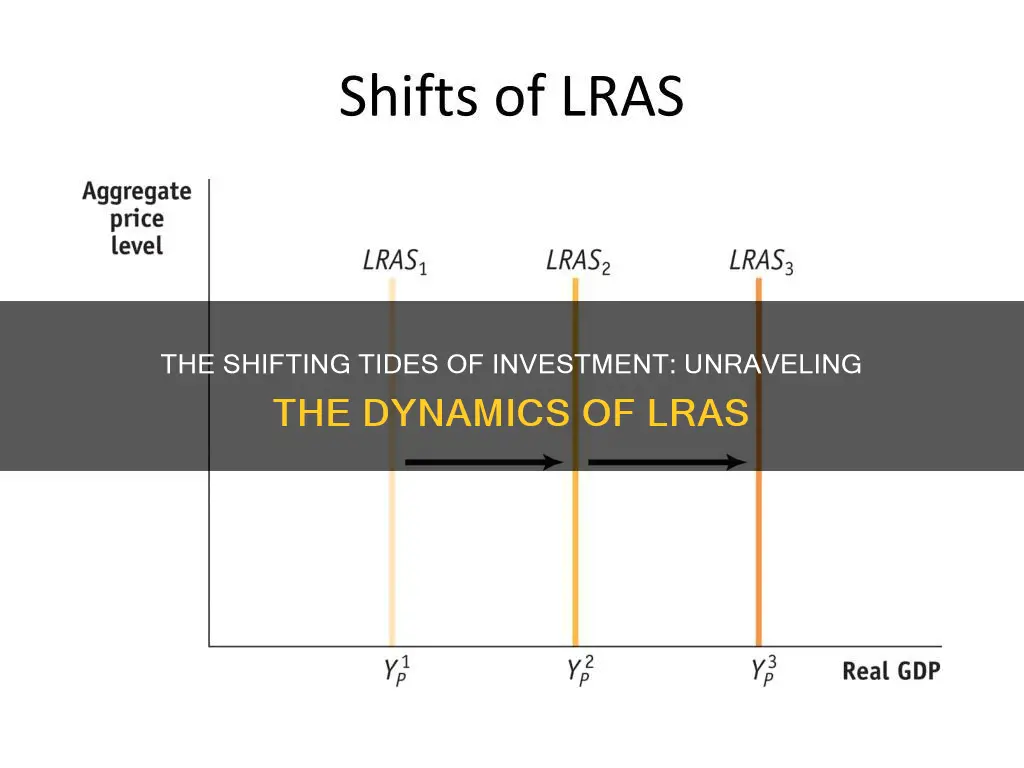
Investment can lead to a shift in LRAS, or Long-Run Aggregate Supply, which is an approach that explains how much an economy can produce by using all factors of production to their optimum capacity. In the long run, when all factors become variable and there is full economic employment, the output obtained does not depend on the price level. LRAS is influenced by the resources used, such as technology, capital, labour, and natural resources. An increase in investment can boost economic growth and productive capacity, leading to a shift in LRAS. For example, investing in new technology and capital can increase productivity and the economy's productive capacity, resulting in a rightward shift of LRAS.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Investment type | Private sector investment or investment from overseas |
| Investment in | Skills, education, new technology, capital, physical capital |
| Effect of investment | Increase in productive capacity of the economy |
| Long-Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS) | Explains how much an economy can produce by using all factors of production to their optimum capacity |
| LRAS curve shift | To the right |
| Factors influencing LRAS curve shift | Labour supply, natural resource, human resource supply, technological development, physical capital supply |
What You'll Learn
- Investment in skills and education can increase labour productivity
- Investment in new technology and capital can increase productivity
- Investment in physical capital, such as plant and machinery, can lead to a rise in production level
- Investment in software and hardware can lead to a rise in production level
- Investment in property can lead to a rise in production level

Investment in skills and education can increase labour productivity
The productivity of an economy is closely tied to the skills and education of its workers. As the number of educated workers increases, so too does the economy's productivity, as skilled workers can perform tasks more efficiently. This is particularly true for industries with higher education and training requirements, which tend to pay workers higher wages due to a smaller labour supply capable of operating in those fields.
The benefits of education extend beyond simply increasing productivity. Education helps to eliminate inequalities and improves economic growth. It also plays a role in developing new industries, such as science and technology, and can lead to entrepreneurial ventures and technological breakthroughs.
The relationship between education and productivity is further nuanced when considering factors such as age and gender. For example, younger workers and women tend to experience a "wage-compression effect", where their wages are compressed despite increases in productivity. This may be due to labour market regulations, such as minimum wage laws, that primarily affect lower-wage earners, who tend to be younger or female.
Overall, investment in skills and education is a key driver of economic growth and can increase labour productivity, leading to a shift in the LRAS.
Property Rights: Investment's Foundation
You may want to see also

Investment in new technology and capital can increase productivity
Additionally, investment in human capital, such as education and training, can increase productivity by enhancing the skills and knowledge of workers. This form of investment can lead to a more educated and skilled workforce, which can result in higher labour productivity.
Furthermore, investment in tangible assets, such as plant and equipment, housing, consumer durables, and infrastructure, can also contribute to increased productivity. This type of investment provides workers with better tools and resources to work with, enabling them to produce more in the same amount of time.
By increasing productivity through investment in new technology and capital, businesses can improve their operational efficiency, produce goods and services more effectively, and ultimately, drive economic growth.
Smart Ways to Invest $20,000
You may want to see also

Investment in physical capital, such as plant and machinery, can lead to a rise in production level
Investment in physical capital, such as plant and machinery, can indeed lead to a rise in production level. This is because physical capital allows for increased work productivity, which in turn can create more goods and raise the standard of living.
Physical capital is one of the four major factors of production, the others being land, labour, and entrepreneurship. It refers to the tangible assets that are used to produce goods or services. Examples include manufacturing plants, machinery, computers, vehicles, and production equipment.
Capital investment is a means for a company to further its business objectives. It is a long-term strategy that allows companies to generate revenue for many years by adding or improving production facilities and boosting operational efficiency. By investing in new equipment or technology, companies can improve efficiency, lower costs, and increase output. This can also lead to improvements in the quality of goods produced.
In the long run, investment in physical capital can increase the productive capacity of the economy and lead to economic growth. This is because physical capital, such as plant and machinery, is one of the resources that determine the level of output an economy can produce. The other resources are labour, technology, and natural resources. When these resources are used to their optimum capacity, the output obtained does not depend on the price level.
Retirement Strategies of the Rich
You may want to see also

Investment in software and hardware can lead to a rise in production level
LRAS is an approach that explains how much an economy can produce by using all factors of production to their optimum capacity. In the long run, when all factors become variable and there is full economic employment, the output obtained does not depend on the price level. The resources used are capital, labour, technology, and natural resources, which do not adjust with price changes in the short run. However, in the long run, prices do not impact the supply because wages and other factors adjust to price changes, resulting in a vertical long-run aggregate supply graph.
An increase in physical capital, such as investments in software and hardware, leads to a rise in the production level. This is because workers and employees will be using better equipment that is technologically advanced. Thus, there is a shift in long-run aggregate supply to the right.
Software is a huge industry, with its presence in critical components of everything from pacemakers to cars. It is a vital component of modern life, and its importance will only grow as technology continues to advance.
While hardware may not get the same respect it did in previous decades, it is still a key part of the technology world. Although software is increasingly replicating hardware functions, there is still a significant market for many hardware types, and the sector is not as obsolete as many believe.
College Loans or Investments: Navigating the Financial Crossroads
You may want to see also

Investment in property can lead to a rise in production level
Investment in property can lead to a rise in the production level. Here are some ways in which this can happen:
Direct Impact on Production Capacity
Investing in property can provide the physical space and infrastructure necessary to increase production capacity. For example, a business may invest in a new factory or office building, enabling it to expand its operations and produce more goods or services. This is especially true for businesses that require specific types of real estate to function, such as manufacturing, warehousing, or research and development.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Well-chosen property investments can improve operational efficiency and productivity. For example, investing in a modern facility with upgraded technology and better layout can streamline production processes, reduce bottlenecks, and enhance overall efficiency. This, in turn, can lead to increased output without necessarily requiring more resources or labour.
Indirect Impact through Economic Growth
Property investment also contributes to economic growth by creating a ripple effect in the economy. For instance, investing in a new commercial property can create jobs during the construction phase and further jobs once the building is operational. This increase in employment can lead to higher consumer spending, which boosts demand for goods and services, encouraging businesses to produce more.
Impact on Aggregate Demand and Supply
As mentioned earlier, property investment is a component of aggregate demand (AD). An increase in investment can boost AD and stimulate short-term economic growth. Additionally, property investment can influence the supply side of the economy by increasing the productive capacity of the nation. This is achieved through investments in physical capital, such as plants, machinery, and technology, which can lead to a rightward shift in the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve.
Long-Term Strategic Advantage
Investing in property can provide a long-term strategic advantage by securing a vital asset that appreciates over time. This can be especially beneficial for businesses that require a physical presence, such as retail stores, hotels, or restaurants. By investing in property, businesses can stabilise their operations, reduce uncertainty, and focus on expanding their production capacity.
In conclusion, investment in property can have a direct impact on production capacity and efficiency, as well as indirect effects on economic growth, aggregate demand, and supply. Therefore, businesses and investors seeking to increase production levels may find that strategic property investments play a crucial role in achieving their goals.
Mortgage Freedom: Weighing the Pros and Cons of a $200K Payoff
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Investment influences the LRAS because it is a component of aggregate demand (AD) and influences the productive capacity of the economy. An increase in investment boosts AD and economic growth, and if there is spare capacity, it can also cause a multiplier effect. Effective investment increases the productive capacity of the economy and can lead to a significant increase in productivity, which can shift the LRAS to the right.
The LRAS can be shifted by changes in labour supply, human resource supply, technological development, and physical capital supply. For example, an improvement in human resources will shift the LRAS to the right, while a decrease in the labour force will shift it to the left.
Investment is one of the most important factors for shifting the LRAS and achieving long-term economic growth. However, it is not the only factor. For instance, technological development and labour supply can also play a significant role in shifting the LRAS.







