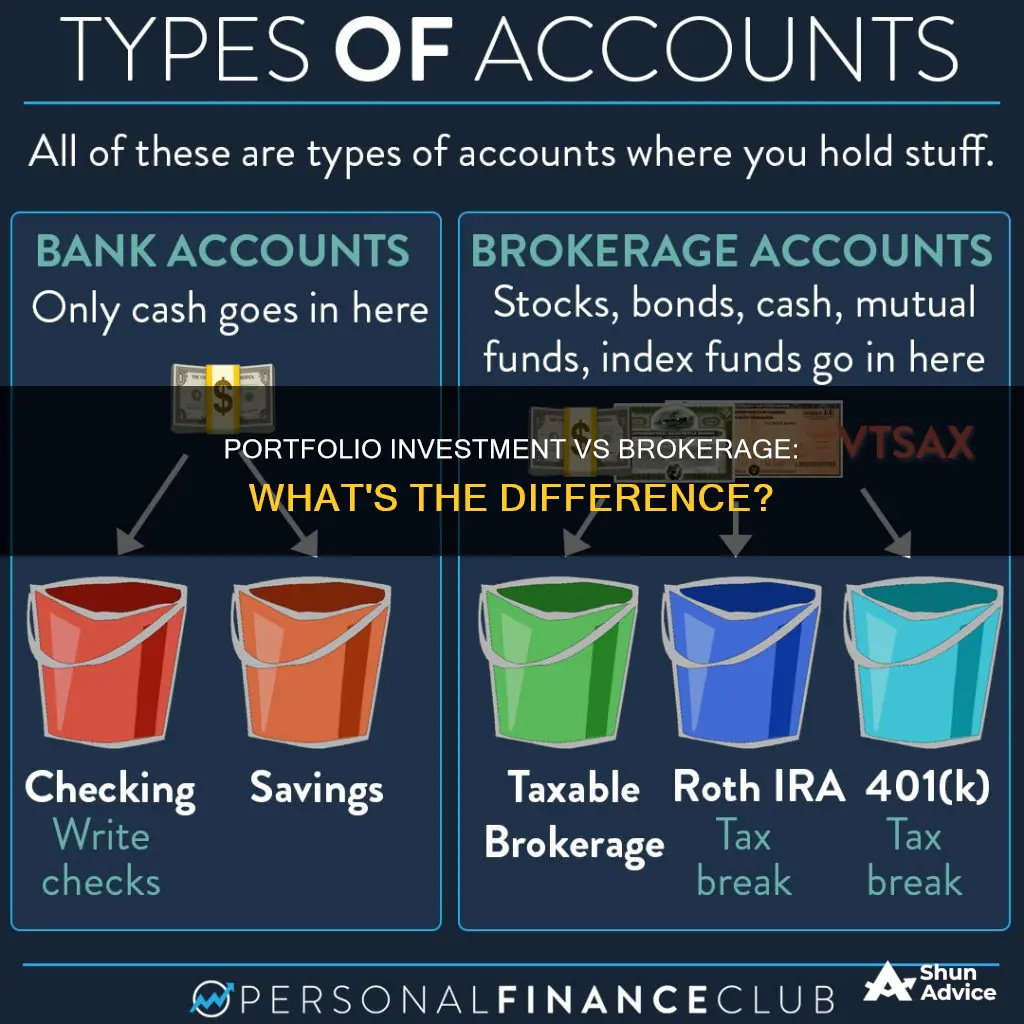
Investment portfolios and brokerage accounts are two different concepts in the world of finance. An investment portfolio is a collection of assets, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). It represents an individual's collection of investments, which can be held in various types of accounts, such as a 401(k), an individual retirement account (IRA), or a taxable brokerage account. On the other hand, a brokerage account is a specific type of investment account held at a licensed brokerage firm, where investors deposit funds to buy and sell securities like stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and ETFs.
While an investment portfolio refers to the collection of assets an individual owns, a brokerage account is the vehicle through which these assets are bought, held, and sold. Brokerage accounts can be of different types, including full-service, discount, online, and robo-advisor accounts, each offering varying levels of service, fees, and investment choices.
It is important to understand the differences between these concepts, as they play a significant role in an individual's investment strategy and financial goals.
What You'll Learn
- Investment advisers are paid a flat fee or a percentage of AUM, while brokers are paid commissions
- Investment advisers and brokers are regulated by different bodies
- Brokers execute trades or buy and sell assets for clients
- Investment advisers advise clients on securities and manage portfolios
- Investment advisers are held to a higher legal standard than brokers

Investment advisers are paid a flat fee or a percentage of AUM, while brokers are paid commissions
Investment advisers are financial professionals who provide investment advice and manage portfolios for their clients. They are paid either a flat fee or a percentage of the assets under management (AUM). This fee-based system allows investment advisers to offer advice that caters to the specific needs of their clients. In addition to providing investment advice, they may also assist clients with tax, estate, and mortgage planning. It is important to note that investment advisers are held to a higher legal standard than brokers and are required to act in the best interests of their clients.
On the other hand, brokers are typically paid commissions for executing trades or buying and selling assets for their clients. Before the advent of online trading, accessing a broker was a luxury reserved for the rich, as brokers charged very high commissions. However, with the emergence of web-based discount brokerages, individuals can now trade on the stock market directly without the need for a broker, and many brokers have expanded their services to include personalized investment management to justify higher commissions.
While brokers focus on executing trades, investment advisers take on a more advisory role, providing guidance and managing portfolios for their clients. The fee structure also differs, with investment advisers charging flat fees or a percentage of AUM, while brokers are compensated through commissions. It is important to understand these distinctions when deciding whether to engage the services of an investment adviser or a broker for your financial needs.
Building an Investment Portfolio: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Investment advisers and brokers are regulated by different bodies
Brokers, on the other hand, are regulated by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA). They are defined by the SEC as "any person engaged in the business of effecting transactions in securities for the account of others".
These differences in regulation are due to the distinct roles that investment advisers and brokers play in financial services. Investment advisers offer advice and manage portfolios for a flat fee or a percentage of assets under management (AUM). They often work with clients to create a wealth management framework, which may include tax, estate, and mortgage planning.
Brokers, on the other hand, execute trades or buy and sell assets for clients in exchange for commissions. While they may also provide investment advice, they are not held to the same fiduciary standards as investment advisers.
It is important to understand these differences in regulation and role when deciding whether to engage the services of an investment adviser or a broker to meet your financial goals.
Monetary Policy: Investing and Saving Explained
You may want to see also

Brokers execute trades or buy and sell assets for clients
A broker is a company or individual that is licensed to sell securities and execute trades or buy and sell assets for clients. They earn commissions for their services.
Brokers play a crucial role in facilitating investment activities, especially for individuals who want to invest in long-term financial growth and earn passive income. They provide intermediary services, connecting buyers and sellers in various industries, including finance, real estate, and insurance.
- Client Instructions: Brokers act on behalf of their clients, executing trades or buying and selling assets according to their clients' instructions. They facilitate the purchase or sale of various investment vehicles, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
- Market Access: Brokers provide access to financial markets, allowing clients to buy and sell securities on the stock exchange. They help individuals navigate the complex world of investing and make profitable decisions.
- Information and Support: In addition to trade execution, brokers provide clients with information and support related to economic standards, trends, and activities. They may also facilitate loan requests and approvals within established margin transactions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Brokers are regulated by entities like the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and are legally prohibited from giving advice that conflicts with their clients' interests.
- Fee Structures: Brokers typically charge commissions for their services, which can vary depending on the broker and the type of trade. Full-service brokers may charge higher fees, while discount brokers and online brokerages tend to offer lower commissions or even zero-commission trades.
- Advisory Services: While brokers primarily execute trades, some brokers also offer advisory services, providing investment advice and wealth management services for an additional fee.
- Licensing and Qualifications: Becoming a broker typically requires specific licenses or certifications, ensuring that individuals are qualified to provide brokerage services.
- Evolution of Brokerage: The advent of online trading and discount brokerages has made investing more accessible. Individuals can now execute trades independently through online platforms, reducing the reliance on traditional brokers for each transaction.
- Dual Roles: In some cases, brokers may also act as investment advisors, providing a more comprehensive range of financial services to their clients.
- Client Base: Brokers typically work with individual clients, helping them navigate their investment options and make informed decisions about their financial assets.
In summary, brokers play a vital role in facilitating trades and buying and selling assets for their clients. They provide the necessary expertise and access to financial markets, ensuring that individuals can effectively manage their investments and work towards their financial goals.
Rebalancing Investment Portfolios: Yearly Refresh for Optimal Returns
You may want to see also

Investment advisers advise clients on securities and manage portfolios
Investment advisers are paid a flat fee or a percentage of the assets under management (AUM) to advise clients on securities and manage their portfolios. They are legally required to act in their clients' best interests and are held to a higher legal standard than brokers.
Investment advisers provide advice and investment management services to their clients. They may work with a client to create a wealth management framework, including tax, estate, and mortgage planning. They are also known as asset managers, investment managers, and wealth managers.
Investment advisers are registered with and regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and/or a state regulatory body. To dispense financial advice for a fee, they are required to pass the Series 65 exam.
Investment advisers charge their clients a fee for their services, which is usually based on the size of the account or a percentage of the assets under management. This fee-based system is different from brokers, who are paid commissions for executing trades or buying and selling assets for clients.
Investment Advisers: Managing Portfolios and Advising on Securities
Investment advisers play a crucial role in helping clients manage their investment portfolios and make informed decisions about securities. By providing expert advice and guidance, they assist clients in navigating the complex world of investing and work to protect their clients' best interests.
Role and Responsibilities
Investment advisers are financial professionals who offer advice and services related to securities and portfolio management. They provide valuable insights and strategies to help clients achieve their financial goals. Advisers may work with individuals or institutions, offering personalized advice and investment plans.
Fees and Compensation
Investment advisers typically charge a flat fee for their services or a percentage of the assets under their management (AUM). This fee structure ensures that the adviser's interests are aligned with those of their clients, as they only profit when their clients' portfolios perform well.
Regulatory Requirements
To protect investors, investment advisers are subject to strict regulatory requirements. In the United States, they must adhere to the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, which imposes a fiduciary duty on advisers. This legal standard mandates that advisers act with utmost good faith and full disclosure, always putting their clients' interests first.
Qualifications and Examinations
To become a registered investment adviser, individuals must pass the Series 65 exam. This examination covers a range of topics, ensuring that advisers have the necessary knowledge and skills to provide sound investment advice. It is a crucial step in establishing the competence and integrity of investment advisers.
Services Offered
Investment advisers offer a range of services, including portfolio management, investment strategy formulation, and wealth management. They may also assist clients with tax planning, estate planning, and other financial matters. By providing comprehensive advice, they help clients make well-informed decisions and build robust investment portfolios.
In summary, investment advisers play a vital role in the financial industry by guiding clients through the complexities of investing. Their expertise and fiduciary duty make them trusted advisors who help clients manage their portfolios and achieve their financial goals.
Investing Aggressively at 75: Is It Too Late?
You may want to see also

Investment advisers are held to a higher legal standard than brokers
Brokers, on the other hand, are defined by the SEC as "any person engaged in the business of effecting transactions in securities for the account of others". They are regulated by the SEC and a self-regulatory organization such as the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA). While brokers and investment advisers are both legally prohibited from giving advice that conflicts with their clients' needs, the fiduciary duty of investment advisers means they are held to a higher standard.
The different regulations and requirements for investment advisers and brokers also extend to their testing and licensing. For example, future investment advisers are required to pass the Series 65 exam before they can dispense financial advice for a fee, while brokers have to pass the Series 7 exam.
Building a Balanced Investment Portfolio: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A portfolio is a collection of invested assets such as stocks, bonds, and funds. A brokerage, on the other hand, is a company or individual that facilitates the buying and selling of securities on behalf of clients.
A brokerage account is a taxable account, allowing you to freely buy and sell investments without contribution limits or penalties for withdrawals. In contrast, an IRA is a tax-advantaged account designed for retirement savings, with strict contribution limits and potential penalties for early withdrawals.
While both share similar financial goals, there are key distinctions. Brokerages provide a range of financial services to help clients create passive income streams, whereas investment banks focus on long-term wealth building. Additionally, investment bankers typically work with corporate clients, while brokerages cater to individual and private clients.