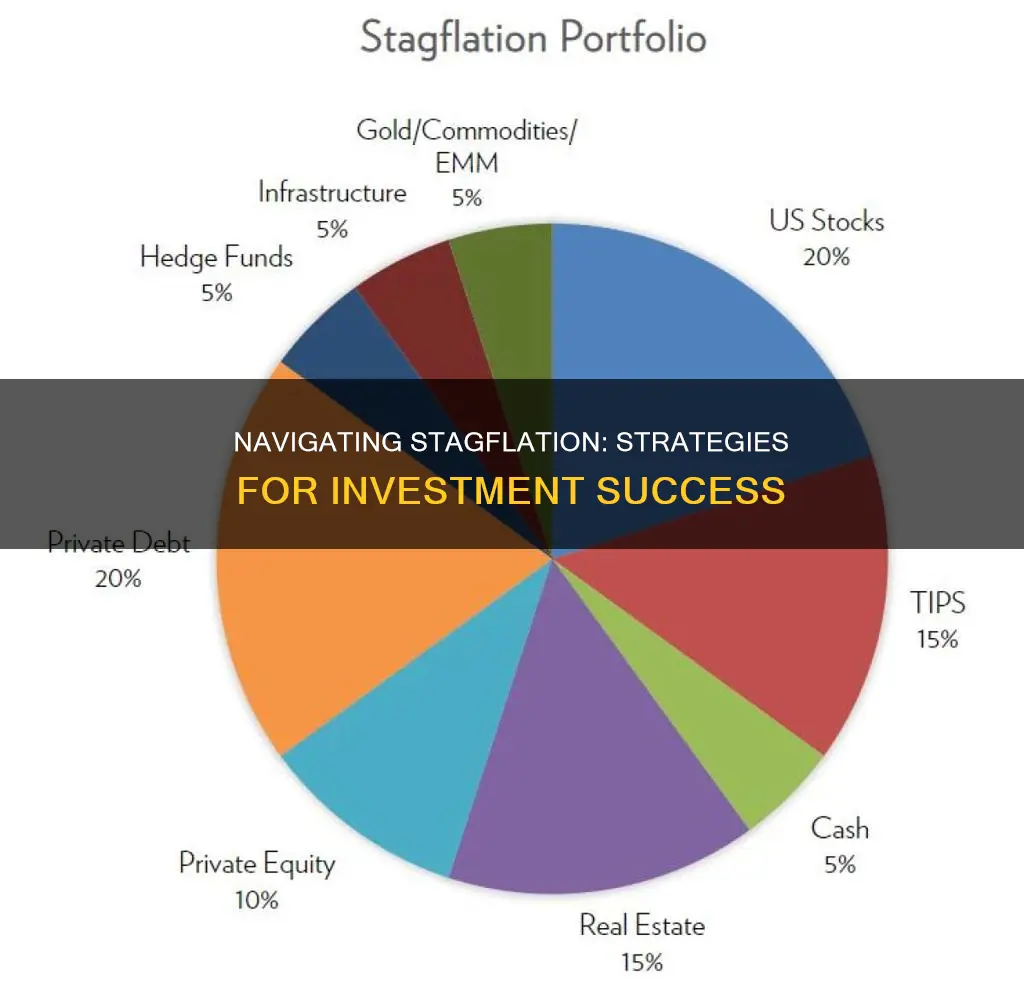
Stagflation, a challenging economic environment characterized by high inflation and stagnant growth, demands strategic investment choices. This paragraph introduces the topic by highlighting the importance of understanding investment strategies that can thrive in such a complex market. It emphasizes the need for investors to identify assets that can navigate the dual pressures of inflation and economic slowdown, offering a balanced approach to capital preservation and growth. The discussion will explore various investment options, including those that have historically demonstrated resilience during stagflationary periods, providing insights into how investors can build a diversified portfolio to weather these economic conditions.
What You'll Learn
- Stocks: Focus on defensive sectors like utilities and consumer staples
- Bonds: Short-term bonds offer better protection than long-term ones
- Real Estate: Invest in rental properties or REITs for inflation-resistant returns
- commodities: Gold, silver, and agricultural products can hedge against stagflation
- Inflation-indexed Bonds: These bonds adjust their value to match inflation

Stocks: Focus on defensive sectors like utilities and consumer staples
In times of stagflation, where inflation persists alongside high unemployment and stagnant wages, certain investment strategies can help navigate the challenging economic environment. One effective approach is to focus on defensive sectors, particularly utilities and consumer staples, which tend to exhibit resilience during such periods.
Defensive sectors are characterized by their ability to maintain stable or even growing revenues and profits, regardless of economic cycles. Utilities, for instance, provide essential services such as electricity, water, and gas, which are relatively inelastic in demand. This means that even during economic downturns, people still need these utilities, ensuring a consistent revenue stream for utility companies. Similarly, consumer staples, which include household essentials like food, beverages, and personal care products, are less susceptible to price fluctuations and tend to experience steady sales.
Investing in utility companies and consumer staples stocks can provide a hedge against stagflation. These companies often have strong balance sheets, allowing them to maintain dividends and share buybacks, which can be attractive to income-seeking investors. Additionally, their consistent revenue streams and ability to manage costs effectively make them less sensitive to economic downturns. As a result, their stock prices may be more stable compared to cyclical stocks, which are more volatile during stagflationary periods.
When considering specific investments, it's important to look for companies with a history of strong performance during past stagflationary periods. These companies often have a diversified revenue base, robust market positions, and a track record of successful cost management. For utilities, look for regulated monopolies or strong multi-utility companies with a history of stable dividends. In the consumer staples sector, focus on brands with a wide customer base, strong market positions, and a history of innovation to maintain their relevance.
Diversification is also key during stagflation. Consider building a portfolio that includes a mix of utility and consumer staples stocks, as well as other defensive sectors like healthcare and consumer non-durables. This diversified approach can help mitigate risks and provide a more stable investment return, even in challenging economic conditions.
The Wealthy Retiree's Investment Playbook: Strategies for Preserving and Growing Your Nest Egg
You may want to see also

Bonds: Short-term bonds offer better protection than long-term ones
In times of stagflation, where inflation is high and economic growth is stagnant, investors often seek safe-haven assets that can provide stability and protect their capital. Bonds, particularly short-term ones, can be an effective investment strategy during such periods. Here's why short-term bonds offer better protection compared to their long-term counterparts:
Maturity and Interest Rates: Short-term bonds have a maturity period of less than one year, which means they are less sensitive to changes in interest rates. When central banks raise interest rates to combat inflation, long-term bonds are more likely to experience price declines as their future cash flows become less attractive. In contrast, short-term bonds, with their shorter duration, are less affected by these rate hikes, providing a more stable investment.
Liquidity and Flexibility: Stagflationary environments often lead to market volatility, and investors may need quick access to their funds. Short-term bonds offer higher liquidity, allowing investors to redeem their investments more frequently without incurring significant losses. This flexibility is crucial when navigating uncertain economic conditions.
Reduced Credit Risk: During stagflation, credit risk can become a significant concern. Short-term bonds, being less sensitive to interest rate changes, often have lower credit risk compared to long-term bonds. This is especially true for government-issued short-term securities, which are considered low-risk investments. Investors can benefit from the stability of these bonds while still enjoying the protection against inflation.
Capital Preservation: The primary goal during stagflation is to preserve capital. Short-term bonds excel in this aspect. Their shorter duration means they are less exposed to the volatility associated with long-term investments. By focusing on short-term bonds, investors can ensure that their capital remains relatively stable, providing a solid foundation for potential future growth when economic conditions improve.
In summary, short-term bonds are a valuable addition to an investment portfolio during stagflation. Their maturity, liquidity, and reduced credit risk make them an attractive option for investors seeking protection and stability. While long-term bonds may offer higher potential returns, the risks associated with stagflationary conditions make short-term investments a more prudent choice.
Five Things to Avoid When Trading Investments
You may want to see also

Real Estate: Invest in rental properties or REITs for inflation-resistant returns
In times of stagflation, when the economy is stuck in a vicious cycle of high inflation and stagnant growth, traditional investments like stocks and bonds may not offer the protection investors seek. This is where real estate can step in as a powerful hedge against stagflationary pressures. Real estate investments, whether in the form of purchasing rental properties or investing in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), have historically demonstrated resilience during such economic conditions.
Rental properties provide a tangible asset that can act as a hedge against inflation. As inflation rises, the cost of living increases, and so do the rents that landlords can charge. This dynamic allows property owners to maintain or even increase their income streams, ensuring that their returns keep pace with or exceed the rising inflation rate. Moreover, rental properties offer a degree of financial security and stability, providing a consistent cash flow that can be particularly valuable during economic downturns.
For those who prefer a more liquid investment option, REITs are an excellent alternative. REITs are companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate across various sectors, including office, retail, and residential. By investing in REITs, you gain exposure to the real estate market without the need to directly purchase and manage properties. REITs have a strong track record of outperforming the broader market during stagflationary periods due to their diverse portfolio of assets and the ability to leverage real estate's inherent inflation-resistant nature.
When investing in rental properties, it's crucial to consider factors such as location, market demand, and property management. Researching and selecting areas with strong rental demand and a history of steady population growth can ensure a more stable and profitable investment. Additionally, engaging professional property management services can help mitigate the risks associated with tenant turnover and maintenance, allowing investors to focus on other opportunities.
In summary, stagflation presents unique challenges for investors, but real estate investments offer a compelling solution. Whether through direct property ownership or REITs, real estate provides a tangible asset class that can act as a hedge against inflation. By strategically selecting rental properties and leveraging the power of REITs, investors can build a robust portfolio that withstands the test of stagflationary economic conditions. This approach not only preserves capital but also provides a means to grow wealth over time, making it an attractive strategy for those seeking long-term financial security.
Renewables: Why the Reluctance?
You may want to see also

commodities: Gold, silver, and agricultural products can hedge against stagflation
In times of stagflation, when the economy is stuck in a vicious cycle of high inflation and stagnant growth, traditional investments like stocks and bonds may not offer the best protection. This is where commodities come into play as a powerful hedge against stagflation. Among the various commodities, gold, silver, and agricultural products stand out as effective tools to safeguard your wealth.
Gold, a timeless asset, has long been regarded as a safe-haven investment. Its value tends to increase during periods of economic uncertainty and inflation. When stagflation hits, central banks often reduce interest rates to stimulate the economy, which can lead to a decline in the value of fiat currencies. Gold, being a tangible asset, provides a store of value that is not subject to the same fluctuations as paper money. It is a hedge against inflation and a means to protect your purchasing power.
Silver, often referred to as the 'poor man's gold,' is another excellent commodity to consider. It is a relatively inexpensive alternative to gold and can be a cost-effective way to diversify your portfolio. Silver, like gold, is a precious metal that retains its value even during economic downturns. Its industrial applications and limited supply make it a valuable commodity, especially when inflation is high. Investing in silver can provide a hedge against stagflation and offer a hedge against the erosion of currency value.
Agricultural products, such as grains, oilseeds, and livestock, also play a crucial role in stagflation hedging. These commodities are essential for human consumption and have a relatively inelastic supply, meaning their production cannot be quickly adjusted to meet sudden changes in demand. During stagflation, the prices of agricultural products often rise due to increased demand and supply chain disruptions. Investing in agricultural futures or purchasing physical commodities can provide a hedge against rising food prices and protect your purchasing power in a stagflationary environment.
In summary, commodities like gold, silver, and agricultural products offer a robust strategy to navigate stagflation. These investments provide a hedge against inflation, currency devaluation, and supply chain disruptions. By allocating a portion of your portfolio to these tangible assets, you can safeguard your wealth and maintain your purchasing power when traditional investments may falter. Remember, during times of economic uncertainty, commodities can be a reliable anchor for your investment strategy.
Unemployed and Unretired: Navigating Investment Strategies for a Secure Future
You may want to see also

Inflation-indexed Bonds: These bonds adjust their value to match inflation
Inflation-indexed bonds, also known as inflation-linked or index-linked bonds, are a type of fixed-income security designed to protect investors from the erosion of purchasing power caused by inflation. These bonds are particularly relevant during stagflationary periods when the economy experiences high inflation and stagnant or negative economic growth. Here's how they work and why they can be a valuable addition to an investment portfolio during such challenging economic times.
When an economy is in stagflation, traditional fixed-income investments, such as conventional bonds, may not provide adequate protection against the rising costs of living. Inflation-indexed bonds, however, offer a unique advantage. These bonds have a special feature: their principal value (the initial amount invested) is adjusted periodically to reflect changes in a relevant inflation index. The most common index used is the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures the average change over time in the prices paid by consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services.
As inflation rises, the bond's principal value increases, ensuring that the bond's value keeps pace with the rising prices. This means that even if inflation erodes the purchasing power of the bond's face value, the adjusted principal value will provide a more real value over time. For instance, if you invest $1,000 in an inflation-indexed bond with a 5% inflation indexation and inflation rises by 3% over the year, your bond's principal value will increase to $1,030. This adjusted value will then be used to calculate the interest payments, ensuring that the bond's income stream keeps up with inflation.
The appeal of inflation-indexed bonds lies in their ability to provide a real return, which is the return after accounting for inflation. During stagflation, when inflation is high and volatile, these bonds can offer a stable and reliable source of income. They are particularly attractive to risk-averse investors who want to protect their capital from the adverse effects of inflation. Additionally, these bonds often have a lower credit risk compared to conventional bonds, as they are backed by the government or a government-related entity, making them a safer investment option.
In summary, inflation-indexed bonds are a powerful tool for investors seeking to navigate stagflationary environments. By adjusting their value to match inflation, these bonds ensure that investors' purchasing power remains intact, providing a more secure and reliable investment during times of economic uncertainty and high inflation. This investment strategy allows individuals to maintain their standard of living and potentially build wealth even in the face of challenging economic conditions.
Chymall Investment: Unlocking the Secrets of Smart Financial Strategies
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Stagflation is an economic condition characterized by high inflation and stagnant economic growth, often accompanied by high unemployment. This unique economic environment can significantly impact investments as traditional safe-haven assets like government bonds may not offer sufficient protection against inflation, while riskier assets might face challenges due to economic uncertainty.
During stagflation, stock market performance can be volatile. While some sectors may benefit from inflation, such as utilities and consumer staples, others might struggle. Cyclical sectors like energy and industrials could see a temporary boost, but overall market sentiment may remain cautious. Investors often seek defensive stocks that can provide stable returns, such as those in the consumer goods or healthcare sectors.
Yes, certain investment strategies can perform well during stagflation. One approach is to focus on high-quality, dividend-paying stocks that can provide a steady income stream, even in challenging economic times. Another strategy is to invest in inflation-resistant assets like real estate investment trusts (REITs) or commodities, which have historically held their value during stagflation.
Alternative investments can offer diversification benefits during stagflation. Precious metals like gold and silver are often considered safe-haven assets and can act as a hedge against inflation. Additionally, inflation-indexed bonds, which adjust their value with inflation, can provide a hedge against rising prices. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) that focus on inflation-resistant properties can also be a viable option.