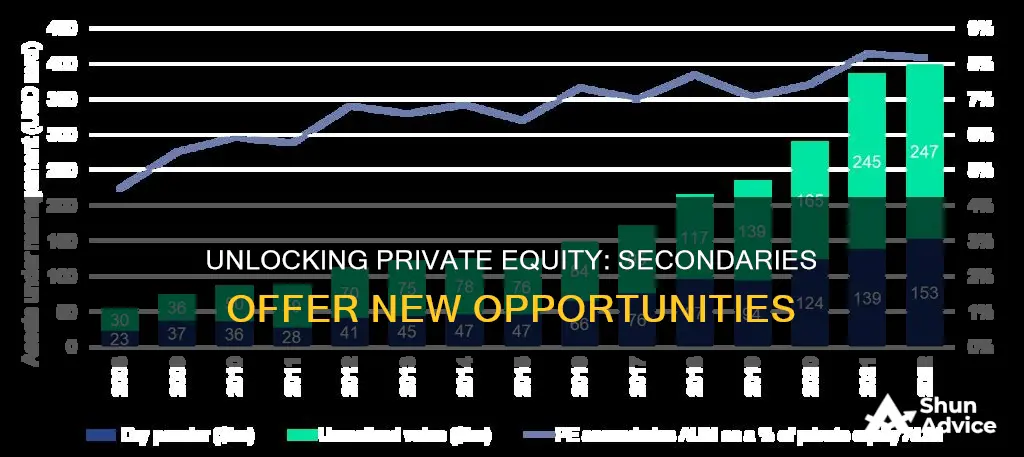
Investing in private equity secondaries is an increasingly popular option for those looking to diversify their portfolios. The private equity secondary market refers to the buying and selling of pre-existing investor commitments to private equity funds during a fund's lifetime. This market has grown steadily since the turn of the century, with the total volume of secondary deals hitting a record $132 billion in 2021.
There are several benefits to investing in private equity secondaries. For buyers, they offer a more attractive entry point compared to primary private equity funds due to their unique risk and return profile. Secondaries are generally more diversified than primary private equity funds because they assume pre-existing commitments across multiple funds, providing significant diversification across managers, industries, geographies, strategies, and vintage years. This approach offers private equity exposure with less risk than investing in a single primary private equity fund.
Additionally, secondaries often have a shorter duration and faster return of capital. Primary private equity funds typically take three to five years to deploy capital, while secondary strategies deploy capital faster and distributions may begin quickly, sometimes as soon as the fund's inception. This is because the investment is in mature underlying funds, which have already gone through the initial high-risk stage.
Another advantage of private equity secondaries is the ability to mitigate blind pool risk. Investors in primary funds don't know in advance which investments the fund manager will make, but in the case of secondaries, investors are buying pre-existing assets and portfolios, so they know exactly what they're acquiring. This enhances the potential for due diligence and provides visibility into potential future performance.
Furthermore, sellers of private equity secondaries can benefit from increased liquidity, providing them with a stream of cash that can be deployed into new investment opportunities or used to meet urgent capital needs.
However, it's important to remember that private equity is a high-risk investment, and investors should be prepared to lose all their money. The private equity secondary market is complex and labour-intensive, and pricing levels can adjust downward during periods of market volatility. Therefore, it's crucial to carefully consider the risks and select experienced managers who are focused on downside protection and have a proven track record of navigating market cycles.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Transactions in which an investor buys an existing interest or asset from primary private equity fund investors |
| Market Size | $134 billion in 2021 |
| Investor Profile | Institutional and individual investors |
| Investor Benefits | Shorter duration, faster return of capital, discounted access, enhanced transparency, diversification |
| Seller Benefits | Liquidity, ability to rebalance a portfolio |
| Types of Transactions | LP-led, GP-led, direct secondary transactions |
| Risk | High-risk investment, unlikely protection in case something goes wrong |
What You'll Learn

Access to liquidity
The private equity secondary market provides access to liquidity for investors. It refers to the buying and selling of pre-existing investor commitments to private equity funds during a fund's lifetime. This market has grown steadily since the turn of the century, and the benefits have become increasingly difficult to ignore.
Types of Secondary Transactions
There are several types of secondary transactions that can be leveraged to access liquidity:
- LP secondary transactions: This is the most common type of secondary transaction, where an existing Limited Partner sells its assets to a secondary buyer, who then assumes all the rights and obligations of the Limited Partner in the fund.
- GP-led transactions: The most popular variation of this is the 'continuation vehicle transaction', which occurs when a General Partner needs to extend the investment period of a fund that has reached the end of its life. Portfolio companies or a single asset are moved to a new fund vehicle, enabling additional follow-on capacity and extended hold periods. Existing Limited Partners can choose to 'roll over' their interest or cash out to a secondary buyer.
- Direct secondary transactions: This involves the trade of directly held ownership interest in a company from Limited Partners to an existing investor. It provides an opportunity to sell stock before the entire portfolio of companies has been sold.
Benefits of Secondary Transactions
Secondary transactions can offer a valuable mechanism to better manage otherwise illiquid private equity portfolios. They can create a stream of cash that is ready to be deployed into new investment priorities or satisfy an urgent need for capital.
For buyers, investing in a private equity fund secondary can result in faster returns on capital compared to primary investments. This is because secondary strategies deploy capital faster, and distributions typically begin quickly, sometimes as soon as the fund's inception. This is because the investment is in mature underlying funds.
Additionally, secondary transactions can help mitigate "Blind Pool Risk", which refers to the uncertainty faced by Limited Partners when committing capital to a portfolio that is yet to be constructed. In the case of secondaries, especially those purchased late in a fund's lifetime, investors know which companies they are investing in and can analyse their performance to calculate future value potential.
Angel Investing in India: A Beginner's Guide
You may want to see also

A faster return of capital
Investing in private equity secondaries can offer a faster return of capital. This is due to the shortened J-curve associated with secondary investments. The J-curve depicts an initial loss followed by a large gain as the investments mature. Secondary investments typically bypass the initial developmental stages of the J-curve, allowing investors to enter at a point where the curve begins to ascend, potentially leading to quicker positive returns.
In private equity secondaries, investors buy and sell pre-existing commitments to private equity funds. These transactions occur during a fund's lifetime, providing liquidity to investors looking to exit their positions earlier than the traditional lock-up period. This liquidity is a key benefit of private equity secondaries, allowing investors to free up capital for other investments.
The secondary market has grown steadily since the turn of the century, with the total volume of secondary deals reaching a record high of $132 billion in 2021. This growth is driven by various benefits that private equity secondaries offer, including faster returns.
Private equity secondaries provide investors with the opportunity to invest in funds or companies that are midway through their life cycles. This leads to shorter holding periods and quicker returns compared to primary private equity investments, which typically have longer gestation periods.
In summary, private equity secondaries offer a faster return of capital due to the shortened J-curve, the liquidity provided by the secondary market, and the ability to invest in mature assets with shorter times to return realisation. These factors make private equity secondaries an attractive investment option for those seeking faster returns.
Tech Giants Eyeing India: Where's the Investment Focus?
You may want to see also

Mitigating blind pool risk
Blind pool risk refers to the uncertainty associated with investing in a blind pool private equity fund, where investors commit capital to a portfolio that is yet to be constructed. This means that investors are unaware of the specific investments the fund will make, and as a result, face a high level of risk. However, there are several strategies that can be employed to mitigate this blind pool risk:
- Due Diligence: Before investing, it is crucial to conduct thorough due diligence on the fund manager's experience, track record, and investment strategy. Investors should also research the underlying investments, management team, and previous performances to evaluate their capability and credentials.
- Diversification: Investing in multiple blind pool private equities can help spread the risk by reducing the impact of any single investment's failure on the overall portfolio. This diversification can be achieved by investing in different blind pools with varying investment objectives and manager styles.
- Lock-up Period: Blind pool private equities usually have a lock-up period during which investors cannot redeem their investments. It is important for investors to be aware of this period and ensure they can commit to the required time frame.
- Fee Structure: Investors should carefully review the fund's fee structure, including management fees and performance fees, as these can significantly impact the overall returns on their investment.
- Regular Monitoring: Staying up-to-date on the fund's progress and performance is essential. Regular communication with the fund manager and access to reports can help investors make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
- Expertise: Blind pool private equity funds are managed by experienced professionals with expertise in mergers and acquisitions. Leveraging the expertise of these individuals can help mitigate the risks associated with blind pool investments.
- Limited Partner Transactions: In the secondary market, Limited Partner transactions are common, where an existing Limited Partner sells its assets to a secondary buyer, who then assumes all rights and obligations. This provides an opportunity for investors to purchase stakes in companies that are already known, allowing for a more informed analysis of their performance and future value potential.
By implementing these strategies, investors can enhance their understanding of blind pool private equity funds, make more informed decisions, and effectively mitigate the inherent blind pool risk.
Flat Fee Investment Management: Understanding the Basics
You may want to see also

Discounted access to private equity funds
Private equity secondaries offer investors an opportunity to access private equity funds at a discount. This is a unique feature of the secondary market, providing investors with the ability to acquire private equity assets at a lower cost than they would typically find in the primary market.
The discounted nature of private equity secondaries is primarily due to the nature of the transactions. On the secondary market, investors are purchasing existing private equity fund interests from other investors, who may be looking to exit their investments early. As such, these interests are often available at a discount to their underlying value, providing an attractive entry point for new investors.
There are several reasons why interests in private equity funds may be available at a discount on the secondary market. One key reason is the illiquid nature of private equity investments, which typically come with long lock-up periods in the primary market. Investors looking for an early exit may be willing to accept a discount in exchange for accessing their capital sooner. Additionally, the secondary market can provide a solution for investors facing end-of-fund-life issues, allowing them to exit their positions in older funds and opening up opportunities for new investors to acquire these interests at a discounted price.
The discount available on private equity secondaries can vary depending on various factors, including the age of the fund, the performance of the underlying investments, and the specific circumstances of the seller. Nonetheless, the potential for discounted access to private equity funds is a consistent feature of the secondary market, making it an appealing prospect for investors.
By investing in private equity secondaries, investors can take advantage of this discount to access high-quality private equity funds at a lower cost. This enhanced entry point can positively impact the overall return potential of the investment, as any future gains will build on this higher starting value. As such, private equity secondaries offer a unique and attractive opportunity for those seeking exposure to private equity assets.
Meeder Investment Management: Is It a Reliable RIA?
You may want to see also

Enhanced transparency into the underlying portfolio
The secondary market for private equity offers enhanced transparency into the underlying portfolio for investors. This is because secondary funds consist of existing assets of the underlying fund, providing better visibility into holdings and potentially mitigating downside risk.
When investing in a new primary private equity fund, investors may not know the future holdings. In contrast, secondary funds consist of existing assets, providing greater transparency into the underlying portfolio. This enhanced transparency can help investors make more informed decisions about their investments and potentially mitigate downside risk.
During the seven worst public market drawdowns in the past 20 years, secondary PE declined by 3.7% on average, while primary PE fell by 10.4% and public equities lost 24.9%. This highlights the potential risk mitigation benefits of enhanced transparency in secondary PE investments.
In addition, secondary investors buy pre-existing assets and portfolios, allowing them to engage in more thorough due diligence and make more accurate predictions about the future performance of their investments. This is in contrast to primary fund investors who take on blind pool risk, where they invest in a fund without knowing the eventual contents of their investment.
Furthermore, secondary investors can benefit from the work already done by primary investors. They can potentially take on less risk as the investee companies are further along their growth journey and closer to exit. This can result in shorter investment durations and faster returns for secondary investors.
Overall, the enhanced transparency into the underlying portfolio provided by the private equity secondary market can lead to more informed investment decisions, potentially reduced risk, and faster returns for investors.
What Makes a Registered Managed Investment Scheme a Disclosing Entity?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Private equity secondaries offer several benefits to investors. Firstly, they provide access to liquidity, enabling investors to sell stakes and deploy capital into new investment opportunities or address urgent capital needs. Secondly, they offer a faster return profile by investing in mature underlying funds, reducing the time until cash is returned. Lastly, they help mitigate blind pool risk by allowing investors to analyse the performance and value potential of the underlying companies before investing.
Investing in private equity secondaries carries high risks. The complexity of transactions, including sourcing, due diligence, and execution, requires specialised expertise and resources, creating barriers to entry for potential investors. Additionally, pricing levels in the secondary market can adjust downward during market volatility, impacting the buying opportunities for secondary fund managers.
Private equity secondaries offer diversification across managers, industries, geographies, strategies, and vintage years. By assuming pre-existing commitments in multiple funds, secondaries enable investors to spread their risk and gain exposure to a diverse range of assets and investment strategies.







