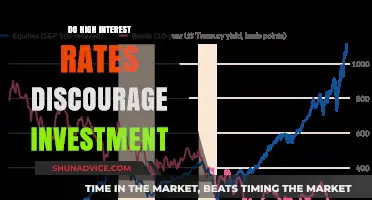
The relationship between interest rates and saving and investment behavior is a crucial aspect of economic theory. When interest rates increase, it often has a significant impact on the decisions individuals and businesses make regarding savings and investments. Higher interest rates can encourage people to save more, as the returns on savings accounts and bonds become more attractive. However, this increased saving can also lead to a decrease in consumer spending, which may affect businesses and the overall economy. On the other hand, rising interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, potentially discouraging investment in new projects or ventures. This dynamic interplay between interest rates, savings, and investment is a key factor in understanding economic trends and policy decisions.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Saving | - Higher interest rates can encourage saving as individuals may prefer to keep their money in savings accounts or other low-risk investments. - People might save more to take advantage of the higher returns, especially if they perceive a risk of inflation. - Increased saving can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, which may impact the economy. |
| Investment | - Rising interest rates often make borrowing more expensive, which can reduce investment in businesses and real estate. - Investors may shift their focus to fixed-income securities like bonds, as they offer higher yields. - The cost of capital increases, potentially discouraging long-term investments and projects with high upfront costs. |
| Consumer Behavior | - Higher interest rates can lead to a shift in consumer spending patterns, with people potentially saving more and spending less on discretionary items. - This may result in a decrease in the demand for non-essential goods and services. |
| Economic Impact | - Increased saving and reduced investment can slow down economic growth. - It may also impact the housing market, making it less attractive for buyers who take out mortgages. - Central banks often use interest rates as a tool to manage inflation and economic stability. |
| Financial Markets | - Interest rate hikes can cause volatility in financial markets, affecting stock prices and bond yields. - Investors might rebalance their portfolios to include more fixed-income investments. |
| Long-Term Savings | - Over time, higher interest rates can benefit long-term savers, especially those with retirement plans or long-term financial goals. |
| Inflation | - Rising interest rates are often used to combat inflation by reducing the money supply and slowing economic growth. - This can make borrowing more expensive, potentially impacting investment decisions. |
What You'll Learn
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Higher rates prompt more savings, shifting spending to investment
- Savings Incentive: Increased rates encourage saving, as returns on savings grow
- Investment Demand: Higher rates attract investment, as returns on investments increase
- Consumption Impact: Rising rates may reduce consumption, freeing up funds for savings
- Economic Effect: Higher interest rates can stimulate investment and economic growth

Interest Rate Sensitivity: Higher rates prompt more savings, shifting spending to investment
The relationship between interest rates and savings behavior is a fascinating aspect of economic dynamics. When interest rates rise, it triggers a chain reaction that significantly impacts individuals' savings and investment decisions. This phenomenon is often referred to as 'Interest Rate Sensitivity'.
As interest rates increase, the cost of borrowing becomes more expensive. This directly influences consumers' spending habits. Higher interest rates discourage borrowing for discretionary spending, such as luxury purchases or vacations. Instead, individuals tend to save more, viewing it as a more attractive option due to the potential for earning higher returns. The increased savings rate is a direct response to the higher interest rates, as individuals aim to maximize the value of their money over time.
This shift in behavior has a ripple effect on the investment landscape. With more people saving, there is a larger pool of funds available for investment. Higher interest rates also make fixed-income investments, such as bonds and fixed deposits, more appealing. As a result, individuals may redirect their savings towards these secure investment options, seeking capital preservation and income generation. This shift in spending and saving patterns can stimulate investment in various sectors, including real estate, infrastructure, and the stock market, as investors seek opportunities to grow their wealth.
The impact of higher interest rates on savings and investment is a delicate balance. While increased savings can provide a financial cushion and contribute to economic stability, it may also lead to reduced consumer spending in the short term. This potential trade-off highlights the importance of understanding interest rate sensitivity and its implications for personal finance and economic policy.
In summary, higher interest rates have a profound effect on savings and investment behavior. They encourage individuals to save more, leading to a potential increase in investment opportunities. This sensitivity to interest rate changes underscores the dynamic nature of financial markets and the intricate relationship between monetary policy and individual economic decisions.
Understanding Interest: How Simple and Compound Rates Impact Your Investment Growth
You may want to see also

Savings Incentive: Increased rates encourage saving, as returns on savings grow
Increased interest rates can significantly impact savings and investment behaviors, primarily through the incentive they provide for savers. When interest rates rise, the returns on savings accounts and fixed-income investments also increase. This is a direct and powerful incentive for individuals to save more. Here's a detailed breakdown of how this works:
Attracting Savings: Higher interest rates make savings accounts more attractive to potential depositors. When the interest rate on a savings account increases, the account holder will earn more on their deposits over time. This encourages people to open new savings accounts or move their money from lower-yielding accounts to higher-yielding ones. As a result, banks and financial institutions may see an increase in the number of new savings accounts opened and a higher volume of deposits.
Encouraging Long-Term Savings: The incentive provided by higher interest rates can also encourage individuals to save for the long term. People are more likely to open a savings account with a higher interest rate, knowing that their money will grow faster over time. This is particularly beneficial for retirement planning, education funds, or any long-term financial goals, as the compound interest effect becomes more pronounced.
Impact on Investment Decisions: The effect of increased interest rates on savings can also influence investment decisions. When savings accounts offer competitive returns, investors might be less inclined to seek alternative investments with potentially lower yields. This shift in investment behavior can lead to a more balanced approach, with a portion of the portfolio allocated to savings accounts and other fixed-income securities.
Financial Planning and Security: Higher interest rates provide an incentive for individuals to engage in more comprehensive financial planning. With the potential for greater returns, people may be motivated to review their financial strategies, consider tax-efficient savings options, and explore ways to maximize their savings and investments. This can lead to improved financial security and a more stable financial future.
In summary, increased interest rates serve as a powerful incentive for saving and investing. They encourage individuals to save more, attract new savers, and promote long-term financial planning. Understanding these effects can help individuals make informed decisions about their savings and investment strategies, ultimately contributing to a more secure financial future.
Unlock Argentina's Investment Potential: Navigating Interest Rates for Success
You may want to see also

Investment Demand: Higher rates attract investment, as returns on investments increase
When interest rates rise, it has a significant impact on investment demand, primarily because higher rates offer more attractive returns on investments. This phenomenon is a fundamental principle in the world of finance and economics. As interest rates increase, the cost of borrowing money becomes more expensive, which may discourage some individuals and businesses from taking out loans. However, for investors, this higher cost of borrowing translates into higher potential returns on their investments.
In the context of investment demand, higher interest rates can stimulate economic activity. When rates are elevated, investors are more inclined to channel their funds into various investment vehicles such as bonds, stocks, real estate, or other financial instruments. This is because these investments provide the potential for higher returns, which can be particularly appealing during periods of economic uncertainty when other investment options may offer less favorable outcomes. As a result, the increased demand for investments can lead to a surge in capital flowing into the market, driving up asset prices and potentially creating a positive feedback loop.
The relationship between interest rates and investment demand is a delicate balance. While higher rates can attract investors, they may also lead to a shift in investment strategies. Some investors might opt for safer, lower-risk investments as the higher rates make these options more appealing. This shift can impact the overall risk profile of the investment market, potentially affecting the allocation of capital across different sectors and industries.
Additionally, the impact of rising interest rates on investment demand can have a ripple effect on the broader economy. Increased investment activity can stimulate business expansion, job creation, and overall economic growth. It encourages businesses to invest in new projects, hire more employees, and expand their operations, which, in turn, can lead to higher consumer spending and increased demand for goods and services. This positive economic cycle can further reinforce the initial effect of higher interest rates on investment demand.
In summary, higher interest rates have a direct and positive influence on investment demand. They encourage investors to seek out more lucrative investment opportunities, leading to increased capital allocation and economic activity. This mechanism is a crucial aspect of monetary policy and can be a powerful tool for central banks and governments to manage economic growth and stability. Understanding this relationship is essential for investors, policymakers, and anyone interested in the intricate dynamics between interest rates and the financial markets.
Unlocking the Secrets: Are You Ready to Invest?
You may want to see also

Consumption Impact: Rising rates may reduce consumption, freeing up funds for savings
The relationship between interest rates and consumption is a complex one, and understanding its dynamics is crucial for individuals and policymakers alike. When interest rates rise, it can have a significant impact on consumer behavior, particularly in terms of spending and saving patterns. Here's an exploration of how higher interest rates might influence consumption and the potential benefits for savings.
As interest rates increase, borrowing becomes more expensive. This is especially true for consumers who rely on credit cards, personal loans, or variable-rate mortgages. When the cost of borrowing rises, individuals may be incentivized to reduce their spending on discretionary items. For instance, a higher interest rate environment might discourage people from making impulse purchases, such as buying the latest electronic gadgets or taking frequent vacations. This shift in behavior can lead to a decrease in overall consumption, as individuals opt to save more instead of spending on non-essential goods and services.
The reduction in consumption can have a ripple effect on the economy. Lower consumption might lead to decreased demand for goods and services, which could potentially slow down economic growth. However, this impact is often temporary, as consumers may adjust their spending habits over time. Many individuals might start prioritizing savings, especially if they anticipate future rate hikes or economic uncertainties.
This shift towards saving can have several positive outcomes. Firstly, it provides individuals with a financial cushion, allowing them to build an emergency fund or save for specific goals. Higher interest rates can encourage people to open savings accounts or invest in fixed-income securities, such as bonds, which offer higher returns. As a result, the funds that would have been spent on consumption are now being channeled into savings and investments, potentially increasing the overall savings rate.
Moreover, the increased savings can contribute to a more stable financial environment. With more money being saved, there is a reduced reliance on credit, which can lead to a healthier balance sheet for individuals and potentially lower the risk of widespread defaults on loans. This stability can, in turn, encourage businesses to invest, knowing that consumer spending might not be as volatile.
In summary, rising interest rates can indirectly influence consumption patterns, leading to a more prudent approach to spending. While this may result in a temporary reduction in consumption, it also presents an opportunity for individuals to enhance their savings and investment strategies. Understanding these dynamics is essential for making informed financial decisions and can contribute to a more robust and resilient economy.
Interest Groups' Financial Investment in Political Candidates: A Deep Dive
You may want to see also

Economic Effect: Higher interest rates can stimulate investment and economic growth
Higher interest rates can have a significant impact on the economy, particularly in stimulating investment and fostering economic growth. When interest rates rise, it creates a ripple effect throughout the financial system, influencing the decisions of both individuals and businesses. One of the primary effects is on savings and investment behavior. As interest rates increase, the opportunity cost of saving money becomes higher. This means that individuals may be less inclined to save a large portion of their income, as the returns on savings accounts or bonds become more attractive. As a result, people might opt to spend more, which can boost consumption and, in turn, stimulate economic activity.
For businesses, higher interest rates can have a dual impact. On the one hand, borrowing costs for companies increase, which may discourage new investments, especially for those with high capital requirements. However, this effect is often offset by the positive impact on business confidence and investment in the long term. When interest rates rise, it signals a stronger economy and reduced inflationary pressures, which can encourage businesses to invest in expansion projects, research and development, and capital improvements. This increased investment can lead to job creation, higher productivity, and ultimately, economic growth.
The relationship between interest rates and investment is particularly important in the context of capital allocation. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, which can lead to a shift in investment decisions. Businesses may choose to invest in projects with higher expected returns, as the cost of capital becomes a more significant factor in their calculations. This can result in a more efficient allocation of resources, as funds are directed towards ventures with the highest potential for growth and profitability. As a result, the economy benefits from increased productivity and innovation.
Additionally, higher interest rates can attract foreign investment, further stimulating economic growth. When interest rates rise, foreign investors may be more inclined to park their funds in domestic markets, as the potential returns become more attractive. This influx of foreign capital can strengthen the local currency, making exports more expensive and potentially reducing their competitiveness. However, it also brings in much-needed capital for businesses and individuals, fostering investment and contributing to economic expansion.
In summary, higher interest rates can have a powerful effect on the economy by stimulating investment and driving economic growth. While there may be some short-term challenges for savers and businesses, the long-term benefits include increased investment, improved business confidence, and a more robust and resilient economy. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for policymakers and investors alike, as it highlights the importance of managing interest rates strategically to promote sustainable economic development.
Higher Interest Rates: A Catalyst for Investment or a Hindrance?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
When interest rates rise, it typically encourages people to save more. Higher interest rates mean that savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and other fixed-income investments will yield more attractive returns, making saving more appealing to individuals. This can lead to an increase in personal savings and potentially more funds available for investment.
Rising interest rates can influence investment choices in several ways. Firstly, investors might shift their focus towards fixed-income securities like bonds, as these offer higher returns compared to the lower yields of savings accounts. This shift can impact the stock market, where investors may sell stocks to lock in profits and move their capital to bond markets. Additionally, higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, potentially discouraging businesses from investing in expansion projects, which could have a ripple effect on the overall investment landscape.
Absolutely. Interest rates play a crucial role in the savings-investment cycle. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, and people may be more inclined to take out loans for investments or consumption. This can stimulate economic growth but may also lead to a decrease in personal savings. Conversely, when interest rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive, potentially reducing investment spending. However, higher interest rates also encourage saving, as mentioned earlier, which can lead to increased investment in the long term as more funds are available for productive purposes.