Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are investments like bonds that are created by bundling together many mortgages and selling shares of the resulting pool to investors. As of 2021, the volume of MBS in the United States has surpassed $12 trillion, reflecting the increasing role of MBS in the financing of residential real estate and their importance in the overall financial system and housing market. MBS can help stimulate economic growth, provide liquidity to the mortgage market, and make borrowing more accessible and affordable. However, MBS have also been associated with increased risks, including the potential for default and the impact of economic conditions, interest rates, and housing market dynamics.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Nature of Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) | MBS are investments like bonds created out of residential mortgages, providing income to investors. |
| MBS Market Size | As of 2021, the volume of MBS outstanding in the US has surpassed $12 trillion, marking significant market growth. |
| MBS Market Influence | MBS help keep the financial system running, influence mortgage qualifications and interest rates, and stimulate or slow down the economy. |
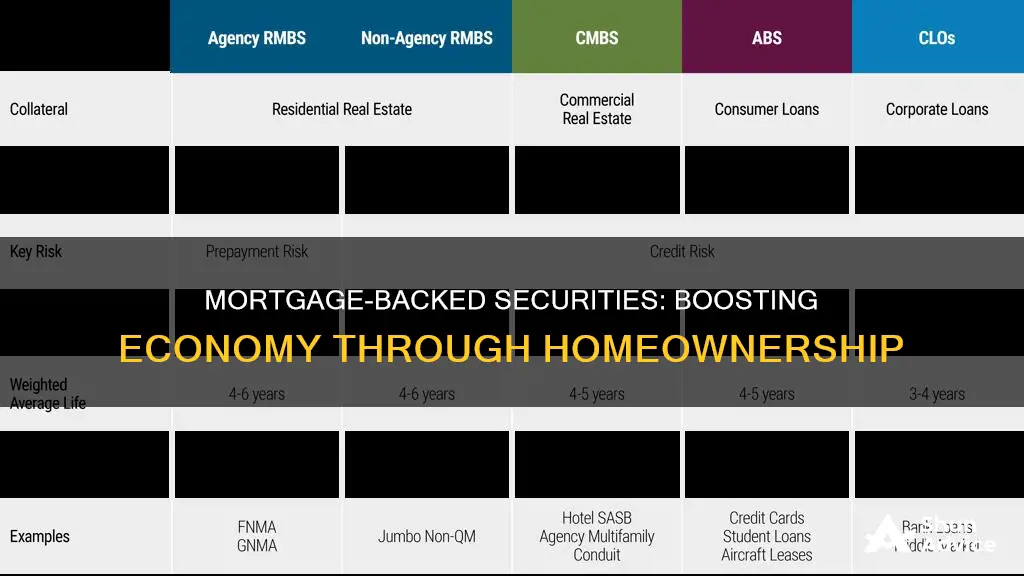
| MBS Credit Risk | MBS credit risk depends on the likelihood of borrowers repaying on time. MBS backed by GNMA have negligible default risk, while those issued by FHLMC and FNMA have some risk. |
| MBS Prepayment Risk | As interest rates fall, homeowners may refinance their mortgages, leading to quicker MBS pay-downs. This risks investors reinvesting at lower yields. |
| MBS Extension Risk | When interest rates rise, homeowners are unlikely to prepay their mortgages, potentially delaying MBS principal repayment and impacting reinvestment opportunities. |
| MBS Yield | MBS typically have higher yields than US Treasuries, making them attractive for reducing reinvestment risk. |
| MBS Government Backing | MBS may be backed by the US government, with agency MBS considered more stable and less risky than non-agency MBS. |
| MBS Liquidity | MBS transform illiquid financial assets into liquid and tradable capital market instruments, providing liquidity to the mortgage market. |
| MBS Specialization | MBS facilitate greater specialization among financial institutions by moving interest rates out of the banking sector. |
What You'll Learn

MBSs can help stimulate economic growth through monetary policy
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are investments that are similar to bonds. They are created by bundling together multiple mortgages and selling shares of the resulting pool to investors. MBSs are considered liquid and tradable capital market instruments. They can be used to replenish funds for mortgage originators, allowing for additional origination activities and providing liquidity to the mortgage market. MBSs also enable Wall Street banks to monetise the credit spread between the origination of an underlying mortgage and the yield demanded by bond investors.
MBSs have a significant impact on the economy, particularly through monetary policy. The Federal Reserve can buy and sell MBSs to stimulate the economy or slow it down, helping to manage inflation. The growth of the MBS market is attributed to increasing demand, global economic expansion, and efforts to stimulate economic growth through monetary policy. MBSs can influence the availability of mortgage credit and qualifications for mortgages, affecting who obtains loans and the loan amounts.
MBSs provide a monthly pro-rata distribution of principal and interest payments made by homeowners to investors. They offer relatively high yields compared to short-term securities, attracting investors seeking stable, fixed-income returns. MBSs can be structured to offer different risks and cash flows, and they are often diversified across numerous mortgages. The credit risk of MBSs depends on the likelihood of borrowers repaying on time. MBSs may be backed by government entities, reducing default risk and making them attractive to investors.
MBSs have experienced significant growth, surpassing $12 trillion in the United States as of 2021. This expansion reflects their increasing role in financing residential real estate and their importance in the financial system and housing market. MBSs can influence interest rates and facilitate specialisation among financial institutions. They provide capital for housing and contribute to economic growth. However, MBSs have also been associated with the rise of the subprime industry and the creation of hidden systemic risks, as evidenced by their role in the 2007-2008 financial crisis.
Freedom From Mortgage: A Dream Come True
You may want to see also

MBSs can help manage inflation
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are investments like bonds that consist of a bundle of home loans and other real estate debt bought from banks or government entities. MBSs are issued and sold to investors, who receive periodic payments, including interest and principal repayments from the underlying mortgages.
- MBSs provide investors with a monthly pro-rata distribution of any principal and interest payments made by homeowners. This regular cash flow can help investors keep pace with inflation, as they receive a steady stream of income that can be used to offset the effects of rising prices.
- MBSs are often backed by the US government, which provides additional security to investors. Government-backed MBSs are considered low-risk investments, as they have a negligible risk of default. This makes them attractive to investors seeking stable, fixed-income returns during inflationary periods.
- MBSs facilitate greater specialization among financial institutions. By allowing for the securitization of mortgages, MBSs enable financial institutions to focus on specific areas of the mortgage market, such as underwriting, servicing, or investing. This specialization can lead to improved efficiency and risk management practices, helping to mitigate the impact of inflation on the financial system.
- MBSs can be structured to offer different risks and cash flows. This flexibility allows investors to choose MBSs that align with their risk tolerance and investment goals during inflationary periods. For example, investors can select MBSs with shorter maturities to reduce the impact of inflation on the value of future repayments.
- MBSs provide liquidity to the mortgage market, making it easier for borrowers to access capital. This increased liquidity can help stimulate economic growth, which can, in turn, help manage inflation.
- MBSs are often a more efficient and lower-cost source of financing compared to traditional bank and capital market alternatives. This efficiency can help reduce the overall cost of borrowing, which can have a positive impact on inflation by reducing the demand for credit and easing pressure on interest rates.
Jared Vennett's Guide to Modern Mortgages Explained
You may want to see also

MBSs can provide liquidity to the mortgage market
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are investments like bonds that are created out of residential mortgages, providing income to investors. Each MBS consists of a bundle of home loans and other real estate debt bought from the banks that issued them. The MBS market has evolved significantly since the 2007-2008 financial crisis, which was largely triggered by the collapse of the subprime mortgage market and the complex web of MBS and related derivatives.
MBSs also allow issuers to remove assets from their balance sheets, which can help improve various financial ratios, utilize capital more efficiently, and achieve compliance with risk-based capital standards. The growth of the MBS market can be attributed to increasing demand for these securities, global economic expansion, and ongoing efforts to stimulate economic growth through monetary policy. As of 2021, the volume of MBSs outstanding in the United States has surpassed 12 trillion U.S. dollars, marking significant growth in the market size.
MBSs have helped move interest rates out of the banking sector and facilitated greater specialization among financial institutions. They have also contributed to the standardization of fixed-rate mortgages, making them more accessible to borrowers. However, it is important to note that MBSs may have led to the rise of the subprime industry and created hidden systemic risks. The complex nature of MBSs and their role in the financial crisis highlight the importance of understanding their impact on the mortgage and housing industries.
Lower Fees, Bigger Benefits: Refinancing Your Mortgage
You may want to see also

MBSs can help borrowers access capital more cheaply
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are investments like bonds that consist of a bundle of home loans and other real estate debt bought from banks. The securitization of mortgages in the 1970s helped provide more capital for housing, which was necessary due to a housing shortage and the inefficiency of the traditional mortgage market. MBSs are national and international in scope and regionally diversified, and they help move interest rates out of the banking sector.
MBSs also help provide liquidity to the mortgage market, creating greater efficiency. MBSs are often backed by the US government, which makes them attractive to investors looking for stable, fixed-income returns. The relatively high yields of MBSs also make them appealing, as investors can enjoy higher returns without sacrificing much yield. MBSs can be structured to offer different risks and cash flows, and they can be highly diversified across thousands of mortgages. This diversification helps to mitigate the risk of default.
Mortgage Rates: Impacting Your Monthly Payment Costs
You may want to see also

MBSs can help banks replenish funds for additional origination activities
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are investments that are similar to bonds. They are created by bundling together multiple mortgages and selling shares of the resulting pool to investors. MBSs are issued by government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) like Ginnie Mae, Freddie Mac, and Fannie Mae.
MBSs can also help banks diversify their financing sources by offering alternatives to traditional forms of debt and equity financing. Additionally, MBSs allow issuers to remove assets from their balance sheets, which can help improve various financial ratios, utilise capital more efficiently, and achieve compliance with risk-based capital standards.
The ability of MBSs to help banks replenish funds for additional origination activities is further enhanced by their role in providing greater specialisation among financial institutions. By moving interest rates out of the banking sector, MBSs facilitate greater specialisation and efficiency in the financial system. This specialisation can lead to improved origination activities and fund replenishment for banks.
Overall, MBSs provide banks with increased liquidity, efficiency, and diversification, which can ultimately support their ability to engage in additional origination activities and replenish their funds.
Gifts, Mortgages, and Parental Money: Impact and Insights
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are investments like bonds. Each MBS consists of a bundle of home loans and other real estate debt bought from the banks that issued them.
MBSs help provide liquidity to the mortgage market, creating greater efficiency. They also allow mortgage originators to replenish their funds, which can then be used for additional origination activities. MBSs can also be used by Wall Street banks to monetize the credit spread between the origination of an underlying mortgage and the yield demanded by bond investors.
MBSs may have "led inexorably to the rise of the subprime industry" and "created hidden, systemic risks". The 2007-2008 financial crisis was largely triggered by the collapse of the subprime mortgage market and the complex web of MBS and related derivatives. MBSs are also subject to prepayment and extension risk.
MBSs typically have higher yields than U.S. Treasuries and can be structured to offer different risks and cash flows. They are also highly diversified across thousands of mortgages. MBSs backed by GNMA carry negligible risk of default.







