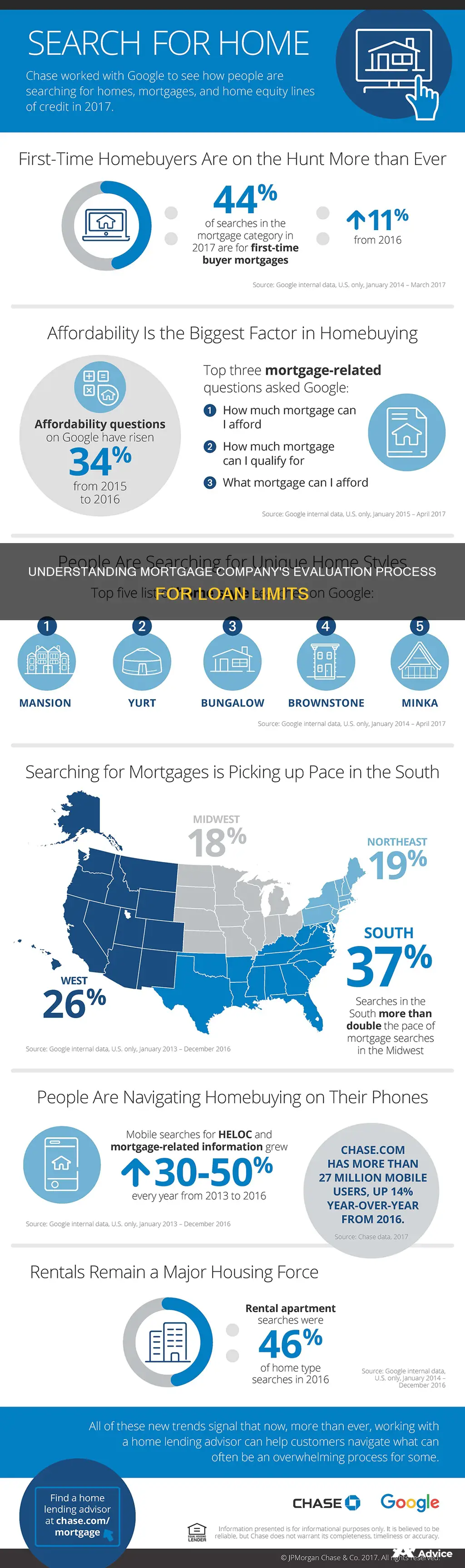
When applying for a mortgage, it is important to understand how much you can afford to pay. Mortgage lenders use a formula to determine the level of risk of a prospective home buyer. This formula is based on several factors, including income, debt, assets, liabilities, and credit score. A general guideline for an affordable mortgage is one that is roughly 200% to 250% of your gross annual income. Lenders also consider an applicant's debt-to-income ratio, credit history, and financial profile to determine the maximum loan amount.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Income | Lenders want to know how much income an applicant makes, how many demands there are on that income, and the potential for both in the future. |
| Debt | Lenders use a formula to determine the level of risk of a prospective home buyer. The formula varies but is generally determined by using the applicant’s credit score. |
| Assets | Lenders will consider an applicant's assets. |
| Liabilities | Lenders will consider an applicant's liabilities. |
| Credit score | A higher credit score generally results in a higher maximum loan amount. |
| Debt-to-income ratio | Lenders will consider an applicant's debt-to-income ratio. |
| Loan length | Lenders will consider the loan length. |
| Loan purpose | Lenders will consider the purpose of the loan. |
| Loan type | Lenders will consider the type of loan. |
| Loan collateral | Lenders will consider whether the loan is backed by collateral. |
| Lender criteria | Lenders will consider their own criteria. |
| Home insurance | Lenders will consider whether the applicant has home insurance. |
| Maintenance | Lenders will consider whether the applicant can maintain the property. |
| Utilities | Lenders will consider whether the applicant can afford utilities. |
| Escrow account | Lenders may require the borrower to pay into an escrow account. |
What You'll Learn

Income
Lenders will also look at your monthly income to determine your mortgage-to-income ratio, also known as the front-end ratio. This is the percentage of your yearly gross income that can be dedicated to paying your mortgage each month. The general rule of thumb is that this should not exceed 28% of your gross income, although lenders may allow borrowers to exceed this, and some even let borrowers exceed 40%. This is also known as the debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, which calculates the percentage of your gross income required to cover your debts, including credit card payments, child support, and other loans.
Calculating your maximum monthly debt based on this ratio can be done by multiplying your gross income by 0.43 and dividing by 12. Lenders recommend that your DTI not exceed 43% of your gross income, although it is possible to qualify with a DTI as high as 50% with some lenders.
In addition to your gross income, lenders will also consider your net income, which is your income after deductions such as taxes, retirement account investments, and other pretax deductions. Using the 35%/45% rule, if your income is $5,000 before deductions, your maximum monthly mortgage payment would be $1,750 ($5,000 x 0.35 = $1,750). If it’s $4,000 after deductions, your upper limit for your monthly payments would be $1,800 ($4,000 x 0.45 = $1,800).
Other factors that will be considered along with your income include your credit score, assets, existing debt, and down payment.
Retirement Savings: Easier Mortgage Approval with a 401k
You may want to see also

Debt
When determining your mortgage limit, lenders will consider your debt situation and how you manage your debt. This is reflected in your credit score and debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, which lenders use to qualify you for a mortgage.
Lenders will look at your credit score, which is influenced by the consistency of your debt payments and the length of your credit history. They will also assess your DTI ratio, calculated by dividing your monthly debt payments, including housing costs and other debts, by your monthly gross income. Most mortgage programs require a DTI ratio of 43% or less.
The type and amount of debt you have will impact your mortgage-borrowing potential. Lenders typically consider the entire balance of your debt to calculate the monthly payments required to clear it. Higher debt balances will work against your mortgage-borrowing potential, as they affect your credit utilization rate and debt service ratios.
To improve your chances of mortgage approval, you can take steps to lower your DTI ratio. This can be achieved by increasing your income, paying down your debt, or considering a less expensive home with a lower mortgage payment. Maintaining a credit utilization ratio below 30% across revolving credit accounts can also support a healthy credit score.
Understanding Your Mortgage Bill: A Breakdown
You may want to see also

Assets
Mortgage lenders will carefully review your application, assessing your income, credit history, employment stability, and other financial factors. They will also look at your recurring monthly debts or liabilities, such as credit card payments, and your debt-to-income ratio. Lenders will also want to see your bank statements, including checking, savings, and other deposit accounts. Statements should cover at least the last two to three months and clearly show your name, account number, and balance.
You can include various assets on your mortgage application. These include money in checking accounts, savings accounts, money market accounts, and certificates of deposit. You should also list all your investment accounts, like brokerage accounts, IRAs, 401(k)s, stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other securities. You can also include any other properties you own, whether they are investment properties or vacation homes, along with their estimated value. Even though vehicles are not typically highly liquid assets, you can still include them on your application, along with valuable items like art, antiques, jewelry, or collectibles.
Physical assets are important to lenders because they can be converted into cash quickly. For example, selling your car or jewelry can be done in a reasonable amount of time. Some assets have a clear value, like cash and stocks, while others, like your car, home, or artwork, may require an appraiser to determine their value.
Retirement assets are often used for down payments, closing costs, and reserves, though underwriters like to see that you also have some money in the bank. If you are using business accounts for assets, you will likely need to be the 100% owner.
Understanding the Components of Your Mortgage
You may want to see also

Liabilities
When evaluating your mortgage application, lenders will assess your liabilities and calculate your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio. This ratio compares your monthly debt payments, including your potential mortgage payment, to your gross income before taxes. A lower DTI ratio is generally preferred by lenders as it indicates a stronger financial position. The DTI ratio is used to determine whether you have sufficient income to afford the mortgage payments.
The maximum amount you can borrow for a mortgage is influenced by your liabilities and DTI ratio. For a qualified mortgage backed by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac, the DTI ratio is typically capped at 43%. Lenders often look for a DTI lower than 36%, with no more than 28% allocated towards the mortgage itself. If your DTI ratio is higher, you may face challenges in obtaining a mortgage or be limited to specific loan options.
Additionally, it is important to note that liabilities can impact your creditworthiness. Your credit score and history are essential factors in the mortgage application process. Higher liabilities may affect your credit score, potentially leading to higher interest rates or difficulties in obtaining a mortgage.
To improve your chances of securing a mortgage, it is advisable to manage your liabilities effectively. This can be achieved by increasing your income, reducing your monthly liabilities, and paying off your debts without incurring new ones. By proactively addressing your liabilities, you can enhance your financial profile and increase your chances of qualifying for a mortgage.
Lawsuits and Mortgages: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Credit score
A higher credit score increases the chances of securing the best mortgage rates. Credit scores in the mid- to high-600s are considered good, and most people need a score of 580-620 to qualify for a home loan. A score at the higher end of this range will bring more options and lower interest rates. Credit scores are based on data from credit reports, including payment history, credit mix, length of credit history, and other criteria. The percentage of the score that reflects payment history is 35%, according to FICO.
To improve one's credit score in preparation for a mortgage application, it is recommended to make timely payments, especially in full on revolving credit, and keep debt at a manageable level. Other suggestions include increasing one's credit limit on existing cards, being cautious when opening or closing accounts, and regularly checking credit reports for errors. Each new credit inquiry temporarily lowers one's score, so it is advisable to avoid applying for new credit before getting a mortgage. Additionally, maintaining a low credit utilisation rate, calculated by dividing total credit card balances by total credit limits, is important for a good credit score.
Valuing Mortgage Servicing Rights: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A mortgage company will determine your limit based on several factors, including your income, debt, assets, and liabilities. They will also consider your credit score and credit history. Your income, down payment, and monthly expenses are generally the base qualifiers for financing, while your credit history and score determine the rate of interest on the financing.
The formula for determining the level of risk of a prospective home buyer varies but is generally determined by using the applicant's credit score. Applicants with a low credit score can expect to pay a higher interest rate, also referred to as an annual percentage rate (APR) on their loan.
A good debt-to-income ratio is generally considered to be 36% or less. Lenders will also consider your loan length, loan purpose, and whether the loan is backed by collateral.