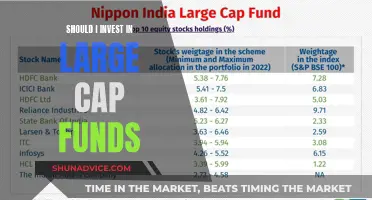
Investing in mutual funds is a popular option for those looking to diversify their portfolios. Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors, allowing them to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. This provides individual investors with access to a professionally-managed portfolio, potentially benefiting from economies of scale while spreading risk across multiple investments.
One of the main advantages of mutual funds is diversification, which reduces the risk of losing all your money if a single company or sector experiences a downfall. Additionally, mutual funds are highly liquid, making them easy to buy or sell. They are also subject to regulations and overseen by regulatory bodies, ensuring transparency and protecting investors.
However, it's important to consider the fees associated with mutual funds, such as management fees, operating expenses, and sales charges, as these can impact overall returns. Mutual funds also carry the risk of underperformance, and investors may not always achieve their desired returns.
Overall, investing in mutual funds can be a safe and effective way to diversify your portfolio, but it's crucial to conduct thorough research, assess your risk tolerance, and seek advice from a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Investment vehicle that pools money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities |
| Accessibility | Accessible way for investors to access a wide mix of assets; most mutual fund investors are middle-income workers |
| Management | Pooled capital is managed by professional money managers; investors benefit from their research and skillful trading |
| Risk | Risk is spread across multiple investments; mutual funds are considered safer than purchasing individual stocks |
| Returns | Returns are not guaranteed but are typically generated through capital gains distributions, dividends, and interest income |
| Fees | Annual fees, expense ratios, and commissions lower overall returns; fees vary depending on the fund structure |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid investments that can be redeemed on any business day |
| Tax implications | Taxes may be owed on capital gains from appreciated investments |
| Suitability | Suitable for investors who want a diversified portfolio but don't want to choose individual investments; may be good for retirement savings |
What You'll Learn

Mutual funds: pros and cons
Mutual funds are a popular investment vehicle, especially for retirement accounts. They are a relatively hands-off way to invest in a diverse range of assets, providing exposure to hundreds of stocks, bonds, or other investments in a single fund.
Pros:
- Diversification: Mutual funds are a quick and cost-effective way to achieve diversification, which reduces investment risk.
- Liquidity: Mutual funds are highly liquid, making them easy to buy and sell.
- Professional Management: Mutual funds are managed by professionals, providing access to their research and trading skills.
- Economies of Scale: Mutual funds enable investors to benefit from economies of scale, as transaction costs are lower when buying and selling large amounts of securities.
- Accessibility: Mutual funds are accessible to individual investors, with relatively low investment minimums.
- Regulation: Mutual funds are subject to industry regulations, ensuring accountability and fairness.
Cons:
- Fees and Expenses: Mutual funds charge various fees and expenses, such as annual fees, expense ratios, and commissions, which can impact overall returns.
- Cash Drag: Mutual funds must hold a significant portion of their portfolios in cash to satisfy daily share redemptions, reducing potential returns.
- Tax Implications: Capital gains taxes may be triggered when a fund sells a security, and these costs can be passed on to investors.
- Underperformance: Mutual funds may not always perform as expected, and there is a risk of underperformance relative to the market.
- Lack of Transparency: Mutual funds may not provide full transparency into their holdings, making it challenging to compare and evaluate funds.
Overall, mutual funds offer a simple and affordable way to access a diversified, professionally managed portfolio. However, investors should carefully consider the fees, potential tax implications, and the possibility of underperformance before investing.
Creating a Successful Investment Fund: Strategies for Beginners
You may want to see also

Mutual funds vs. index funds
Investing in mutual funds is a popular option, especially for retirement accounts. They are a relatively hands-off way to invest in many different assets at once. Mutual funds are also popular because they are simple, affordable, and offer instant diversification.
Index funds are a type of mutual fund. They are passively managed, meaning they are not actively managed by a professional. Instead, they track a specific market index, like the S&P 500 or Dow Jones Industrial Average, and their holdings automatically change to match the index. This passive management style means lower fees for investors.
Actively managed mutual funds, on the other hand, are run by a fund manager who makes all the investment decisions. The goal of an actively managed fund is to beat the market and earn higher returns. However, this comes at a higher price for investors due to the salaries, bonuses, and other costs associated with fund managers.
Over the long term, index funds have often outperformed actively managed mutual funds. This is because it is difficult for fund managers to consistently beat the market, and the higher fees of actively managed funds can eat into returns.
When deciding between index and actively managed mutual funds, investors should consider costs, time horizons, and risk appetite. Index funds offer market returns at lower costs, while active mutual funds aim for higher returns through skilled management that comes at a higher price.
A Simple Guide to Investing in the Nasdaq 100 Index Fund
You may want to see also

Mutual funds vs. ETFs
Mutual funds and ETFs (exchange-traded funds) are both popular investment options, but there are some key differences between the two. Here is a detailed comparison:
Similarities:
Mutual funds and ETFs share some similarities. They are both managed "baskets" or "pools" of individual securities, such as stocks or bonds, providing diversification and reducing risk. They both offer exposure to a wide range of asset classes and niche markets, and they are overseen by professional portfolio managers. Additionally, both options provide access to a variety of investment options, allowing investors to choose based on their personal goals and style.
Differences:
One of the main differences between mutual funds and ETFs lies in how they are traded. Mutual funds are traded only once daily after the markets close, whereas ETFs are traded on stock exchanges like regular stocks, offering more liquidity and flexibility. ETFs can be bought and sold throughout the market hours, and their prices fluctuate based on supply and demand. Mutual funds, on the other hand, are priced at the end of each trading day based on the net asset value (NAV) of the underlying portfolio.
Another distinction is in the minimum investment requirements. ETFs typically have lower minimum investments, often requiring only the price of one share, while mutual funds usually have flat dollar amount minimums, which can range from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars.
ETFs are usually passively managed, tracking a market index or sector sub-index, while mutual funds can be actively or passively managed, with most being actively managed. Actively managed funds tend to have higher fees and expense ratios due to their higher operational and trading costs.
ETFs also tend to have certain tax advantages over mutual funds. As passively managed portfolios, ETFs generally generate fewer capital gains for investors due to their lower turnover. In contrast, sales of securities within a mutual fund may trigger capital gains for shareholders, even if they have an unrealized loss on the overall investment.
In summary, both mutual funds and ETFs offer investors a stake in a diversified portfolio, but they differ in terms of trading flexibility, minimum investment requirements, management style, and tax efficiency. The choice between the two depends on factors such as investment goals, risk tolerance, and the level of control desired over the investment.
A Guide to Mutual Fund Investment in Nigeria
You may want to see also

How to invest in mutual funds
Investing in mutual funds is a relatively straightforward process. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to invest in mutual funds:
Decide between active and passive funds:
Your first decision is to choose between active and passive funds. Active funds are managed by professionals aiming to beat the market, whereas passive funds aim to mimic the market and are often less expensive. While some active funds may outperform the market in the short term, it is challenging to do so consistently over the long term.
Calculate your investing budget:
Mutual funds typically have minimum investment requirements ranging from $100 to $3,000, with some funds offering a $0 minimum. Consider how much money you can comfortably invest and choose an amount that aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals.
Decide where to buy mutual funds:
You can purchase mutual funds through an online broker or directly from the fund manager. If you have an employer-sponsored retirement account, such as a 401(k), you may already be invested in mutual funds. Buying through an online broker offers a wider range of fund choices but may incur transaction fees.
Understand mutual fund fees:
Mutual funds charge various fees that impact your investment returns. These include expense ratios, management fees, 12b-1 fees, and early redemption fees. Be sure to read the fund's prospectus to understand all associated fees.
Choose a mutual fund:
Consider the fund's investment objectives, performance, and fees when making your selection. Ensure that the fund's investment strategy aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance. Conduct thorough research to understand the fund's approach, investment philosophy, and portfolio managers.
Buy mutual fund shares:
You can purchase mutual fund shares through an online broker or the fund manager. Mutual funds are priced based on their net asset value (NAV) at the end of each trading day. When placing an order, you will receive the next day's closing NAV as your price.
Manage your mutual fund portfolio:
Consider rebalancing your portfolio annually to maintain your desired diversification. Avoid chasing short-term performance and stick to your long-term investment plan. Remember that mutual funds are typically long-term investments, and frequent buying and selling may incur unnecessary fees.
A Beginner's Guide to Mutual Fund Investment in Nepal
You may want to see also

Are mutual funds safe?
All investments carry some degree of risk, and mutual funds are no exception. However, they are generally considered a safer option than investing in individual stocks. Here are some key points to consider when assessing the safety of mutual funds:
Diversification
Mutual funds offer instant diversification by pooling money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. This diversification reduces the risk associated with investing in just one or two individual stocks, as mutual funds spread the investment across various companies and sectors.
Professional Management
Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers who invest the pooled money in various financial instruments to generate returns. These managers are legally obligated to follow the fund's stated mandate and work in the best interest of the shareholders. Their expertise and full-time dedication to researching and monitoring investments can benefit individual investors, especially those with limited knowledge or time to research.
Regulation and Transparency
In India, for example, mutual funds are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which has established rules and guidelines to protect investors. These regulations ensure transparency, efficient management, and regular reporting of financial performance. Mutual funds are also subject to periodic audits by independent auditors, further reducing the risk of fraud and mismanagement.
Fees and Expenses
While mutual funds offer many benefits, it is important to carefully consider the associated fees and expenses, such as management fees, operating expenses, and sales charges. These fees can impact investment returns, so investors should review the fee structure and expense ratios before investing.
Historical Performance
Past performance does not guarantee future results, but historical data can provide insights into a fund's potential. It is essential to research the performance history of mutual funds and understand that mutual funds may not always meet expectations.
Suitability for Different Investors
Mutual funds cater to a wide range of investors with different investment goals, risk tolerances, and levels of financial knowledge. They offer a variety of investment options, from conservative to aggressive strategies, and provide exposure to diverse asset classes.
In conclusion, while mutual funds carry some risk, they are generally considered a safe investment option due to the diversification they offer, professional management, regulatory oversight, and the range of investment choices available. However, investors should always consult a financial advisor and carefully consider their own financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance before making any investment decisions.
Liquid Fund Investment: Axis Liquid Fund Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Mutual funds are a good investment because they offer simplicity, affordability, and instant diversification. They are highly liquid, making them easy to buy or sell.
All investments carry some risk, but mutual funds are generally considered safer than purchasing individual stocks. Mutual funds offer more diversification since they hold stocks from many companies within a single investment.
Yes, you can lose money in mutual funds. However, diversification is often built into mutual funds, which means you spread the risk across multiple companies or industries.
It is possible to get rich by investing in mutual funds, especially if you take advantage of compound interest and give your investments enough time to grow.
You can invest in mutual funds by purchasing them through an online brokerage, directly from the company that created the fund, or with the help of a financial advisor.