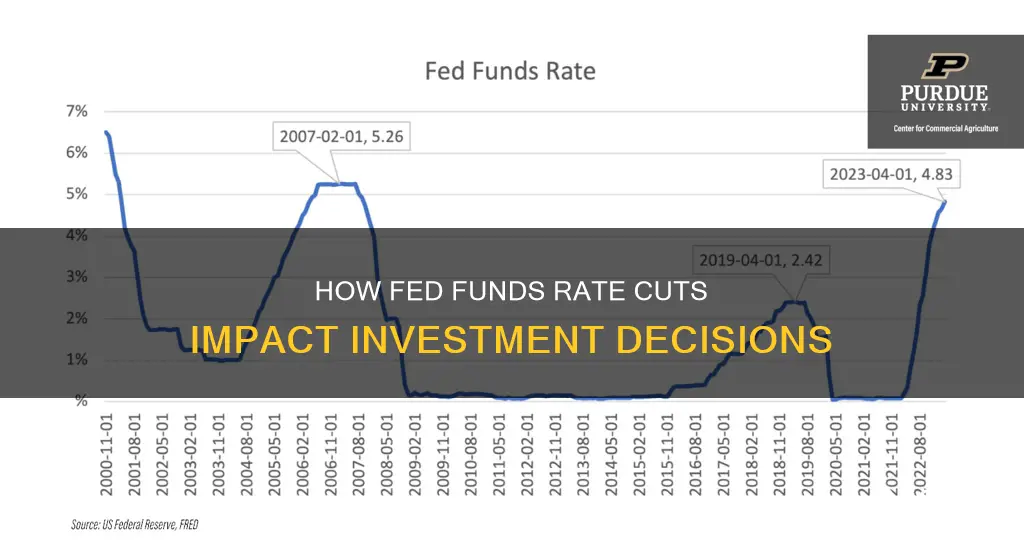
The Federal Reserve's decision to lower interest rates can have a significant impact on investments and the economy as a whole. When the Federal Reserve lowers the federal funds rate, it influences interest rates throughout the economy. This typically makes borrowing more affordable for individuals and businesses, which can stimulate economic growth. Lower interest rates can also make stocks appear more attractive to investors, particularly in sectors like real estate, utilities, and telecom, as they offer steady dividends. Additionally, lower rates can benefit holders of bonds, as their prices tend to rise when interest rates go down. However, it's important to note that the impact of lowering the federal funds rate on the stock market may depend on the broader economic outlook. If the rate cut is accompanied by prolonged economic weakness, it might not be enough to sustain a bull market for stocks.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Interest rates | Dropping interest rates can stimulate the economy and impact financial markets. |
| Investments | REITs and U.S. stocks have historically outperformed other asset classes during low-interest-rate environments. |
| Inflation | The Federal Reserve's mandate is to use monetary policy to help achieve maximum employment and stable prices. |
| Federal funds rate | The Federal Open Market Committee meets eight times a year to discuss whether to adjust the federal funds rate. |
| Banks | Banks lower their interest rates on loans, CDs and savings accounts when the federal funds rate gets lower. |
| Consumers | Lower interest rates make it cheaper for people to borrow money for big purchases. |
What You'll Learn
- Lowering the federal funds rate can make it cheaper for people and businesses to borrow money for big purchases or new ventures
- Lowering the federal funds rate can make it less profitable to keep money in bank accounts
- Lowering the federal funds rate can make stocks more appealing to investors
- Lowering the federal funds rate can make older bonds with higher interest rates more valuable
- Lowering the federal funds rate can help REITs and US stocks outperform other asset classes

Lowering the federal funds rate can make it cheaper for people and businesses to borrow money for big purchases or new ventures
The federal funds rate is a key interest rate that banks charge each other for lending their excess reserves or cash. Banks with excess cash lend to banks with short-term liquidity needs, and the federal funds rate is the target rate set by the Federal Reserve Bank for these transactions. While the federal funds rate directly impacts the rates at which commercial banks lend to each other, it also has a broader impact on the entire economy.
The federal funds rate is used as a basis for setting the prime rate, which is the rate banks offer to their most creditworthy clients. Additionally, mortgage rates, loan rates, and deposit rates for savings accounts are all influenced by changes in the federal funds rate. When the federal funds rate decreases, banks typically adjust their rates on loans, CDs, and savings accounts.
Lower interest rates on loans can benefit both individuals and businesses. For individuals, borrowing costs decrease, making it more affordable to finance purchases with credit cards, car loans, or personal loans. Businesses can benefit from cheaper borrowing costs, which can impact their decisions to hire new workers or invest in new initiatives. Lower borrowing costs can encourage businesses to expand their operations or pursue new projects, contributing to economic growth.
It's important to note that while lowering the federal funds rate can make borrowing more affordable, the availability of credit and the willingness of lenders to lend may also come into play. Additionally, lenders may adjust interest rates based on factors such as borrowers' credit history and market competition.
Smart Strategies for Choosing the Right Mutual Fund
You may want to see also

Lowering the federal funds rate can make it less profitable to keep money in bank accounts
The federal funds rate is the rate that banks charge each other for lending their excess reserves or cash. The Federal Reserve, through the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), adjusts this rate depending on the needs of the economy. If the FOMC believes the economy is struggling or at risk of entering a recession, it will lower the federal funds rate to stimulate lending and economic growth.
When the federal funds rate decreases, banks typically pass on these lower rates to their customers by reducing the interest rates on loans and deposits. This makes borrowing money cheaper for consumers and businesses, which can help boost economic growth. However, it also means that people earn less interest on their bank deposits, making it less profitable to keep their money in these accounts.
As a result, individuals and businesses may be incentivized to invest or spend their money instead of keeping it in low-interest bank accounts. This can kick-start a cycle of increased spending and growth, leading to job creation and healthier inflation levels. While it may take some time for the economy to respond to the rate cut, changes in the stock and bond markets can be immediate.
In addition to making it less profitable to keep money in bank accounts, lowering the federal funds rate can also impact other aspects of the economy. For example, it can make borrowing costs more affordable for consumers and influence the direction of the stock market and the job market. Overall, the Federal Reserve's interest rate decisions have far-reaching consequences for individuals, businesses, and the economy as a whole.
Index Funds: Utopia or Dystopia for Investors?
You may want to see also

Lowering the federal funds rate can make stocks more appealing to investors
Lower interest rates also make stocks relatively more appealing compared to other assets. When interest rates fall, stocks can become more attractive investments relative to bonds and fixed-income investments such as CDs. This is because lower interest rates mean that the returns on these types of investments will also decrease, making stocks a more appealing option.
Lower interest rates can also lead to inflation, which undermines the effectiveness of low rates. Inflation can increase the price of goods and services, which can lead to a decrease in consumer spending and demand. This can have a negative impact on stock prices.
However, the impact of interest rates on stock prices is complex and can vary across different sectors. For example, financial institutions may benefit from higher interest rates as they can increase their profit margins on loans. Additionally, the impact of interest rates on the stock market can depend on the broader economic context, such as the business cycle and the health of the economy.
International Index Funds: Diversify Your Portfolio, Maximize Returns
You may want to see also

Lowering the federal funds rate can make older bonds with higher interest rates more valuable
When interest rates fall, investors can buy new bonds that offer a lower rate of interest. As a result, older bonds that offer a higher rate of interest become more attractive to investors. This increased demand for older, higher-interest bonds drives up their price in the secondary market.
For example, imagine a bond with a face value of $1,000 that pays 5% interest annually ($50 per year) at a fixed rate. This bond is issued when prevailing interest rates are also 5%. A year later, interest rates drop to 1%. Investors can now buy a new bond for $1,000 but will only be paid $10 per year for holding it. The old bond, which pays $50 per year, is now more valuable, and investors will be willing to pay a premium for it in the secondary market.
The Federal Reserve lowered the federal funds rate in September 2024, and investors benefited from the resulting increase in bond values. The Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index was up 4.65% year-to-date as of September 23, 2024.
It's important to note that while lower interest rates can make older bonds more valuable, they also decrease the opportunity for income-oriented investors to earn money from interest on newly issued bonds. Additionally, lower interest rates can prompt investors to move their money from the bond market to the stock market, as stocks become more appealing due to the potential for higher returns.
Emergency Fund Strategies: Philippines Investment Options
You may want to see also

Lowering the federal funds rate can help REITs and US stocks outperform other asset classes
The Federal Reserve, or the Fed, has a dual mandate: to maximise employment and stabilise inflation. One of the ways it achieves this is by decreasing or increasing interest rates. When the US economy shows signs of weakness, the Fed may decide to lower interest rates, specifically the federal funds rate.
Lowering the federal funds rate generally leads to banks lowering their interest rates on loans, making it cheaper for people and businesses to borrow money. It also makes saving less profitable, encouraging individuals and businesses to invest or spend their money instead.
Historically, the S&P 500 index has performed well following interest rate cuts. Lower interest rates can make stocks more appealing to investors as returns on other assets, such as bonds, may decrease. In particular, stocks known for steady dividends, such as real estate, utilities, and telecom, may attract investors away from lower-yielding fixed-income investments.
Lower interest rates can also impact the bond market, making older bonds with higher interest rates more valuable. Investors who already own bonds may be able to sell them at a higher price on the secondary market.
According to data from 1976 to 2023, during low-interest-rate environments, REITs and US stocks have outperformed other asset classes such as international stocks, commodities, bonds, and gold.
However, it is important to note that low-interest rates do not guarantee a bull market for stocks. If economic weakness continues or turns into a recession, the stock market could suffer. Additionally, while rate cuts may stimulate the economy in the short term, they can also contribute to higher inflation in the long run.
In summary, lowering the federal funds rate can help make stocks and REITs more attractive to investors, leading to potential outperformance compared to other asset classes. However, it is essential to consider the broader economic context and potential long-term implications when evaluating the impact of interest rate changes on financial markets.
S&P Mutual Funds: A Smart Investment Strategy
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The fed funds rate is the rate banks charge each other for lending their excess reserves or cash. The federal funds rate is a target rate set by the Federal Reserve Bank and is usually the basis for the rate that commercial banks lend to each other.
The fed funds rate has a sweeping impact on the economy as a whole. It is a key tenet of interest rate markets and is used to set the prime rate, which is the rate banks charge their most creditworthy customers for loans. Mortgage and loan rates, as well as deposit rates for savings, are also impacted by changes in the fed funds rate.
Adjustments to the federal funds rate can affect inflation in the US. When the Fed increases interest rates, it encourages people to save more and spend less, reducing inflationary pressures. Conversely, when the economy is in a recession or growing too slowly, and the Fed reduces interest rates, it stimulates spending and inflation.
Changes in the federal funds rate can impact the US dollar. When the Federal Reserve increases the federal funds rate, it typically increases interest rates throughout the economy, making the dollar stronger.