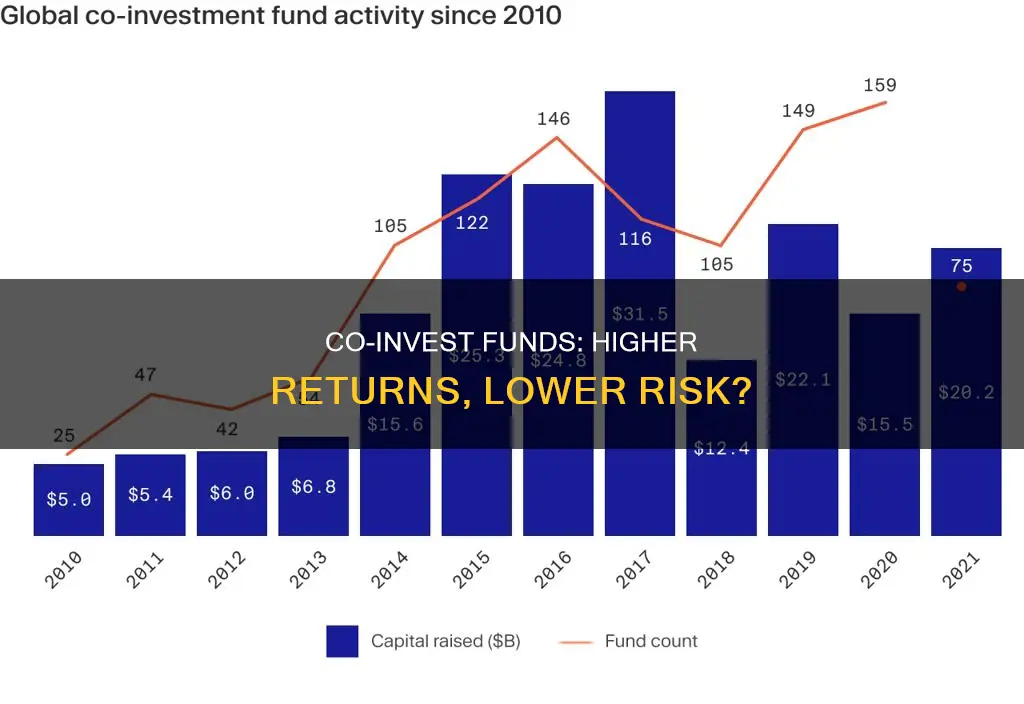
Co-invest funds have higher gross returns due to a variety of factors. Firstly, co-investments enable investors to participate in potentially profitable investments without paying the usual high fees charged by private equity funds. This is because co-investments are typically made outside the existing fund structure, so co-investors often don't pay management fees or carried interest on individual investments. Additionally, co-investments provide access to supplementary capital, allowing private equity funds to make larger single investments. The larger investment size, combined with reduced fees, contributes to higher gross returns. Furthermore, co-investments offer enhanced diversification and exposure to new markets, providing access to alternative investment options. The combination of increased capital, reduced fees, and diversified investments contributes to higher gross returns for co-invest funds.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type of investment | Minority investment |
| Investor type | Institutional or high-net-worth investors |
| Investor privileges | Ownership privileges equal to the percentage of their investment |
| Investor fees | Reduced fees |
| Investor risks | High risk |
| Investor control | Passive, non-controlling investments |
| Investor relationships | Can negatively impact relationships with limited partners |
| Investor costs | Additional costs |
| Investor due diligence | Requires a great deal of transparency and disclosure |
| Investor tax | Pre-tax |
What You'll Learn

Co-investors avoid high fees charged by private equity funds
Co-investors are typically institutional or high-net-worth investors who make their investments alongside private equity or venture capital firms. They are charged a reduced fee for the investment and receive ownership privileges equal to the percentage of their investment.
Co-investors are able to avoid the high fees charged by private equity funds because they are typically charged lower fees for the investment. Private equity funds, on the other hand, typically charge higher fees for their services. Co-investors also have the advantage of not having to pay the usual high fees charged by a private equity fund, as they are investing alongside the fund manager or firm.
In addition, co-investors often have access to enhanced due diligence or GP materials that would otherwise be unavailable, allowing for a deeper understanding and enhanced tailoring of their investment portfolio. This can lead to better decision-making and potentially higher returns.
Furthermore, co-investors can benefit from the sharing of investment risk, increased access to investor capital, and improved marketing and investor relations. The flexibility offered by co-investments can provide upside for funds and LPs in the right circumstances.
However, it is important to note that co-investors typically have no decision-making or voting power over how the investment or fund is operated. The sponsoring firm retains control over how it is managed, including holdings and rebalancing. As such, co-investors should conduct thorough due diligence to ensure that their capital is protected.
Venture Capital Funds Backing Xenex Disinfection Services
You may want to see also

Co-investors have ownership privileges
Co-investors are usually institutional or high-net-worth investors who make their investments alongside private equity or venture capital firms. They are often large institutional investors with a relationship to the private equity fund manager.
Co-investments are typically made outside the existing fund, so co-investors rarely pay management fees or carried interest on individual investments. They are usually passive, non-controlling investments, as the private equity firm involved will exercise control and perform monitoring functions.
Co-investors can benefit from reduced fees and increased exposure to new markets and alternative investment options. They can also share the risk associated with the deal. However, co-investments can be complex and risky, and co-investors should be aware of the potential drawbacks, such as a slow deal process and negative impacts on relationships with limited partners.
Mutual Fund Investment: Planning for Retirement?
You may want to see also

Co-investments open up new markets
Co-investments, also known as equity co-investments, are a type of investment where multiple investors put their money into a single company or venture. This allows investors to access markets that would otherwise be unavailable to them, providing them with alternative investment options.
Co-investments are typically made by institutional or high-net-worth investors, alongside private equity or venture capital firms. These investors are often large institutional investors with relationships with the private equity fund manager.
By participating in co-investments, investors can gain exposure to new markets and mid-market companies, as well as planning-based investment deals. This provides them with the potential for higher returns and lower fees, although it also comes with certain risks and complexities.
The main advantage of co-investments is that they provide access to markets and investment opportunities that would otherwise be out of reach for individual investors. This allows investors to diversify their portfolios and increase their exposure to attractive transactions.
Co-investments also benefit private equity or venture capital firms by providing them with access to supplementary capital and enabling them to make larger single investments. This additional capital can help firms further their investment goals without sacrificing decision-making power.
Overall, co-investments can be a powerful tool for investors and firms alike, providing access to new markets and opportunities while also offering the potential for higher returns. However, it is important for investors to carefully evaluate the risks and complexities associated with co-investments to ensure they make informed decisions.
Key Factors for Choosing the Right Mutual Fund Investments
You may want to see also

Co-investments reduce risk
Co-investments are a great way to reduce risk for both investors and private equity or venture capital firms. By involving multiple investors, co-investments allow for the sharing of risk among the parties involved. This risk-sharing arrangement is particularly beneficial for private equity firms as it enables them to make larger investments without committing too much of their fund's capital to a single transaction.
For investors, co-investments provide an opportunity to invest in potentially highly profitable ventures without paying the usual high fees associated with private equity fund investments. Co-investors are typically charged reduced fees and receive ownership privileges equal to the percentage of their investment. This structure ensures that investors are not burdened with excessive costs and can maintain control over their investment exposure.
Additionally, co-investments offer investors the benefit of enhanced diversification. They provide access to new markets and alternative investment options that may not be available to the average investor. This diversification not only reduces risk but also increases the potential for higher returns.
Co-investments also enable investors to have a deeper understanding of the general partner's (GP) sourcing and due diligence process. This transparency helps to create or strengthen the relationship between the investor and the GP, fostering trust and confidence in the investment opportunity.
From the perspective of private equity (PE) funds, co-investments are an attractive way to gain access to supplementary capital. They provide an opportunity to make larger single investments that may otherwise be unavailable or undesirable. By sharing investment risk with co-investors, PE funds can mitigate their exposure and create a more balanced portfolio.
In conclusion, co-investments offer a valuable risk reduction strategy for both investors and PE funds or venture capital firms. They facilitate the sharing of risk, enhance diversification, provide access to supplementary capital, and foster stronger relationships between investors and fund managers. By collaborating through co-investments, all parties involved can benefit from reduced risk and potentially increased returns.
Vanguard Funds: Where to Invest and Why
You may want to see also

Co-investors have limited decision-making power
Co-investors are usually existing limited partners in an investment fund managed by the lead financial sponsor. They are often institutional or high-net-worth investors who make investments alongside private equity or venture capital firms. These co-investors are charged a reduced fee for the investment and receive ownership privileges equal to the percentage of their investment.
While co-investors may have limited decision-making power, they still benefit from this type of investment. Co-investments offer them a chance to participate in potentially highly profitable investments without paying the usual high fees charged by a private equity fund. Co-investors can also gain access to new markets and alternative investment options that would otherwise be unavailable to them. Additionally, co-investors can benefit from reduced fees and shared risks associated with the deal.
However, it is important to note that co-investors should carefully consider the risks involved. The success or failure of the investment rests on the capabilities of the private equity professionals involved. Co-investors should also be aware of the potential for hidden costs and ensure they have a clear understanding of how the fund is managed and executed.
Mutual Fund Investment: Where to Begin?
You may want to see also