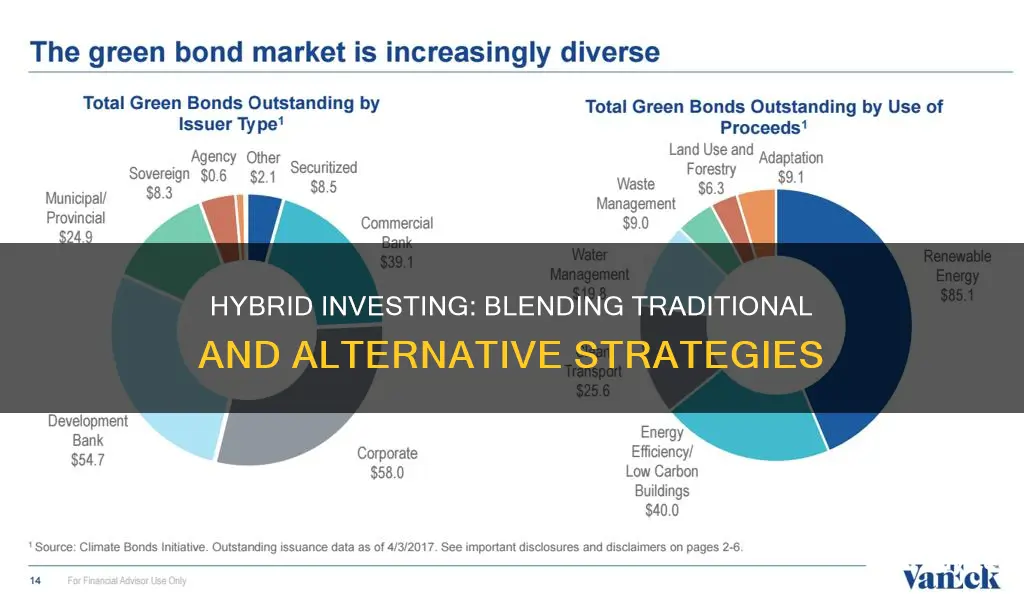
Hybrid investing is a financial strategy that combines elements of both active and passive investment approaches. It involves a blend of traditional stock picking and index-based investing, aiming to optimize returns while managing risk. This method allows investors to benefit from the advantages of both strategies, such as the potential for higher returns from active management while also benefiting from the lower costs and diversification of passive investing. By integrating these two styles, hybrid investing offers a balanced approach that can be tailored to an investor's specific goals and risk tolerance.
What You'll Learn
- Hybrid Models: Combining active and passive strategies for optimal performance
- Risk Management: Balancing risk and return through diversification and asset allocation
- Performance Metrics: Evaluating success through metrics like Sharpe ratio and alpha
- Cost Structure: Understanding fees and expenses in hybrid investment vehicles
- Regulatory Considerations: Navigating legal and compliance aspects of hybrid investments

Hybrid Models: Combining active and passive strategies for optimal performance
Hybrid investing is a strategy that combines elements of both active and passive investment approaches, aiming to optimize performance and potentially offer investors a more balanced and adaptable strategy. This approach recognizes that while active management can provide the potential for higher returns, it often comes with higher costs and the risk of underperformance. Conversely, passive investing, which relies on market-capitalization-weighted indexes, can offer lower costs and diversification but may not outperform the market in the long term.
The hybrid model seeks to address these trade-offs by blending the two strategies. It involves a careful selection of assets, where active management is applied to a portion of the portfolio, typically those with higher potential for outperformance, while the rest is managed passively, following a broad market index. This combination allows investors to benefit from the potential upside of active management while minimizing the associated risks and costs.
In a hybrid model, active management can be employed in various ways. One approach is to use active strategies for a specific sector or asset class that the investor believes has the potential to outperform the market. For example, an investor might use active management in technology stocks, which are known for their high growth potential but also carry higher risks. The rest of the portfolio could be managed passively, tracking a broad market index, ensuring a diversified and cost-effective approach.
Another strategy within hybrid investing is to use a blend of active and passive funds. Investors can choose active-managed funds for specific sectors or asset classes and pair them with passive index funds for the rest of the portfolio. This way, investors can benefit from the active management's potential while still maintaining a broad diversification and lower costs associated with passive funds.
The key to successful hybrid investing is a disciplined approach to asset allocation and regular review. Investors should define their investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Based on these factors, they can allocate assets between active and passive strategies accordingly. Regular reviews are essential to ensure that the portfolio remains aligned with the investor's goals and to make adjustments as market conditions and personal circumstances change. This approach allows investors to take advantage of the strengths of both active and passive strategies while mitigating their respective weaknesses.
Securing Your Future: A Guide to Safe Retirement Investing
You may want to see also

Risk Management: Balancing risk and return through diversification and asset allocation
Hybrid investing is a strategy that combines elements of both active and passive investment approaches, aiming to optimize risk-adjusted returns while managing risk effectively. This approach is particularly appealing to investors who want to benefit from the potential upside of active management while minimizing the associated risks. At its core, hybrid investing involves a careful balance between two key concepts: diversification and asset allocation.
Diversification is a fundamental principle in risk management, which involves spreading investments across various assets, sectors, and geographic regions. By diversifying, investors can reduce the impact of any single investment's performance on their overall portfolio. For instance, if an investor holds a mix of stocks, bonds, and alternative investments, a decline in the stock market might be partially offset by the performance of other asset classes. This strategy is based on the idea that different asset classes move in different ways over time, and thus, a well-diversified portfolio can provide more stable returns.
Asset allocation is the process of determining the percentage of the portfolio that should be invested in different asset classes. This allocation is a critical component of risk management as it directly influences the overall risk and return profile of the portfolio. A common approach is to use a 60/40 model, where 60% of the portfolio is allocated to stocks and 40% to bonds. This allocation provides a balance between growth and stability, as stocks generally offer higher returns but come with higher risk, while bonds offer lower returns but are considered safer. However, this allocation can be adjusted based on an investor's risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon.
In hybrid investing, the goal is to create a portfolio that is both well-diversified and optimally allocated. This involves a thorough analysis of the investor's financial situation, risk tolerance, and investment objectives. For example, a risk-averse investor might prefer a more conservative allocation, while a young investor with a long time horizon might be more comfortable with a higher allocation to stocks. The hybrid approach also allows for active management, where investors can make strategic adjustments to the portfolio based on market conditions and individual asset performance.
By combining diversification and asset allocation, hybrid investing offers a robust framework for managing risk. This strategy enables investors to navigate the complexities of financial markets while aiming for long-term, sustainable returns. It is a flexible approach that can be tailored to individual needs, providing a balanced and informed way to invest in a diverse range of assets. This method is particularly useful for investors who want to optimize their risk-adjusted returns and build a resilient investment portfolio.
Guaranteed Returns: Exploring the 5% Club
You may want to see also

Performance Metrics: Evaluating success through metrics like Sharpe ratio and alpha
Hybrid investing, a strategic approach that combines elements of active and passive management, offers investors a unique way to navigate the markets. When evaluating the success of a hybrid investment strategy, performance metrics play a pivotal role in providing a comprehensive understanding of its effectiveness. One of the most widely recognized metrics in this domain is the Sharpe ratio. This ratio is a measure of risk-adjusted return, calculated by subtracting the risk-free rate from the strategy's excess return and then dividing by the standard deviation of the excess return. A higher Sharpe ratio indicates that the strategy has achieved a better balance between risk and return, offering investors a more attractive proposition. For instance, a Sharpe ratio of 1.5 suggests that for every unit of risk taken, the strategy generates an additional 1.5 units of return, making it a more efficient and potentially more rewarding investment.
Alpha, another critical metric, is a measure of a strategy's performance relative to a benchmark index. It quantifies the excess return generated by an investment manager when compared to the market as a whole. A positive alpha indicates that the strategy has outperformed the benchmark, suggesting that the manager has added value through their investment decisions. For example, if a hybrid investment strategy has an alpha of 0.5, it means that the strategy has consistently generated a 0.5% return above the market's performance over a specific period. This metric is particularly useful for investors as it provides a clear indication of the active management component's contribution to the overall success of the strategy.
The combination of Sharpe ratio and alpha offers a comprehensive view of a hybrid investment's performance. While the Sharpe ratio focuses on risk-adjusted returns, alpha highlights the absolute performance against a benchmark. Together, these metrics enable investors to assess not only the strategy's efficiency but also its ability to consistently outperform the market. For instance, a strategy with a high Sharpe ratio and a positive alpha would be considered highly successful, as it demonstrates both a strong risk-adjusted return and an outperformance of the market.
In the context of hybrid investing, these metrics can be particularly insightful. Hybrid strategies often aim to balance the benefits of active management, such as the potential for higher returns, with the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of passive investing. By evaluating performance through these metrics, investors can better understand whether the hybrid approach has achieved its intended goals. This evaluation process is essential for making informed decisions, especially when considering the long-term sustainability and profitability of the investment strategy.
In summary, when assessing the success of a hybrid investment strategy, metrics like the Sharpe ratio and alpha are invaluable tools. They provide a quantitative framework to measure risk-adjusted returns and the strategy's ability to outperform the market, respectively. By utilizing these performance indicators, investors can make more informed choices, ensuring that their hybrid investment approach aligns with their financial objectives and risk tolerance. This detailed evaluation process is crucial in the dynamic world of investing, where the right strategy can significantly impact an investor's financial journey.
The Cost of Waiting: Why Investing Now Pays Off
You may want to see also

Cost Structure: Understanding fees and expenses in hybrid investment vehicles
Hybrid investing is an innovative approach that combines elements of both traditional active management and passive indexing strategies. This strategy aims to provide investors with a balanced and diversified portfolio while offering the potential for higher returns. However, understanding the cost structure of these investment vehicles is crucial for investors to make informed decisions.
When it comes to hybrid investment vehicles, the cost structure typically includes various fees and expenses that investors should be aware of. One of the primary costs is the management fee, which is charged by the investment manager or advisor. This fee covers the active management aspect of the strategy, where professionals research, select, and manage the portfolio. Management fees can vary depending on the investment strategy, the size of the fund, and the level of active management involved. Investors should carefully review the fee structure to ensure it aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance.
In addition to management fees, hybrid investment vehicles may also incur expenses related to the underlying assets or securities held in the portfolio. These expenses can include transaction costs, such as brokerage fees, which are incurred when buying or selling securities. The frequency and volume of trades in a hybrid strategy can impact these transaction costs. Furthermore, there might be expenses associated with the indexing or tracking of a specific market or sector, which is common in passive elements of hybrid investing. These expenses are often lower compared to active management fees but can still contribute to the overall cost of the investment.
Another aspect of the cost structure is the potential impact of performance fees. Some hybrid investment funds may charge performance fees, which are typically a percentage of the profits generated by the strategy. This fee structure incentivizes the investment manager to deliver positive returns, as they are directly linked to the performance of the fund. However, investors should be cautious as performance fees can significantly increase the overall cost, especially if the strategy underperforms.
Understanding the cost structure is essential for investors to assess the potential returns and the overall value of a hybrid investment vehicle. It allows investors to compare different strategies, evaluate the management's expertise, and make informed decisions regarding their investment allocations. By carefully considering the various fees and expenses, investors can ensure that the hybrid approach aligns with their financial objectives and risk preferences.
Retirement Investing: Navigating the Kiplinger Way
You may want to see also

Regulatory Considerations: Navigating legal and compliance aspects of hybrid investments
Hybrid investments, which combine elements of both equity and debt, present unique regulatory challenges that investors must navigate carefully. These challenges stem from the complex nature of hybrid instruments, which can be structured in various ways and may have different tax implications and regulatory treatments. Understanding the legal and compliance aspects is crucial for investors to ensure they adhere to relevant laws and regulations, mitigate risks, and make informed investment decisions.
One key regulatory consideration is the classification of hybrid investments under securities laws. In many jurisdictions, hybrid instruments may be classified as either securities or debt, depending on their specific characteristics. For instance, a hybrid security that provides a fixed interest rate and principal repayment at maturity might be treated as a debt instrument, while a similar security with a variable interest rate or a longer maturity period could be classified as a security. This classification is significant because it determines the regulatory framework applicable to the investment, including disclosure requirements, investor protection rules, and the ability to offer the investment to the public.
Investors should also be aware of the tax implications associated with hybrid investments. Tax laws often treat hybrid instruments differently based on their tax characteristics. For example, some hybrid securities may be considered tax-efficient for investors due to favorable tax treatments, such as tax-free interest payments or deferred taxation. Understanding these tax implications is essential for investors to optimize their investment strategies and minimize tax liabilities. Regulatory bodies often require investors to provide detailed tax information, especially for hybrid investments, to ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Additionally, the regulatory environment for hybrid investments can vary across different jurisdictions. Each country or region may have its own set of rules and guidelines governing the issuance, offering, and trading of hybrid securities. Investors must stay informed about the specific regulations in their target markets to ensure compliance. This includes understanding the requirements for registration, disclosure, and ongoing reporting obligations. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in legal consequences, fines, or even the disqualification of the investment offering.
To navigate these regulatory considerations, investors should conduct thorough due diligence. This involves examining the legal structure of the hybrid investment, reviewing relevant regulatory documents, and seeking expert advice on tax and compliance matters. Additionally, investors should stay updated on changes in regulations and seek professional guidance to ensure their investment activities remain compliant with the evolving legal landscape. By proactively addressing these regulatory aspects, investors can minimize legal and compliance risks associated with hybrid investments.
Unraveling USAA's Investment Strategies: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Hybrid investing is an investment strategy that combines elements of both active and passive management. It aims to leverage the benefits of both approaches by utilizing a mix of actively managed funds and index-based, passively managed investments. This strategy allows investors to potentially benefit from the expertise of active fund managers while also capturing the market-beating potential of passive indexing.
In traditional active management, investors rely solely on the skills of fund managers who actively select individual securities to build a portfolio. Hybrid investing, however, incorporates a blend of active and passive strategies. It may involve investing in actively managed funds that aim to outperform the market, while also holding a portion of the portfolio in index funds or ETFs to capture the overall market return. This approach offers a more diversified and potentially less risky strategy compared to pure active management.
Hybrid investing offers several potential advantages. Firstly, it can provide access to expert stock-picking abilities of active fund managers, who may identify undervalued securities or niche market opportunities. Secondly, the passive component can help reduce costs and tracking error, as index-based funds aim to mirror the performance of a specific market index. Additionally, hybrid strategies can offer diversification benefits, allowing investors to gain exposure to various asset classes and market segments.
Index funds play a crucial role in hybrid investing as a core component of the passive portion of the strategy. These funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500 or a sector-specific index. By investing in index funds, hybrid strategies can provide broad market exposure, reduce costs associated with active management, and minimize the risk of underperformance compared to the market as a whole. The passive element helps to balance the portfolio and provide a solid foundation for the active management component.