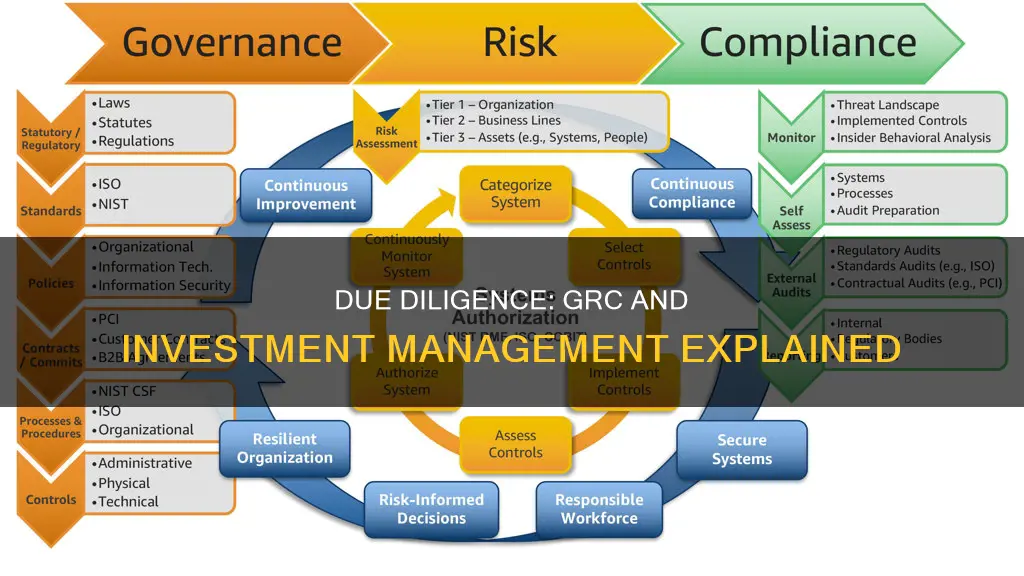
Due diligence is an investigation, audit, or review performed to confirm facts or details of a matter under consideration. In the context of investment management, due diligence involves a thorough examination of a company's financial records, performance, and future prospects before making an investment decision. It is a systematic approach to analysing and mitigating risks associated with investment choices. Due diligence is also a critical component of GRC (governance, risk management, and compliance) as it helps companies comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Due diligence is an investigation, audit, or review performed to confirm facts or details of a matter under consideration. |
| Purpose | Due diligence is a way to reduce risk exposure and ensure that a party is aware of all the details of a transaction before they agree to it. |
| Types | Context-specific due diligence, legal due diligence, financial due diligence, tax due diligence, hard due diligence, soft due diligence |
| Application | Due diligence is performed by equity research analysts, fund managers, broker-dealers, individual investors, and companies considering acquiring other companies. |
| Process | Due diligence involves examining a company's numbers, comparing them over time, and benchmarking them against competitors. |
| Benefits | Due diligence helps investors and companies understand the nature of a deal, the risks involved, and whether the deal fits with their portfolio. |
| Costs | The costs of due diligence depend on its scope and duration, which depend on the complexity of the target company. |
| Network Due Diligence | Companies can use a central platform to connect with other companies, share information, and perform "network due diligence". |
What You'll Learn
- Due diligence in GRC and investment management is an investigation, audit, or review to confirm facts and financial information
- Due diligence is a systematic way to analyse and mitigate risk from business or investment decisions
- Due diligence is mandatory for companies in the fund industry, as per national laws and international regulations
- Due diligence is completed before a deal closes to assure the buyer of what they're getting
- Due diligence helps investors and companies understand the nature of a deal, the risks involved, and whether the deal fits their portfolio

Due diligence in GRC and investment management is an investigation, audit, or review to confirm facts and financial information
Due diligence is a process of verification, investigation, or audit of a potential deal or investment opportunity. It is a systematic way to analyse and mitigate risk from a business or investment decision. Due diligence in Governance, Risk Management and Compliance (GRC) and investment management specifically involves reviewing financial records, benchmarking a company's numbers against competitors, and confirming facts and financial information.
In the context of GRC and investment management, due diligence is often a legal requirement. For example, companies in the fund industry must perform due diligence on their partners, according to national laws and international regulations such as EU directives. Due diligence can also be conducted voluntarily, especially by individual investors.
Due diligence can take many forms, depending on its purpose and context. For instance, commercial due diligence considers a company's market share and competitive positioning, including future prospects and growth opportunities. Financial due diligence involves auditing a company's financial statements and books to ensure no irregularities and confirm solid financial footing.
Due diligence in GRC and investment management can also be categorised as "hard" or "soft". Hard due diligence focuses on the numbers and data found on financial statements, such as balance sheets and income statements. Soft due diligence, on the other hand, takes a more qualitative approach, considering aspects like management quality, employee relationships, corporate culture, and leadership.
Due diligence is a critical step in the decision-making process for investors and companies. It helps them understand the nature of a deal, the associated risks, and whether the deal aligns with their investment strategy and portfolio.
Becoming an Investment Manager: UK Pathways and Steps
You may want to see also

Due diligence is a systematic way to analyse and mitigate risk from business or investment decisions
Due diligence is a systematic process of verification, investigation, or audit to analyse and mitigate risk from business or investment decisions. It is a way to reduce risk exposure and ensure that a party is aware of all the details of a transaction before agreeing to it. Due diligence is often carried out before a deal closes to provide the buyer with assurance about what they are getting. It is also useful for sellers, as it can reveal that the fair market value of their company is more than initially thought.
In the financial world, due diligence involves examining a company's financial records, including financial statements, books, and tax exposure. It also involves reviewing a company's market share, competitive positioning, supply chain, sales pipeline, and overall operations. Due diligence can be categorised as "hard" or "soft". Hard due diligence focuses on the numbers and data found on financial statements, while soft due diligence takes a more qualitative approach, considering aspects such as management quality and customer loyalty.
Due diligence is also important in the context of mergers and acquisitions (M&A). During an M&A transaction, due diligence may involve examining the target company's financial statements, future growth prospects, current practices and policies, and shareholder value. It can also include analysing the company's culture, management, and other human elements.
In the fund industry, companies are legally obligated to perform due diligence on their partners. This includes distributor due diligence, KYC on distributors, and due diligence on cloud service providers and institutional clients, among others. Due diligence processes can be facilitated through the use of networks and central databases, where companies can connect and share information.
Assessing Investment Portfolios: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

Due diligence is mandatory for companies in the fund industry, as per national laws and international regulations
Due diligence is a process of verification, investigation, or audit that is conducted to confirm facts and financial details before entering into a transaction with another party. It is a systematic approach to assess and mitigate risks associated with business or investment decisions. In the context of GRC (governance, risk management, and compliance) and investment management, due diligence plays a crucial role in ensuring informed decision-making and compliance with regulatory requirements.
For companies in the fund industry, due diligence is indeed mandatory, as per national laws and international regulations. This includes directives from the EU, such as MiFID II, which imposes "mandatory" due diligence requirements on asset managers when dealing with distributors. Companies in this sector have to perform due diligence on most, if not all, of their partners. This involves investigating and auditing a range of aspects, including financial statements, company performance, management, ownership, and compliance with laws and regulations.
The scope of due diligence can vary depending on the context and the specific industry. For instance, legal due diligence ensures compliance with all necessary legal, regulatory, and compliance requirements. Financial due diligence involves auditing financial statements and books to ensure accuracy and solid financial footing. Tax due diligence assesses tax exposure and potential liabilities. Commercial due diligence evaluates market share, competitive positioning, and growth opportunities.
Due diligence is a critical tool for reducing risk exposure and ensuring that all parties involved in a transaction are fully informed. It provides assurance to buyers and sellers alike, allowing them to make more confident decisions. In the context of mergers and acquisitions (M&A), due diligence is particularly important, as it helps identify potential defects in the deal, obtain valuable information for valuation, and ensure compliance with investment criteria.
The costs associated with due diligence are justifiable given the potential risks of not conducting it properly. Both buyers and sellers typically bear their own expenses, engaging professionals such as investment bankers, accountants, and attorneys to assist in the process. Due diligence contributes to informed decision-making by enhancing the quality of information available, thereby increasing the chances of success for transactions.
Understanding Investment Management Firms: What, Why, and How?
You may want to see also

Due diligence is completed before a deal closes to assure the buyer of what they're getting
Due diligence is a process of verification, investigation, or audit of a potential deal or investment opportunity. It is completed before a deal closes to provide the buyer with an assurance of what they are getting. Due diligence is a systematic way to analyse and mitigate risk from a business or investment decision.
In the financial world, due diligence requires an examination of financial records before entering into a proposed transaction with another party. Due diligence is performed by equity research analysts, fund managers, broker-dealers, individual investors, and companies that are considering acquiring other companies.
There are several types of due diligence, including:
- Commercial due diligence, which considers a company's market share, competitive positioning, and future prospects.
- Legal due diligence, which ensures a company has all the necessary legal, regulatory, and compliance requirements in place.
- Financial due diligence, which audits a company's financial statements and books to ensure there are no irregularities.
- Tax due diligence, which looks at a company's tax exposure and whether there are any outstanding tax payments.
Due diligence can also be categorised as "hard" or "soft". Hard due diligence focuses on the numbers and data found on financial statements, while soft due diligence takes a more qualitative approach, looking at aspects such as the quality of management and the loyalty of the customer base.
Due diligence is a critical step in the investment process as it helps investors and companies understand the nature of a deal, the risks involved, and whether the deal fits with their portfolio. It is a way to reduce risk exposure and ensure that a party is aware of all the details of a transaction before agreeing to it.
Maximizing Your Savings Account: A Guide to Smart Investing
You may want to see also

Due diligence helps investors and companies understand the nature of a deal, the risks involved, and whether the deal fits their portfolio
Due diligence is a process of verification, investigation, or audit of a potential deal or investment opportunity. It is completed before a deal closes to provide the buyer with an assurance of what they’re getting. Due diligence is a systematic way to analyse and mitigate risk from a business or investment decision.
Due diligence is mandatory for companies in the fund industry, as per national laws and international regulations such as EU directives. It is also legally required for broker-dealers, who must conduct due diligence on a security before selling it.
Due diligence involves examining a company's numbers, comparing them over time, and benchmarking them against competitors. This includes reviewing financial records, analysing the company's market capitalization, revenue, profit, and margin trends, and evaluating competitors and industries.
Additionally, due diligence may include reviewing the company's management, ownership, balance sheet, stock price history, stock options, and expectations. It is a comprehensive process that provides valuable insights and helps make informed investment decisions.
Managing Multi-State Investments: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Due diligence is an investigation, audit, or review performed to confirm facts or details of a matter under consideration. In the financial world, it involves examining a company's financial records before entering into a transaction with another party. Due diligence is a systematic way to analyse and mitigate risk from a business or investment decision.
GRC stands for Governance, Risk Management and Compliance. It is a central place where companies can gather all their due diligence processes and share them with many companies at once.
There are two main types of due diligence: hard and soft. Hard due diligence focuses on the numbers and data found on financial statements, whereas soft due diligence takes a more qualitative approach, looking at aspects such as management quality and customer loyalty.
Examples of due diligence include:
- Property inspection before purchase
- An acquiring company examining a target firm before a merger or acquisition
- A background check on a potential employee
- Risk assessment of product suppliers
- Reviewing financial statements
- Analysing the consumer market
Due diligence is a way to reduce risk exposure. It ensures that a party is aware of all the details of a transaction before they agree to it. It also helps investors and companies understand the nature of a deal, the risks involved, and whether the deal fits with their portfolio.