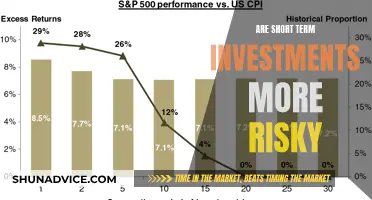
Long-term investment options are a crucial aspect of financial planning, offering a strategic approach to building wealth over time. These options are designed to provide investors with a means to grow their money through various vehicles, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments. The key principle behind long-term investing is to hold assets for an extended period, typically years or even decades, allowing for the potential to weather short-term market fluctuations and benefit from the power of compounding returns. This strategy often involves a diversified portfolio, which can include a mix of growth-oriented stocks, income-generating bonds, and alternative investments like real estate investment trusts (REITs) or mutual funds. Understanding the various long-term investment options available is essential for investors to make informed decisions and build a robust financial future.
What You'll Learn
- Stocks: Investing in individual companies, offering long-term growth potential
- Bonds: Fixed-income securities, providing stable returns over extended periods
- Real Estate: Property investments, offering tangible assets and rental income
- Mutual Funds: Diversified portfolios, managed by professionals, for long-term wealth building
- ETFs: Exchange-Traded Funds, tracking indexes, offering diversification and low costs

Stocks: Investing in individual companies, offering long-term growth potential
Investing in stocks is a fundamental approach to long-term wealth creation, allowing investors to participate in the growth and success of individual companies. This method offers a direct way to build a diversified portfolio and benefit from the expansion of various industries over time. When considering stocks as a long-term investment strategy, it's essential to understand the mechanics and potential advantages.
Stocks, also known as shares or equities, represent ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you become a shareholder, entitling you to a portion of the company's assets and profits. The value of a stock fluctuates based on market conditions, company performance, and investor sentiment. Over the long term, stocks have historically demonstrated the potential for significant growth, outpacing other asset classes like bonds and cash. This is primarily due to the compounding effect of reinvesting dividends and the potential for capital appreciation as the company grows.
One of the key advantages of investing in stocks is the opportunity to benefit from the success of well-managed companies. Successful businesses can drive stock prices higher, providing investors with substantial returns. For instance, investing in a technology company during its early stages could lead to significant gains if the company disrupts its industry and becomes a market leader. Similarly, investing in a healthcare company with innovative products or services could result in long-term growth as the company expands its market share.
Diversification is a critical aspect of stock investing. By spreading your investments across multiple companies and sectors, you reduce the risk associated with any single stock's performance. This approach ensures that your portfolio is not heavily impacted by the decline of a single company or industry. Diversification also allows you to capture the growth potential of various sectors, providing a more stable and consistent long-term return.
To invest in stocks, you can choose between various options, including individual stocks, index funds, or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Individual stocks allow you to select specific companies you believe in and hold them in your portfolio. Index funds and ETFs, on the other hand, provide exposure to a broader market or sector, offering instant diversification. Building a well-researched and diversified stock portfolio requires careful consideration of company fundamentals, market trends, and risk management strategies.
In summary, stocks are a powerful long-term investment option, offering the potential for significant wealth accumulation. By investing in individual companies, you can participate in their growth and success, but it's crucial to conduct thorough research, diversify your portfolio, and remain invested for the long haul to navigate the inherent risks and rewards of the stock market.
Equity or Bonds: Which is Better for Short-Term Investing?
You may want to see also

Bonds: Fixed-income securities, providing stable returns over extended periods
Bonds are a fundamental component of long-term investment strategies, offering investors a stable and predictable source of income. These fixed-income securities represent a loan made by an investor to a borrower, typically a government, municipality, or corporation, in exchange for the promise to repay the principal amount (the loan) along with regular interest payments over a specified period. This makes bonds an attractive option for those seeking a steady income stream, especially in volatile markets where other investments may fluctuate.
The appeal of bonds lies in their ability to provide a consistent return, often with less risk compared to stocks. When you buy a bond, you are essentially lending money to the issuer, who uses this capital for various projects or operations. In return, the issuer agrees to pay you a fixed rate of interest at regular intervals, known as the coupon rate. This structured repayment of interest ensures a steady income for bondholders, making it a reliable long-term investment strategy.
One of the key advantages of bonds is their diversification potential. They are considered a low-risk asset class, especially when compared to stocks. By including bonds in an investment portfolio, investors can reduce overall risk while still benefiting from the potential for capital appreciation and stable income. This is particularly important for long-term investors who aim to build wealth over time, as bonds can provide a solid foundation for their investment strategy.
Bonds come in various forms, each with its own characteristics and risk profile. Government bonds, for instance, are issued by national governments and are often considered the safest investment option due to the inherent creditworthiness of the issuing government. Municipal bonds, on the other hand, are issued by local governments or municipalities to fund public projects, offering tax-exempt interest income, which can be an attractive feature for investors in higher tax brackets. Corporate bonds, issued by businesses, provide an opportunity to invest in the growth of companies, but they carry a higher risk compared to government bonds.
In summary, bonds are a critical long-term investment option, offering stability, predictability, and diversification benefits. They provide a consistent income stream through regular interest payments, making them an attractive choice for investors seeking a reliable and low-risk investment strategy. Understanding the different types of bonds and their respective risks can help investors make informed decisions to align their portfolios with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Balancing Act: Merging Short-Term Gains with Long-Term Wealth Creation
You may want to see also

Real Estate: Property investments, offering tangible assets and rental income
Real estate investment is a popular and tangible way to build wealth over the long term. It involves purchasing properties, which can be residential or commercial, and holding them as an asset for an extended period. This strategy offers investors a unique opportunity to benefit from both the potential for property value appreciation and a steady stream of rental income.
When investing in real estate, one of the primary advantages is the physical, tangible nature of the asset. Unlike some other investment vehicles, such as stocks or bonds, real estate provides a concrete, visible asset. This can be particularly appealing to investors who prefer a more hands-on approach and want to see the value of their investments in a physical form. For instance, buying a house allows investors to own a piece of property, which can be a source of pride and a tangible marker of their financial success.
The rental income generated from property investments is another significant benefit. By leasing out properties, investors can create a consistent cash flow, providing a steady income stream. This is especially attractive for long-term investors who seek a reliable, recurring revenue source. Over time, as the property appreciates in value, the rental income can also increase, offering a dual benefit. Additionally, real estate investments often provide tax advantages, such as deductions for mortgage interest, property taxes, and depreciation, which can further enhance the overall return on investment.
Diversifying one's portfolio with real estate can be a strategic move. It allows investors to spread their risk across different property types and geographic locations. For example, an investor might choose to own a mix of single-family homes, multi-unit apartments, and commercial spaces. This diversification can help mitigate the risks associated with any single property and provide a more stable investment portfolio. Furthermore, real estate investments can offer a hedge against inflation, as property values and rental income often increase over time, outpacing the effects of inflation.
In the long term, real estate investments can be a powerful tool for wealth creation. The potential for property values to rise, combined with the steady rental income, can lead to substantial returns. However, it is essential to conduct thorough research and due diligence before making any investment decisions. Factors such as location, market trends, and local regulations can significantly impact the success of a real estate investment. Therefore, investors should carefully consider their investment strategy, including the type of property, the location, and the potential for long-term growth, to ensure a successful and rewarding venture.
Shiba Inu: A Long-Term Investment Strategy?
You may want to see also

Mutual Funds: Diversified portfolios, managed by professionals, for long-term wealth building
Mutual funds are an excellent long-term investment option for those seeking to build wealth over time. These funds offer a unique approach to investing by pooling money from multiple investors to create a diversified portfolio. Here's a breakdown of why mutual funds are a smart choice for long-term wealth creation:
Diversification: One of the key advantages of mutual funds is the inherent diversification they provide. When you invest in a mutual fund, your money is spread across a carefully selected group of securities, including stocks, bonds, and other assets. This diversification reduces risk because it minimizes the impact of any single investment's performance on your overall portfolio. By holding a variety of assets, mutual funds aim to provide a more stable and consistent return over the long term.
Professional Management: Mutual funds are managed by experienced investment professionals who have the expertise and resources to make informed decisions on your behalf. These fund managers research and analyze various investment opportunities, decide on asset allocations, and make strategic adjustments to the portfolio. Their goal is to optimize returns while managing risk, which is particularly beneficial for long-term investors who want to avoid the stress of constant market monitoring.
Long-Term Wealth Building: Mutual funds are designed with a long-term perspective in mind. They are structured to weather short-term market fluctuations and focus on consistent growth over an extended period. This makes them ideal for investors who want to build substantial wealth over time, such as for retirement or other long-term financial goals. The power of compounding returns, where earnings generate additional earnings, can significantly boost your investment over the years.
When investing in mutual funds, it's essential to consider your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial goals. Different mutual funds have varying levels of risk and investment strategies, so choosing the right fund that aligns with your objectives is crucial. Additionally, regular review and rebalancing of your portfolio by the fund manager can help ensure that your investments stay on track.
In summary, mutual funds offer a powerful tool for long-term wealth accumulation through diversification, professional management, and a focus on consistent growth. They provide an accessible and efficient way to invest in a wide range of assets, making them an attractive choice for investors looking to build a secure financial future.
Master Short-Term Investing: Strategies for Profiting from Futures
You may want to see also

ETFs: Exchange-Traded Funds, tracking indexes, offering diversification and low costs
Exchange-Traded Funds, or ETFs, are a popular long-term investment option that offers a unique blend of diversification, low costs, and flexibility. These funds are designed to track a specific index, such as the S&P 500 or the NASDAQ-100, and they trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks. This trading mechanism provides investors with a simple and efficient way to gain exposure to a broad market segment or a particular asset class.
One of the key advantages of ETFs is their ability to provide instant diversification. When you invest in an ETF, you are essentially buying a basket of securities that represent the entire index it tracks. For example, an S&P 500 ETF would hold all 500 stocks in the S&P index, allowing investors to own a piece of the entire market with a single purchase. This diversification strategy is particularly appealing for long-term investors as it reduces the risk associated with individual stock volatility. By holding a diverse range of assets, ETFs help smooth out the impact of market fluctuations, providing a more stable investment experience.
The low-cost nature of ETFs is another attractive feature. These funds typically have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed mutual funds. The expense ratio represents the annual management fee charged by the fund, and ETFs generally incur lower transaction costs due to their passive management approach. This cost-effectiveness is a significant advantage for long-term investors, as it allows them to keep more of their returns over time. Lower costs also mean that investors can achieve their financial goals with less capital outlay, making ETFs accessible to a wider range of investors.
In addition to diversification and low costs, ETFs offer flexibility in terms of trading and investment strategies. They can be traded throughout the day, just like stocks, providing investors with the ability to buy or sell at any time during market hours. This liquidity is advantageous for both long-term and short-term investors, allowing them to adjust their positions based on market conditions or personal financial needs. Furthermore, ETFs can be used in various investment strategies, such as buy-and-hold, momentum trading, or even as a tool for hedging, making them versatile instruments for different investment approaches.
For long-term investors, ETFs provide an efficient way to gain exposure to specific market segments or asset classes. By tracking indexes, ETFs offer a simple and cost-effective way to invest in a diverse range of securities. This approach aligns with the principles of long-term investing, which often emphasizes diversification and minimizing transaction costs. Additionally, the transparency and liquidity of ETFs allow investors to monitor their holdings and make informed decisions, ensuring that their investment strategy remains aligned with their financial goals.
In summary, ETFs are a powerful long-term investment option that offers diversification, low costs, and flexibility. By tracking indexes, these funds provide investors with a simple and efficient way to gain exposure to various market segments or asset classes. The low expense ratios and trading flexibility of ETFs make them an attractive choice for long-term investors seeking to build a robust and cost-effective investment portfolio.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Investing: Which Strategy is Right for You?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
For new investors, long-term investment options often include index funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and mutual funds. These are considered low-risk and provide diversification, making them a great starting point for building a portfolio over time.
Selecting a strategy depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Consider consulting a financial advisor who can assess your situation and recommend a plan. They might suggest a mix of stocks, bonds, and alternative investments to align with your objectives.
Yes, real estate can be a lucrative long-term investment. It offers the potential for rental income and property value appreciation. However, it requires significant capital and can be illiquid, meaning it may take time to buy or sell properties.
Bonds are generally considered less risky than stocks and can provide a steady income stream through regular interest payments. They are often used for long-term wealth building and can offer a more stable investment compared to volatile equity markets.
Diversification is key to managing risk. Consider investing in various asset classes such as stocks, bonds, commodities, and real estate. You can also explore international markets and different sectors to spread your investments and potentially benefit from a wide range of economic conditions.