Bitcoin has been described as a speculative bubble by several prominent investors and economists, including Warren Buffett, George Soros, Jack Ma, and Jamie Dimon. On the other hand, some argue that Bitcoin is much more than a bubble and has emerged and sustained itself worldwide despite the problems encountered by cryptocurrencies. So, is Bitcoin an investment bubble?
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Lack of intrinsic value | Bitcoin doesn't have yields or cash flow |
| Price driven by speculation | Bitcoin's price is driven by speculation and fear of missing out |
| Prone to huge price crashes | Bitcoin is prone to huge price crashes due to leveraged positions |
| No income or utility | Bitcoin doesn't generate income or utility for its owners |
| No assets | Bitcoin doesn't hold assets |
| No revenue | Bitcoin doesn't generate revenue |
| No regulation | Bitcoin is unregulated |
| No transparency | Bitcoin's market is not transparent |
| Illicit transactions | Bitcoin is often used for illicit transactions and money laundering |
What You'll Learn

Bitcoin's lack of intrinsic value
Bitcoin is often criticised for its lack of intrinsic value. This is because, unlike stocks, it does not pay dividends or interest. It is also not backed by a company, government, or debt, and exists solely as an electronic way to transfer value from one party to another.
Bitcoin's value is derived from its limited supply and worldwide network. Its supply is fixed at a maximum of 21 million bitcoins, which is set in its code. An increase in supply would go against the economic interests of the Bitcoin community. In contrast, leading world currencies like the US dollar have no maximum limit and are created through debt issuance, a process often attributed to boom and bust cycles.
Some analysts argue that Bitcoin's value can be determined using the principles of supply and demand. As a result, if demand outpaces the number of new bitcoins mined, its price will increase. If demand drops, its price will fall. This is similar to precious metals with limited supplies, which are generally considered to have more intrinsic value.
Another argument for Bitcoin's value is its utility as a store of value. During the COVID-19 pandemic, investors turned to Bitcoin and experienced tremendous gains. Those who held on to or purchased Bitcoin during the crypto winter of 2022 and 2023 saw their investment nearly quadruple in value by January 2024.
Despite these arguments, critics maintain that Bitcoin has no intrinsic value. They argue that Bitcoin is a convertible currency that must be converted to a government-backed currency to be used, even in countries where it is recognised as legal tender. Additionally, they claim that Bitcoin is not linked to current financial systems and is not used by enough people to have a widespread impact.
In conclusion, while Bitcoin has seen incredible market value rises since 2009, the debate around its intrinsic value remains ongoing.
The Ultimate Guide to Investing in Bitcoin Shares
You may want to see also

Bitcoin's price being driven by speculation
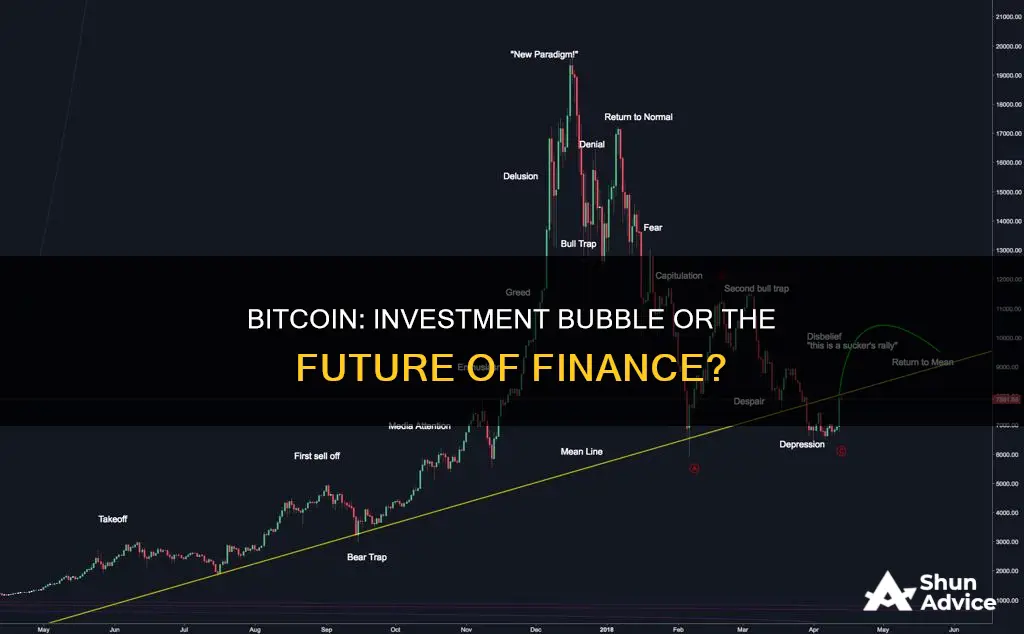
Bitcoin's price is driven by speculation. In financial markets, a bubble refers to an overinflated market that could lead to massive losses for investors if it pops. The term implies that the price is higher than the underlying value and that when the asset's price returns to its intrinsic value, many investors will lose money. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are seen by many as a speculative bubble because the intrinsic value isn't always obvious. They are also intangible.
Bitcoin's spectacular crashes lend some credence to the notion that there are Bitcoin bubble cycles. In an extended fall from grace, BTC dropped from its previous $69,000 all-time high in November 2021 to $15,500 a year later.
Bitcoin's price is determined by the free market, which is excellent at price discovery but often overshoots or undershoots. Initially, trading markets are guesses at value or, at best, speculation. The perils of wild speculation are not unique to cryptocurrency bubbles. Similar dynamics can be observed in the dot-com bubble of the late 1990s and the real estate market explosion in the early 2000s, which led to the Great Financial Crisis.
The price of Bitcoin is determined by the free market, which can be influenced by various factors such as news, expectations, and the actions of prominent investors. For example, positive news about George Soros's family office holding Bitcoin contributed to a blazing rally that helped Bitcoin shoot up by nearly 50% in two weeks.
The limited supply of Bitcoin, with a maximum of 21 million bitcoins, and its worldwide network also contribute to its price. The rate of new bitcoins produced by miners has recently halved, and these Bitcoin halvings occur every four years. This limited supply can be anti-inflationary compared to the supply of money from central banks.
However, critics argue that Bitcoin's price is driven purely by speculation and that it lacks intrinsic value. Unlike stocks or real estate, Bitcoin doesn't have yields or cash flow. It is just numbers on a screen, and anyone can copy Bitcoin's open-source code to create another cryptocurrency. This ease of replication raises questions about why Bitcoin has any value at all.
The high volatility of Bitcoin, with multiple steep price drops and dramatic surges, also contributes to the perception that its price is driven by speculation. Bitcoin's price movements can be influenced by factors such as regulatory changes, adoption by countries like El Salvador, and the actions of large investors.
In summary, Bitcoin's price is influenced by a combination of market forces, news, expectations, and the actions of prominent investors. While some argue that Bitcoin's price is driven purely by speculation, others highlight its limited supply, worldwide network, and potential as an inflation hedge. The ease of replicating Bitcoin and its high volatility contribute to the perception of speculative influence.
Apple's Bitcoin Investment: Did it Happen?
You may want to see also

Bitcoin's susceptibility to huge price crashes
This volatility is driven by several factors. Firstly, Bitcoin is a digital asset with no intrinsic value. It does not generate cash flow or yield profits, unlike traditional investments. Its value is based solely on speculation and the expectation that it will increase in price. This makes it prone to significant price crashes when the market corrects itself.
Secondly, Bitcoin is highly susceptible to leverage trades and liquidations. When Bitcoin experiences a loss, it often triggers a downward spiral as long positions are liquidated, forcing further sales and driving the price even lower.
Additionally, Bitcoin's value is influenced by media attention and the actions of high-profile individuals. Positive news, such as the approval of a Bitcoin-based exchange-traded fund, can drive up its price, while negative comments from prominent investors or government regulations can cause significant price drops.
The lack of regulation in the cryptocurrency market also contributes to Bitcoin's price volatility. The absence of oversight allows for the use of high leverage, which can amplify price movements, both positive and negative.
Finally, Bitcoin's value is influenced by its limited supply and the actions of miners. The rate at which new Bitcoins are produced recently halved, reducing the supply and potentially impacting its value.
In conclusion, Bitcoin's susceptibility to huge price crashes is a significant risk factor for investors. Its lack of intrinsic value, high volatility, and susceptibility to market sentiment and regulatory changes make it a highly speculative investment.
Chap Invest: Exploring Bitcoin Opportunities
You may want to see also

Bitcoin's limited supply and decentralisation
The limited supply of bitcoin is often cited as a reason for its potential to be a good store of value. In economic theory, a limited supply of money is anti-inflationary. Bitcoin's decentralised nature also plays a role in its potential as a store of value. It is the first fully decentralised store of value, with no need for verification or oversight from a third party. This feature is particularly attractive in an era of growing mistrust in centralised institutions and concerns about the misuse and monetisation of data by companies.
The decentralised nature of bitcoin also contributes to its security and immutability. Bitcoin's network consists of a worldwide community of node operators who enforce the limit on bitcoin's supply by choosing which version of the code to run. This decentralised network makes it extremely difficult to tamper with bitcoin's monetary policy.
While bitcoin's limited supply and decentralisation are often touted as its strengths, some critics argue that these very features make it unsuitable as a currency. They argue that growth and inflation are essential for a healthy economy and that a deflationary commodity like bitcoin cannot function as a currency.
Despite these criticisms, bitcoin's limited supply and decentralisation have contributed to its popularity and perceived value. Its potential as a store of value, hedge against inflation, and alternative to traditional fiat currencies has attracted investors and even led some countries to adopt it as legal tender.
Bitcoin or Ether: Which Crypto is the Better Investment?
You may want to see also

Bitcoin's role as a hedge against inflation
Limited Supply and Decentralization
Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins, and its decentralized nature ensures it cannot be diluted through inflation. This makes it an attractive alternative to traditional inflationary fiat currencies. The limited supply of Bitcoin also contributes to its anti-inflationary properties when compared to the supply of money from central banks.
Price Volatility
Bitcoin's price is primarily driven by market demand and supply, and it can be highly volatile. This volatility can pose risks for investors, especially those who need to liquidate their holdings during market stress. Between late 2017 and early 2018, Bitcoin's price swung dramatically from nearly $20,000 down to just above $3,000.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies is constantly evolving, and it can impact the value and liquidity of Bitcoin. Instances of governments restricting or banning cryptocurrency use, as seen in China and India, have affected the market. Therefore, regulatory uncertainties add another layer of risk to investing in Bitcoin.
Historical Performance
Bitcoin's historical performance suggests an overall positive trend, even during inflationary periods. However, its relatively short history compared to traditional investment vehicles like gold makes it challenging to fully evaluate its stability and longevity in diverse economic scenarios.
Alternative Currency
Some countries, like El Salvador, have adopted Bitcoin as an alternative currency, and even mine it to add to their state coffers. This increasing adoption and utility of Bitcoin demonstrate its potential as a hedge against inflation, particularly in countries experiencing high inflation or facing limitations with traditional fiat currencies.
In conclusion, while Bitcoin has its unique advantages as a decentralized, limited-supply asset, it also comes with inherent volatility and regulatory risks. Therefore, when considering Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation, a careful, well-researched approach, and diversification within a broader investment portfolio, are recommended.
Mining Bitcoin: Free, Fast, and Easy?
You may want to see also







