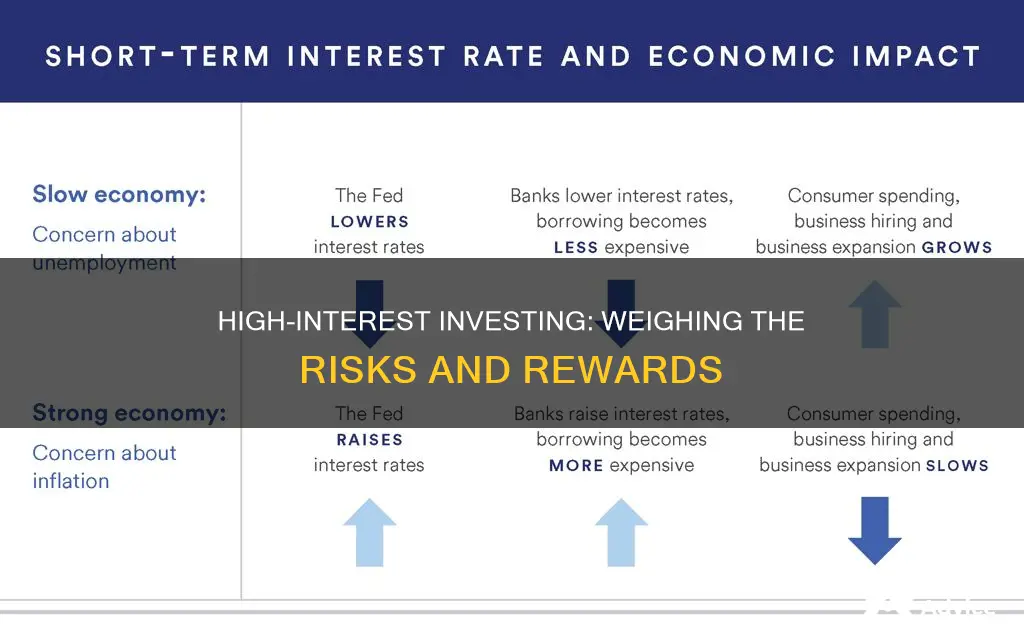
When deciding whether to invest in high or low-interest options, it's essential to consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and the current economic climate. High-interest investments often offer the potential for greater returns but come with higher risks, while low-interest options may provide more stability and security. Understanding the trade-offs between risk and reward is crucial in making an informed decision that aligns with your investment strategy and long-term financial objectives.
What You'll Learn
- Risk Tolerance: Assess your risk tolerance to determine the interest rate level that aligns with your financial goals and comfort
- Investment Horizon: Consider your investment time horizon; longer-term investments may benefit from higher interest rates
- Market Conditions: Understand current market conditions and economic trends to make informed decisions about interest rate investments
- Diversification: Diversify your portfolio to manage risk and optimize returns across various interest rate environments
- Tax Implications: Be aware of tax consequences associated with different interest rates to make tax-efficient investment choices

Risk Tolerance: Assess your risk tolerance to determine the interest rate level that aligns with your financial goals and comfort
When considering whether to invest in high or low-interest options, understanding your risk tolerance is crucial. Risk tolerance refers to your ability and willingness to withstand fluctuations in the value of your investments. It's a personal assessment of how comfortable you are with potential losses and the impact they might have on your financial goals. Here's how you can evaluate your risk tolerance and make an informed decision:
Evaluate Your Financial Goals: Start by defining your short-term and long-term financial objectives. Are you saving for a specific purchase, such as a house or a car? Or are you planning for retirement, education, or a business venture? Your financial goals will dictate the level of risk you can take. For instance, if you need the money for a down payment on a house in a few years, you might opt for a lower-risk investment to ensure liquidity. In contrast, if you're investing for retirement, you may be more open to higher-risk, potentially higher-reward options.
Assess Your Comfort with Risk: Consider your emotional and psychological comfort with risk. Do you have a high tolerance for volatility, meaning you can withstand significant market fluctuations without getting anxious? Or are you more risk-averse, preferring a steadier, more predictable return? Your risk tolerance will influence the types of investments you choose. For example, if you're comfortable with risk, you might consider high-interest investments like stocks or real estate, which can offer substantial returns but also come with higher risks.
Understand the Risks: Educate yourself about the risks associated with different types of investments. High-interest investments often carry higher risks, such as market volatility, interest rate changes, and potential losses if the investment value drops. On the other hand, low-interest investments might offer more stability but may also provide lower returns. Understanding these risks will help you make a more informed decision.
Diversify Your Portfolio: Risk tolerance is not just about individual investments but also about portfolio diversification. Diversifying your investments across different asset classes can help manage risk. For instance, you could allocate a portion of your portfolio to high-risk, high-reward stocks and another portion to low-risk, stable bonds or savings accounts. This approach ensures that even if one investment underperforms, others may compensate for it.
Regularly Review and Adjust: Risk tolerance is not a static concept; it can change over time due to various factors, including life events, market conditions, and personal circumstances. Regularly review your investment strategy and risk tolerance to ensure they remain aligned with your financial goals. As you achieve milestones or encounter life changes, you may need to adjust your investment approach, including the allocation of high or low-interest investments.
Navigating Market Shifts: Strategies for Rising Interest Rates
You may want to see also

Investment Horizon: Consider your investment time horizon; longer-term investments may benefit from higher interest rates
When considering your investment strategy, it's crucial to evaluate your investment horizon, which refers to the length of time you plan to hold your investments. This is an essential factor to consider when deciding whether to invest in high or low-interest options.
For those with a long-term investment horizon, higher interest rates can be advantageous. This is because longer-term investments often align with the natural economic cycle, where interest rates tend to rise and fall over time. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging businesses and consumers to take out loans, which can stimulate economic growth. As the economy expands, central banks may increase interest rates to control inflation, making borrowing more expensive. This shift in interest rates can create opportunities for investors with a long-term perspective.
Long-term investments, such as buying and holding stocks or bonds for an extended period, can benefit from higher interest rates in several ways. Firstly, rising interest rates can lead to increased bond prices. When interest rates go up, newly issued bonds offer higher yields, making older bonds with lower yields less attractive. As a result, investors may buy these older bonds at a discount, benefiting from the higher interest rates over time. Secondly, higher interest rates can improve the profitability of companies, especially those with significant debt. As interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing decreases, allowing companies to manage their debt more efficiently and potentially increasing their overall profitability.
However, it's important to note that the relationship between interest rates and investment horizons is not always straightforward. During periods of economic uncertainty or market volatility, short-term fluctuations in interest rates can impact investments. Investors with a shorter time horizon may need to be more cautious, as they might not have the luxury of waiting for the long-term benefits of higher interest rates. In such cases, a balanced approach could involve diversifying investments across different interest rate environments to manage risk effectively.
In summary, for investors with a long-term investment horizon, higher interest rates can present opportunities. Longer-term investments, such as stocks and bonds, may benefit from rising interest rates through increased bond prices and improved corporate profitability. However, it is essential to remain vigilant and adapt investment strategies as interest rates and market conditions evolve, especially for those with shorter investment periods.
Unleash the Power of Compound Interest: Your Guide to Smart Investing
You may want to see also

Market Conditions: Understand current market conditions and economic trends to make informed decisions about interest rate investments
Understanding market conditions and economic trends is crucial when deciding whether to invest in high or low-interest securities. The current economic climate significantly influences the performance of these investments, and making an informed decision can help you navigate the market effectively. Here's a breakdown of how to approach this:
Economic Indicators: Start by analyzing key economic indicators that provide insights into the overall health of the economy. Interest rates are often set by central banks based on these indicators. For instance, if inflation is high, central banks might raise interest rates to control spending and borrowing, which could impact the value of your investments. Conversely, low or falling inflation might prompt central banks to lower interest rates, potentially benefiting certain investment types.
Market Sentiment and News: Stay updated on market sentiment and news related to interest rates. Economic policies, geopolitical events, and global market trends can all influence interest rates. For example, a change in government might lead to a shift in economic policies, affecting interest rates and, consequently, investment strategies. Keeping an eye on these developments ensures you're aware of potential opportunities or risks.
Historical Data and Trends: Examining historical data and trends can provide valuable context. Reviewing past interest rate cycles and their impact on various asset classes can help you understand the potential outcomes of your investment decisions. For instance, during periods of rising interest rates, fixed-income securities might perform well, while during low-interest-rate environments, alternative investments could be more attractive.
Economic Forecasts: Economic forecasts and projections are essential tools for investors. These forecasts can help you anticipate future market conditions and make more accurate predictions about interest rate movements. By staying informed about economic analysts' views, you can align your investment strategy with the expected economic trajectory.
Diversification: Market conditions can vary, and a well-diversified portfolio is essential. Consider how different market scenarios might affect various asset classes. For instance, during a recession, low-interest rates might be maintained to stimulate the economy, potentially impacting the performance of different investment vehicles. Diversifying your portfolio across various interest rate environments can help mitigate risks and optimize returns.
Unlocking Wealth: The Power of Compound Interest in Investment Choices
You may want to see also

Diversification: Diversify your portfolio to manage risk and optimize returns across various interest rate environments
Diversification is a key strategy to consider when navigating the complexities of investing in high or low-interest environments. It involves spreading your investments across various assets, sectors, and geographic regions to reduce the impact of any single investment's performance on your overall portfolio. By diversifying, you can effectively manage risk and optimize returns, ensuring that your portfolio is well-prepared for different market conditions.
In a high-interest rate environment, certain investments may become less attractive. For instance, bonds, which typically offer fixed interest rates, might yield lower returns compared to the rising interest rates in the market. In such cases, diversifying your portfolio can help mitigate the risk associated with the potential decline in bond prices. Consider allocating a portion of your investments to alternative assets like real estate investment trusts (REITs) or dividend-paying stocks, which can provide a steady income stream and potentially outperform in a high-interest rate scenario.
Conversely, during periods of low-interest rates, fixed-income investments may become more appealing. However, diversifying is still crucial to manage the inherent risks. You could explore opportunities in emerging markets, where higher interest rates might offer more attractive returns, or consider investing in inflation-indexed bonds, which are designed to protect against the erosion of purchasing power caused by low or negative interest rates.
The goal of diversification is to create a balanced portfolio that can weather various economic cycles. By holding a mix of assets, you reduce the volatility of your investments and ensure that your portfolio can generate returns even when specific asset classes underperform. For example, a well-diversified portfolio might include a combination of stocks, bonds, commodities, and alternative investments, each contributing to the overall risk and return profile.
In summary, diversification is a powerful tool for investors to navigate the challenges of high and low-interest rate environments. It enables you to manage risk effectively, optimize returns, and maintain a consistent investment strategy regardless of the prevailing market conditions. By carefully selecting and allocating investments, you can build a robust portfolio that aligns with your financial goals and provides long-term wealth creation.
Uncover the Interest-Earning Potential of Your Investments
You may want to see also

Tax Implications: Be aware of tax consequences associated with different interest rates to make tax-efficient investment choices
When considering investments, understanding the tax implications of different interest rates is crucial for making informed and tax-efficient choices. Interest rates play a significant role in the overall returns on your investments, and the tax treatment of these returns can vary depending on the type of investment and the jurisdiction. Here's a detailed look at how tax consequences can influence your investment decisions:
Capital Gains Tax: One of the primary tax considerations is capital gains tax. When you invest in assets like stocks, bonds, or mutual funds, you may realize capital gains if the asset's value increases over time. The tax rate on these gains can vary based on your income level and the holding period. In many countries, short-term capital gains (held for a year or less) are taxed at a higher rate than long-term gains (held for more than a year). For instance, in the United States, short-term capital gains are taxed as ordinary income, while long-term gains are taxed at a lower rate. Understanding these rates can help you decide whether to invest in assets that are likely to appreciate quickly or those that provide steady, long-term growth.
Dividend Taxation: Interest-bearing investments, such as bonds, often pay dividends. The tax treatment of these dividends can vary. In some cases, dividends may be taxed at the same rate as your ordinary income, while in other scenarios, they might qualify for a lower tax rate if held in a tax-advantaged account. For example, in the US, qualified dividends are taxed at a lower rate than ordinary income. Investors should consider the tax efficiency of dividend-paying investments, especially if they are in a higher tax bracket.
Tax-Efficient Accounts: The choice of investment account can also impact tax implications. Traditional brokerage accounts are subject to taxes on all gains and dividends, but tax-advantaged accounts like retirement accounts (e.g., 401(k)s or IRAs) offer tax benefits. Contributions to these accounts are often tax-deductible, and earnings can grow tax-free until withdrawal. Understanding the rules and limitations of these accounts can help you make strategic investment decisions to minimize tax liabilities.
Interest Rate Environment: The current interest rate environment significantly influences investment choices. During periods of low interest rates, fixed-income investments like bonds may offer less attractive returns, potentially leading to higher capital gains when sold. Conversely, high-interest rate environments can provide more favorable conditions for bond investments. Investors should consider the potential tax implications of selling these investments and the impact of changing interest rates on their overall portfolio.
Tax-Loss Harvesting: This strategy involves selling investments that have decreased in value to offset capital gains and use the losses to reduce taxable income. It is particularly useful in a high-interest rate environment where bond prices may decline. Tax-loss harvesting can be a tax-efficient way to manage your portfolio and potentially lower your overall tax burden. However, it requires careful planning and an understanding of the tax rules surrounding investment sales.
Lower Interest Rates: Spending Boost or Investment Misstep?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The choice between high-interest and low-interest investments depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. High-interest investments, such as bonds or certain stocks, can offer higher returns but may come with higher risks. Low-interest investments, like savings accounts or certificates of deposit (CDs), are generally safer but may provide lower returns. Consider your time frame and the level of risk you're willing to take. If you're saving for a short-term goal, low-risk options might be preferable. For long-term wealth accumulation, you might consider a mix of both strategies to balance risk and return.
When deciding on interest rates, it's essential to understand your investment objectives and risk profile. Higher interest rates often indicate higher risk, such as in the case of stocks or certain real estate investments. These options can offer significant returns but may also be more volatile. Lower interest rates are typically associated with safer investments like government bonds or savings accounts, which provide a steady return but with less potential for growth. Evaluate your financial situation, the time you can commit to the investment, and the level of risk you're comfortable with to make an informed decision.
Yes, investing in low-interest options has several advantages. Firstly, they are generally less risky, making them suitable for risk-averse investors or those with a shorter investment horizon. Low-interest investments often provide a stable and predictable return, which can be useful for meeting short-term financial goals or building an emergency fund. Additionally, these investments are often more accessible and liquid, allowing investors to access their funds without significant penalties. This makes low-interest options an attractive choice for those seeking a more conservative and secure investment strategy.
When making this decision, several key factors come into play. Firstly, assess your investment goals. Are you saving for retirement, a house, or a specific goal with a defined timeline? This will help determine the level of risk you can take. Secondly, evaluate your risk tolerance, which is your ability to handle market fluctuations and potential losses. Higher-interest investments may suit those with a higher risk tolerance. Thirdly, consider the time you can commit to the investment. Some high-interest options may require a longer investment period. Finally, research and compare different investment vehicles, understanding their historical performance, fees, and potential risks to make an informed decision that aligns with your financial objectives.