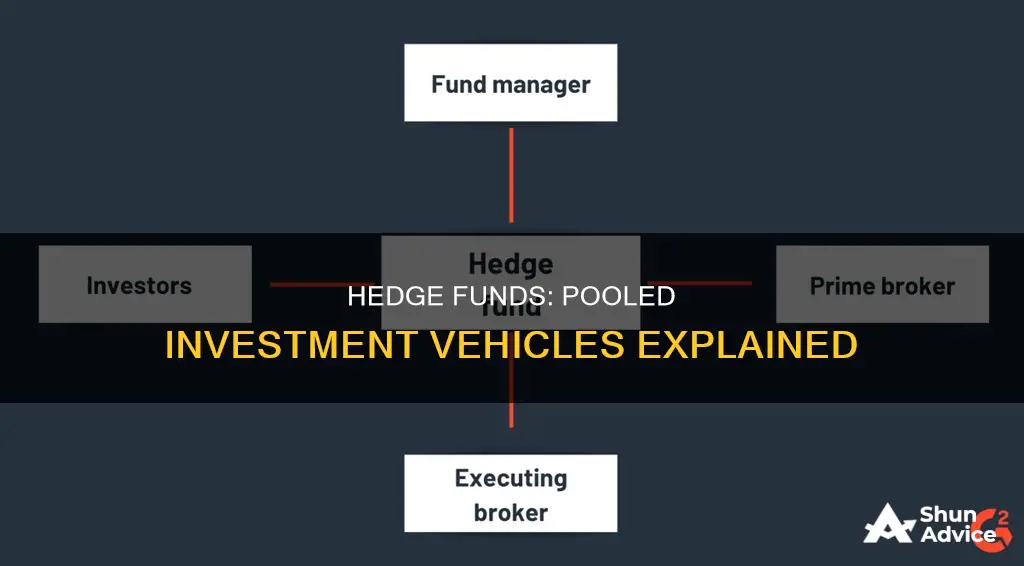
A hedge fund is a type of pooled investment vehicle. Pooled investment vehicles are products used by investors to gain positive returns. They can be low-risk or carry a greater degree of risk. Hedge funds are run by money managers or registered investment advisors who use investor funds to buy and sell investments according to a set strategy. They are considered a type of private fund, which is a pooled investment vehicle excluded from the definition of an investment company by the Investment Company Act.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A pooled investment vehicle is an entity, often referred to as a fund, that an adviser creates to pool money from multiple investors. |
| Investor Action | Each investor adds money to the pool to buy shares of the investment. |
| Nature of Investment | Basically, it’s one large portfolio funded by several investors. |
| Returns | Returns are realized in the form of dividend or interest distributions and/or price appreciation as the investment’s per-share price rises. |
| Management | Pooled investments are overseen by a management team that makes decisions about which securities to buy or sell within the investment. |
| Investor Expense | In exchange, investors pay an expense ratio to hold the investment. This expense ratio reflects the cost of owning the fund on a yearly basis. |
| Types | Pooled investment vehicles can take the form of mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), hedge funds, private equity funds, venture capital funds, and more. |
| Investor Profile | Institutional investors who invest in pooled investment vehicles include banks, mutual funds, hedge funds, pension funds, insurance companies, and some investment advisors. |
What You'll Learn

Hedge funds are a type of pooled investment vehicle
A pooled investment vehicle is an investment vehicle where multiple investors pool their money to gain certain advantages not available to individual investors. Hedge funds are a type of pooled investment vehicle.
Hedge funds are a way to put your money into the stock market alongside other investors. Each investor adds money to the pool to buy shares of the investment. It is one large portfolio funded by several investors. Returns are realised in the form of dividends or interest distributions and/or price appreciation as the investment's per-share price rises.
Hedge funds are overseen by a money manager or registered investment advisor. The fund manager is responsible for using investor funds to buy and sell investments, according to a set strategy. For example, some hedge funds are funds of funds, while others invest exclusively in emerging markets or real estate.
Hedge funds can offer diversification because fund managers can pursue investment strategies that may not be an option with other types of pooled investment vehicles, such as mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Other types of pooled investment vehicles include mutual funds, pension funds, private funds, unit investment trusts (UITs), and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Real Estate Fund Investment: A Beginner's Guide to Success
You may want to see also

They are run by money managers or investment advisors
Hedge funds are a type of pooled investment vehicle. Pooled investment vehicles are products used by investors to gain positive returns. They are so-called because multiple investors pool their money to gain certain advantages they wouldn't have as individual investors.
Hedge funds are run by money managers or registered investment advisors. The fund manager is responsible for using investor funds to buy and sell investments according to a set strategy. For example, some hedge funds are funds of funds, while others invest exclusively in emerging markets, and some focus on real estate.
The fund manager of a hedge fund must disclose the exact nature of the program so that any legal issues can be vetted before the launch of the fund. For instance, a gambling attorney would need to be consulted for a fund that pools money and allocates it to traders (live or online) who then play with the money.
Hedge funds can offer diversification because fund managers can pursue investment strategies that may not be an option with other types of pooled investment vehicles, such as mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Short-Term Investment Strategies: Where to Park Your Money
You may want to see also

Hedge funds are often risky and involve high fees
Hedge funds are a type of pooled investment vehicle where money from private investors is combined and managed by professional fund managers. These funds employ complex investment strategies, such as the use of leverage, derivatives, and alternative asset classes, to target above-average returns. While this approach offers the potential for higher returns, it also comes with significant risks and fees that investors should carefully consider.
One of the main risks associated with hedge funds is their aggressive and unique investment strategies. Hedge funds have more flexibility than traditional investment funds, often utilising derivatives and leverage to boost performance. While these strategies can lead to high returns, they also carry the risk of significant losses. For example, the hedge fund Melvin Capital lost about 53% in a month due to its large short position in GameStop.
Hedge funds are also known for their high fees, often following the "`2 and 20`" fee structure, which includes a 2% management fee on assets under management and a 20% performance fee on profits. These fees can significantly impact investors' returns, especially when compared to cheaper alternatives like passive funds or private equity investments.
Additionally, hedge funds are considered illiquid investments. They often have lock-up periods, typically of one year, during which investors cannot redeem their investments. Even after the lock-up period, withdrawals may only be allowed at certain intervals, such as quarterly or biannually. This lack of liquidity can be a concern for investors who may need to access their funds quickly.
Furthermore, hedge funds are loosely regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This lack of strict regulation allows hedge funds to take on more risk and invest in a broader range of assets, including options and derivatives. However, it also means that investors have less protection compared to more traditional investments.
Overall, while hedge funds offer the potential for higher returns and diversification benefits, they also come with significant risks and fees. Investors considering hedge funds should carefully evaluate the fund's investment strategy, fee structure, and liquidity rules to ensure they are comfortable with the level of risk involved.
DSP Blackrock Micro Cap Fund: A Guide to Investing
You may want to see also

They are less liquid than other investment vehicles
Hedge funds are pooled investment vehicles, which aggregate capital from a number of individuals to invest as one giant portfolio. They are considered alternative investments, which are distinct from mutual funds and ETFs as they can employ more complex investment techniques and are not subject to the same restrictions.
Hedge funds are less liquid than other investment vehicles, such as mutual funds and cash equivalents. Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be converted to cash, and hedge funds are considered to have lower liquidity due to a few factors. Firstly, hedge funds employ complex trading and risk management techniques, such as short-selling and the use of derivatives, which can make it more difficult to quickly convert assets to cash. Secondly, hedge funds often invest in relatively liquid assets, but they are usually open-ended, allowing investors to withdraw capital periodically. This means that hedge funds need to maintain a certain level of liquidity to meet potential redemption requests from investors. Thirdly, hedge funds may employ leverage, or borrowing money to increase their investment capacity, which can further reduce their liquidity.
Additionally, hedge funds may use a lock-up period, during which investors cannot withdraw their capital. This is done to protect the fund and investors by allowing for an orderly liquidation of assets and avoiding fire sales, but it also reduces the liquidity of the investment. Furthermore, hedge funds that experience high inflows or outflows of capital may be forced to sell assets at unfavourable prices, impacting their liquidity risk exposure.
The lack of liquidity in hedge funds can be a concern for investors, especially during times of market stress when liquidity is already low. It is important for investors to carefully consider the liquidity constraints of hedge funds and weigh them against the potential benefits of the investment.
Bernie Madoff's Ponzi Scheme: Avoiding Client Fund Investments
You may want to see also

Hedge funds are more diverse than mutual funds or ETFs
Hedge funds, mutual funds, and ETFs (exchange-traded funds) are all pooled investment vehicles where investors entrust their money to fund managers who invest on their behalf in different kinds of publicly traded securities. However, hedge funds are more diverse than mutual funds or ETFs in several ways.
Firstly, hedge funds are private investments that are only available to accredited investors, whereas mutual funds are regulated investment products offered to the public and available for daily trading. Mutual funds are also available to all types of investors, while hedge funds target high-net-worth investors.
Secondly, hedge funds are known for using higher-risk investing strategies with the goal of achieving higher returns, whereas mutual funds tend to take more constrained risks and thus earn smaller returns. Hedge funds may use options, leverage, short-selling, and other alternative strategies. They are usually managed much more aggressively than mutual funds and often seek to achieve returns in falling markets.
Thirdly, hedge funds are less regulated than mutual funds and ETFs. They are not subject to the same regulatory requirements as mutual funds and are not comprehensively regulated by directives such as the Securities Act of 1933 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, which govern mutual funds.
Finally, hedge funds are very illiquid compared to mutual funds and ETFs. They often have a lock-in period of one year, whereas mutual fund investors can redeem their units on any business day and receive the net asset value (NAV) of that day. ETFs are also traded intra-day like stocks, providing liquidity that is comparable to mutual funds.
In summary, hedge funds are more diverse than mutual funds or ETFs in terms of their investor base, investment strategies, regulatory environment, and liquidity. These differences make hedge funds a more aggressive and flexible investment vehicle, which can lead to higher returns but also entails greater risks.
T-Bills vs Short-Term Bond Funds: A Safer Investment Bet?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A pooled investment vehicle is an entity where multiple investors pool their money to invest in the stock market.
Mutual funds, pension funds, hedge funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are all examples of pooled investment vehicles.
Hedge funds are private funds that pool client money to make risky investments, often using leverage and exotic securities, with the aim of achieving higher-than-usual returns.
Hedge funds offer investors the opportunity to pursue investment strategies that may not be available with other types of funds, such as mutual funds or ETFs. They also provide diversification and access to opportunities typically only available to large-scale investors.
Hedge funds can be more expensive due to higher fees and may be less liquid, making it challenging to sell shares when needed.







