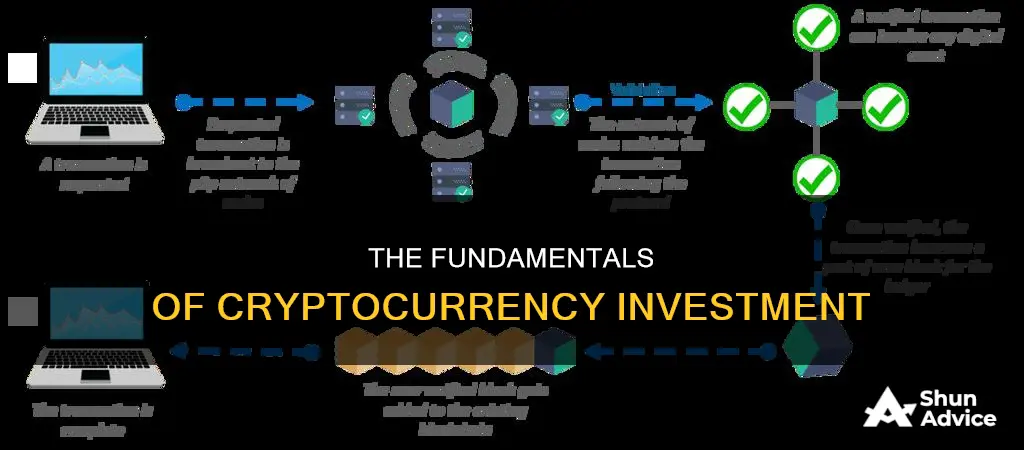
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that is secured by cryptography, making it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Cryptocurrencies are powered by a technology known as blockchain, which maintains a tamper-resistant record of transactions and keeps track of who owns what. The use of blockchains addressed a problem faced by previous efforts to create purely digital currencies: preventing people from making copies of their holdings and attempting to spend them twice.
When you invest in cryptocurrency, you are typically buying and holding one or more crypto coins. However, there are other ways to invest in this asset class, such as investing in cryptocurrency companies, funds, or even becoming a crypto miner or validator. It's important to understand the risks involved in investing in cryptocurrency, as it is a highly volatile and speculative asset. The prices of cryptocurrencies can be very unpredictable, and there are also regulatory, security, and tax considerations to keep in mind.
What You'll Learn
- Crypto wallets: Hot wallets are convenient for frequent trading but vulnerable to hacking, while cold wallets are more secure but less convenient
- Crypto volatility: Crypto is highly volatile and may be more susceptible to market manipulation than securities
- Crypto risks: Regulatory changes could affect the future value of crypto
- Crypto security: Crypto investors should be aware of user, regulatory, counterparty, management, programming, and market manipulation risks
- Crypto taxes: Crypto is taxed as property, rather than currency, in the US

Crypto wallets: Hot wallets are convenient for frequent trading but vulnerable to hacking, while cold wallets are more secure but less convenient
When you buy cryptocurrency, you are investing in a digital currency that is secured by cryptography, making it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Cryptocurrencies are generally used to pay for services or as speculative investments.
Now, when it comes to storing your cryptocurrency, you can use either a hot wallet or a cold wallet. Hot wallets are always connected to the internet, making them convenient for frequent trading and spending. They are accessible from various internet-enabled devices, such as mobile phones, tablets, and laptops. However, due to their connection to the internet, hot wallets are more vulnerable to hacking and theft. It's important to only keep small amounts in your hot wallet and use it primarily for transactions.
On the other hand, cold wallets are offline storage solutions that are not connected to the internet. They can come in the form of hardware devices, such as USB sticks, or even paper wallets. Cold wallets are more secure than hot wallets since they are not susceptible to online attacks. However, they are less convenient for frequent trading as they require additional steps to connect to the internet. Cold wallets are better suited for long-term storage and keeping larger amounts of cryptocurrency.
To ensure the safety of your cryptocurrency, it is recommended to use a combination of both hot and cold wallets. This way, you can store smaller amounts for frequent trading in a hot wallet while keeping the majority of your cryptocurrency secure in a cold wallet.
KDA Coin: A Smart Investment Move?
You may want to see also

Crypto volatility: Crypto is highly volatile and may be more susceptible to market manipulation than securities
Crypto is highly volatile and susceptible to market manipulation. Its value can fluctuate dramatically in a short period, and it is prone to speculative investing and pump-and-dump schemes.
The volatile nature of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin is influenced by several factors, including supply and demand, investor sentiment, media hype, and government regulations. As a relatively new asset, Bitcoin is still in the price discovery phase, and its value is yet to stabilise. Its limited supply of 21 million coins also contributes to price volatility.
The actions of "whales", or investors with large holdings, can significantly impact the market. A sudden liquidation of their Bitcoin could cause a panic that drives prices down. Conversely, their continued accumulation can signal confidence and attract more investors.
The decentralised nature of crypto makes it vulnerable to market manipulation. Techniques like spoofing, where large buy or sell orders are placed and then cancelled, can simulate market demand and influence prices. Pump-and-dump schemes, where false information is spread to drive up prices, are also common. These schemes take advantage of the lack of transparency and regulation in the crypto market.
To combat market manipulation, regulatory organisations like the SEC are implementing and enforcing regulations. Additionally, technological advancements and user education are crucial for protecting investors and maintaining a fair and stable crypto market.
Mcontent Coin: A Worthy Investment?
You may want to see also

Crypto risks: Regulatory changes could affect the future value of crypto
The cryptocurrency market is susceptible to regulatory changes, which can significantly impact the value of crypto assets. The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is rapidly evolving, with governments and financial authorities worldwide taking a more active role in overseeing the industry. While some countries, like Japan and South Korea, have embraced crypto and implemented favourable regulations, others, like China, have imposed strict bans on crypto-related activities. This divergence in global regulatory approaches can create uncertainty and affect the future value of cryptocurrencies.
In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been particularly active in enforcing regulations on the crypto industry. Following a series of high-profile scandals and bankruptcies, such as the collapse of FTX, the SEC has increased its scrutiny of crypto exchanges, tokens, and service providers. The SEC's actions include requiring certain crypto exchanges to register as securities trading platforms and enhancing anti-fraud and disclosure standards. These regulatory changes can influence the perception of cryptocurrencies as investment vehicles and impact their liquidity and accessibility.
Additionally, the classification of cryptocurrencies as securities or commodities remains ambiguous. The SEC has taken the stance that cryptocurrencies meeting the Howey Test criteria are subject to its regulatory authority. However, the Supreme Court ruling in Loper Bright Enterprises v. Raimondo in June 2024 may shift the regulatory landscape by requiring Congress to clearly define crypto regulation through legislation. This ruling underscores the dynamic nature of crypto regulations and the potential for future regulatory changes that could significantly affect the value of crypto assets.
The lack of consistent global regulations also poses challenges. The International Organization of Securities Commissions has emphasised the need for global standards to address the cross-border nature of crypto markets and reduce the "significant risk of harm" to investors. Without a coordinated global approach, the effectiveness of national regulatory efforts may be limited, and the risk of crypto assets being used for money laundering, terrorism financing, and capital outflows remains.
Furthermore, regulatory changes can directly impact the utility and adoption of cryptocurrencies. For example, the European Union's Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) imposes licensing requirements on crypto companies and enhances customer protection measures. While these regulations aim to protect investors and improve market integrity, they may also affect the ease of transacting with cryptocurrencies and potentially hinder innovation in the industry.
In summary, regulatory changes are a significant factor that can influence the future value of cryptocurrencies. The evolving global regulatory landscape, divergent approaches across countries, and ongoing legal debates contribute to the uncertainty surrounding crypto assets. Investors should carefully consider the potential impact of regulatory changes on the value and utility of cryptocurrencies before investing in this volatile market.
Dogelon Mars Coin: A Worthy Investment?
You may want to see also

Crypto security: Crypto investors should be aware of user, regulatory, counterparty, management, programming, and market manipulation risks
When you buy cryptocurrency, you are investing in a digital or virtual currency that is secured by cryptography, which makes it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Cryptocurrencies are decentralised networks based on blockchain technology—a distributed ledger enforced by a disparate network of computers.
Crypto investors should be aware of the following risks:
- User risk: There is no way to reverse or cancel a cryptocurrency transaction after it has been sent.
- Regulatory risks: The regulatory status of some cryptocurrencies is still unclear in many areas, with some governments seeking to regulate them as securities, currencies, or both. A sudden regulatory crackdown could make it challenging to sell cryptocurrencies or cause a market-wide price drop.
- Counterparty risks: Many investors and merchants rely on exchanges or other custodians to store their cryptocurrency. Theft or loss by one of these third parties could result in losing one's entire investment.
- Management risks: Due to the lack of coherent regulations, there are few protections against deceptive or unethical management practices. Many investors have lost large sums to management teams that failed to deliver a product.
- Programming risks: Many investment and lending platforms use automated smart contracts to control the movement of user deposits. An investor using one of these platforms assumes the risk that a bug or exploit in these programs could cause them to lose their investment.
- Market manipulation: Market manipulation remains a substantial problem in cryptocurrency, with influential people, organisations, and exchanges acting unethically.
Jamaicans: Your Guide to Investing in Bitcoin
You may want to see also

Crypto taxes: Crypto is taxed as property, rather than currency, in the US
When investing in cryptocurrency, you are investing in a digital currency that can be used to buy goods and services or traded for profit. Bitcoin is the most widely used cryptocurrency. It was initially developed to be a form of payment without the need for a central bank.
In the US, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats cryptocurrencies as property for tax purposes, rather than as a currency. This means that if you sell or use your cryptocurrency and it is worth more than when you bought it, you will pay taxes on the capital gains. If you receive crypto as payment for business purposes, it is taxed as business income. If you are a cryptocurrency miner, the value of your crypto at the time it was mined counts as income.
The tax implications of cryptocurrency can be complex, and it is important to consult with an accountant or tax professional familiar with cryptocurrency and current practices to ensure you are reporting your taxes correctly.
Gold Coin Investment: Which is the Best Buy?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency secured by cryptography, which makes it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Cryptocurrencies are decentralised and exist on distributed ledgers, which are enforced by a disparate network of computers.
Cryptocurrencies are highly volatile and susceptible to market manipulation. They are also not insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) or the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC). However, cryptocurrencies can be used to generate returns, and they streamline remittances.
You can buy cryptocurrency using a crypto exchange or through certain broker-dealers. Once you own it, you can store, manage, and even buy or sell your crypto in a wallet. You can also invest in companies with a partial or total focus on cryptocurrency, or cryptocurrency-focused funds.







