Paying off a loan can be considered a financing activity, as it involves the repayment of debt. This is distinct from investing activities, which reflect a company's purchases and sales of capital assets. Financing activities are transactions between a business and its lenders and owners, involving the acquisition or return of resources. These activities include issuing and repurchasing equity, borrowing and repaying short-term and long-term debt, and dividend payments. A company's financing activities are reflected in its cash flow statement, which provides insight into its financial health and capital management.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type of Activity | Financing Activity |
| Involves | Transactions between a business and its lenders and owners |
| Purpose | To acquire or return resources |
| Includes | Issuing and repurchasing equity; borrowing and repaying short-term and long-term debt; other contributions from, or distributions to, owners |
| Cash Flow Statement Section | One of three sections, the other two being operating and investing activities |
| Indicates | How a business is funded, how it raises capital and pays back its investors |
| Impact | A positive number indicates the business has received cash, while a negative number indicates the business has paid out capital |
What You'll Learn

Issuing and repaying equity
Equity financing can come from various sources, including personal savings, friends and family, professional investors, or an initial public offering (IPO). The advantage of equity financing is that there is no obligation to repay the funds received from investors, which can alleviate the financial burden on the company. Additionally, equity financing can provide long-term support from investors who are invested in the company's success.
However, one of the disadvantages of equity financing is that it involves giving up ownership and control of the business. When a company receives equity financing, the investors become part-owners and are entitled to a share of the profits. This means that as the company grows and becomes profitable, the investors can be repaid through profit-sharing and dividends.
Repaying equity investors typically involves sharing the company's profits and can also include preferred stock dividends. Unlike debt financing, where there is a fixed obligation to repay the loan, equity investments are permanent and do not have a set timeline for repayment. Once investors hold equity, it is challenging to remove their ownership stake, making equity financing a more permanent investment.
Energy Investment: Now or Never?
You may want to see also

Borrowing and repaying short-term debt
Short-term debt can be beneficial for a company in several ways. It can provide quick access to new capital, which can be used to fund equipment, labour, and supplies. It also usually has relaxed eligibility requirements, a fast approval timeline, and a short repayment period.
However, there are also drawbacks to short-term debt. It often comes with higher interest rates compared to other types of debt, and there is a high-cycle risk if payments are missed. The short repayment period means that monthly payments will be much higher than with other types of borrowing.
Some common types of short-term debt include short-term bank loans, accounts payable, wages, lease payments, and income taxes payable.
Dollar General: A Smart Investment Move?
You may want to see also

Borrowing and repaying long-term debt
Long-term debt is defined as debt that matures in more than one year. It is often treated differently from short-term debt. Companies take on long-term debt to obtain immediate capital, for example, to cover startup costs or fund regular capital expenditures and expansion projects. Long-term debt instruments include credit lines, bank loans, and bonds.
When a company borrows money by issuing long-term debt, it receives a cash inflow, which is recorded as a debit to cash assets and a credit to the debt instrument. This is reported on the company's balance sheet as a current asset. The debt, on the other hand, is considered a liability on the balance sheet. The portion due within a year is a short-term liability, while the remainder is a long-term liability.
As the company repays its long-term debt, it must carefully track the debt payments to ensure proper accounting and separation of short-term and long-term liabilities. The payments due within a year are recorded as a debit to liabilities and a credit to assets. Once the company has fully repaid its long-term debt, the balance sheet will reflect a cancellation of the principal and liability expenses for the total interest required.
In summary, borrowing and repaying long-term debt involves a company taking on financing activities to obtain capital, resulting in cash inflows and outflows that are recorded and reflected on financial statements and balance sheets. Proper accounting and tracking of debt payments are crucial to ensure compliance with financial reporting standards.
Smart Investment Vehicle Choices
You may want to see also

Issuing and selling stock
Issuing Stock
Issuing stock involves offering shares to shareholders, with the approval of the company's board. The issuance of stock is linked to the maximum number of shares a company can issue, which is typically the total of outstanding treasury stock and shares, along with shares the company has regained ownership of. Companies can issue common and preferred stock, with shareholders having a say in how much capital is reserved. Issuing stock also entails complying with securities laws and providing investors with information and risk disclosures. Employee stock options (ESOs) are another facet, where employees can gain ownership of company stock at favourable prices, incentivising them to boost the company's share price.
Selling Stock
Selling stock in a company can serve multiple purposes, such as raising capital, paying down debts, funding expansion, or diversifying an owner's risk. It can be a complex decision that necessitates careful planning, including understanding the steps involved, accurately valuing the business, and navigating tax implications. There are two primary types of sales: complete and partial. A complete sale typically signifies the owner's departure from the business, while a partial sale can raise capital, incentivise employees, and initiate ownership transitions. Selling to private investors, smaller investors, or employees are all options, each with its own advantages and complexities.
The Process of Selling Stock
The process of selling stock involves several steps, including deciding on the future direction, understanding the goals of stakeholders, determining the business's value, creating a marketing strategy, and getting the business in order. It is a lengthy process that requires patience and preparation. Owners should also be aware of the psychological implications of selling and the increased transparency and accountability that comes with having investors.
Market Volatility: Navigating the Investment Storm
You may want to see also

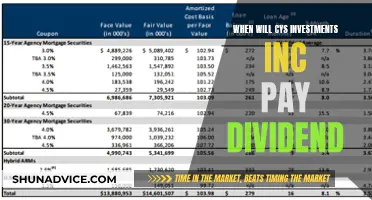
Paying cash dividends
Dividends are a distribution of profits to shareholders, and they represent a cost of equity for the company. Dividend payments are a way for companies to return capital to investors, and they are often favoured by mature companies with limited growth prospects that want to maximise shareholder value.
The payment of dividends is an important consideration for investors when evaluating a company's financial health and capital management. Dividends are usually paid out of the company's profits, and they can be in the form of cash or stock. Cash dividends are the most common form of dividend payment, and they are typically paid out on a quarterly or annual basis.
When a company pays cash dividends, it is important for investors to consider the source of the capital. If the company is relying heavily on debt or issuing new stock to pay dividends, it could be a sign of an unattractive investment opportunity. Therefore, investors should analyse the company's cash flow statement to understand the sources and uses of its cash.
Social Security: Opting In or Out?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Paying a loan is a financing activity. It is a cash outflow from financing activities, which include borrowing and repaying short-term and long-term loans.
Financing activities refer to business transactions involving long-term liabilities, owners' equity, and short-term debts. They reflect the flow of cash and cash equivalents between a company and its sources of finance, such as investors and creditors.
A cash inflow is when a company receives money, such as from issuing notes payable to creditors or issuing stocks to investors. A cash outflow is when a company pays out money, such as when it pays off a debt or distributes dividends to shareholders.
A cash flow statement, or statement of cash flows, is a financial report that shows how much cash a company has raised and spent during a given period. It includes three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
Tracking cash flow from financing activities provides insight into a company's financial health and capital management. It helps investors and analysts determine if a business is on sound financial footing and can indicate the company's intentions for expansion and growth.