you don't owe any taxes. However, if you receive Bitcoin as payment for goods or services, or through mining, the value is immediately taxable as earned income.
Tax Rates:
The tax rate on Bitcoin profits depends on two main factors: the duration of ownership and total income for the year. If you owned Bitcoin for one year or less before selling, your profits are taxed at regular income tax rates, ranging from 10% to 37%. On the other hand, if you held Bitcoin for more than a year, your profits are subject to long-term capital gains tax rates, which range from 0% to 20%.
Reporting Requirements:
The IRS has added specific questions about cryptocurrency transactions on tax return forms, such as "At any time during 2023, did you: (a) receive (as a reward, award, or payment for property or services); or (b) sell, exchange, or otherwise dispose of a digital asset (or a financial interest in a digital asset)?" It is important to carefully record the fair market value of your Bitcoin at the time of acquisition and disposition to ensure accurate reporting.
Tax Deductions and Losses:
If you sell Bitcoin for a loss, you can write off those losses on your tax return, up to a maximum of $3,000 per year. This can help reduce your taxable income. Additionally, unlike stocks, cryptocurrencies are exempt from the wash-sale rule, which means you can sell Bitcoin for a loss, claim the tax break, and immediately buy it back.
Penalties for Non-Compliance:
Failure to report Bitcoin transactions and pay the required taxes can result in penalties and interest charges. The IRS has various methods to track cryptocurrency transactions and enforce tax compliance, including issuing subpoenas to popular crypto exchanges. Underreporting investment earnings may also increase the likelihood of triggering a full-on audit.
Institutional Bitcoin Adoption: Who's In and Why?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are a few ways to calculate your profit margin. One way is to subtract the amount you paid for your Bitcoin from the amount you sold it for. Another way is to use an online calculator, such as the one offered by Forbes or Crypto Profit Calculator. These calculators take into account factors such as investment and exit fees, as well as the initial and selling price of your Bitcoin.
Margin trading, also known as leveraged trading, is a form of trading that uses borrowed funds to trade larger amounts of Bitcoin. For example, if you have 1 Bitcoin, you can borrow up to 2 Bitcoins more and trade as if you had 3 Bitcoins. While this increases your profits when successful, it also accelerates your losses when unsuccessful.
Bitcoin is extremely volatile. In November 2021, it hit an all-time high of just under $69,000, but as of June 2024, it is worth around $24,000. That said, if you bought Bitcoin in January 2021 and sold it at its peak price in November 2021, you would have made a 115% gain.
In the US, you must pay capital gains taxes when you sell Bitcoin for a profit. The IRS treats all cryptocurrencies as capital assets, meaning you will pay capital gains taxes on any profits you make from selling your Bitcoin. The percentage you pay will depend on your federal tax bracket, which can range from 10% to 37%.