A Unit Investment Trust (UIT) is a U.S. investment company that offers a fixed portfolio of securities, typically stocks and bonds, to investors for a specific period. UITs are similar to open-ended and closed-end mutual funds in that they are collective investments where investors pool their funds to be managed by a portfolio manager. However, unlike mutual funds, UITs are not actively traded, and their securities are not bought or sold unless there is a significant change in the underlying investment, such as a corporate merger or bankruptcy. UITs have a predetermined expiration date, providing a clear timeline for investors, and their fixed portfolio offers predictable performance. While UITs provide diversification and tax advantages, they may lack flexibility and control for investors due to their fixed nature.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type of investment company | Unit Investment Trust (UIT) |
| Investment portfolio | Fixed (unmanaged) |
| Investments | Stocks, bonds or other securities |
| Investment period | Specific length of time |
| Investment objective | Capital appreciation, dividend income or both |
| Investment options | Domestic, international or both |
| Investment style | Passive |
| Investment risks | Different risks depending on the UIT |
| Investment fees | Management fees, trustee fees, sales charges |
| Investment information | Prospectus, fees, investment objectives |
| Investment regulation | Registered with the SEC |
What You'll Learn

Fixed unit investment trusts are unmanaged
Fixed unit investment trusts (UITs) are unmanaged. They are a type of investment company that offers a fixed portfolio of securities, typically stocks and bonds, to investors for a specific period. UITs are similar to open-ended and closed-end mutual funds in that they are collective investments where multiple investors pool their funds to be managed by a portfolio manager. However, unlike mutual funds, UITs have a stated expiration date and are not actively traded, meaning that securities are only bought or sold in response to changes in the underlying investment, such as a corporate merger or bankruptcy.
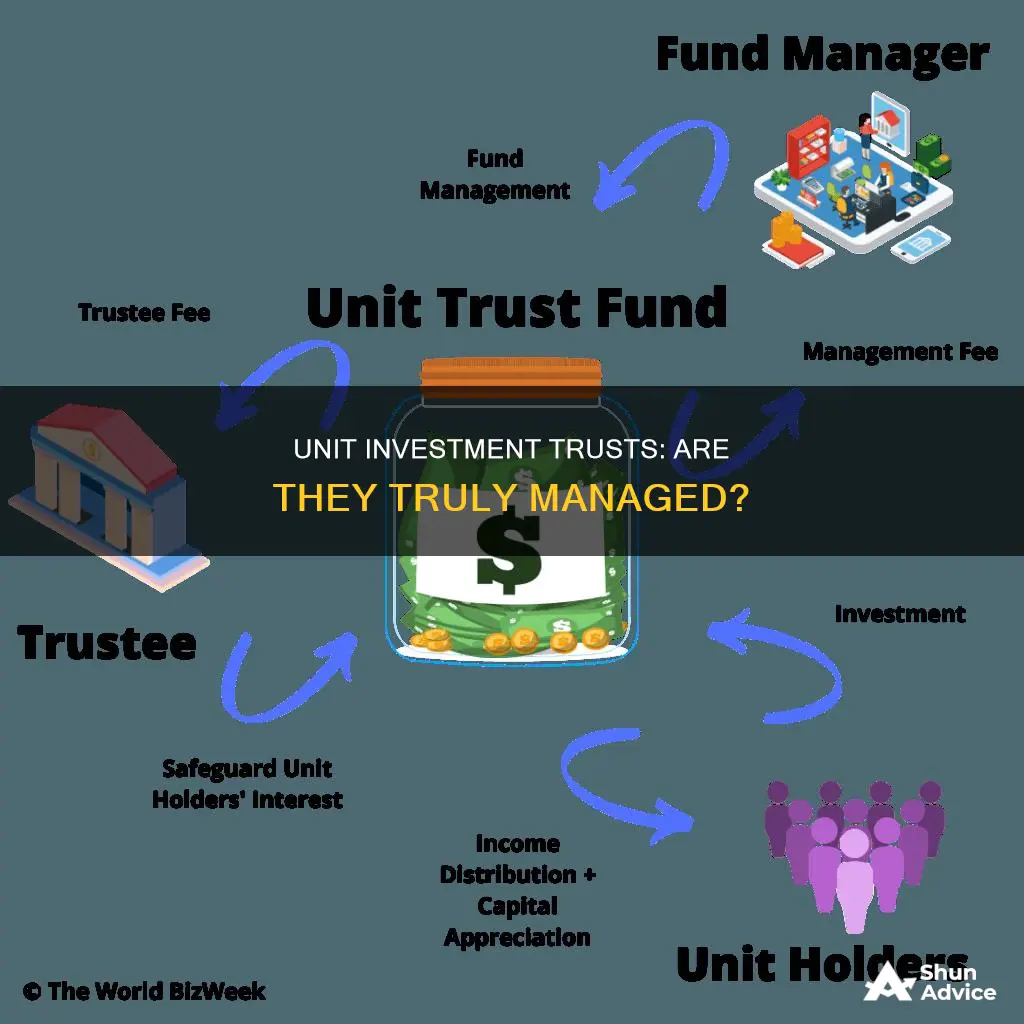
UITs are created by a sponsor who selects and assembles the securities to be included in the fund. The sponsor drafts a document called the Trust Indenture, which names the Trustee and the Evaluator. The trustee is responsible for keeping the securities, maintaining unitholder records, and performing accounting and tax reporting for the portfolio. The largest issuer of UITs is First Trust Portfolios, and most large brokerage firms sell UITs created by sponsors such as Incapital, SmartTrust, and Invesco Unit Trusts.
While UITs do not actively trade their investment portfolios, they can be sold back to the issuing investment company at any time. These early redemptions will be paid based on the current underlying value of the holdings. It is important to note that the amount paid to the investor may be less than what would be received if the UIT was held until maturity, as bond prices fluctuate with market conditions.
UITs are registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and are subject to SEC regulation. They are also required to provide a prospectus to prospective investors, outlining fees, investment objectives, and other important details.
Savings Strategies: Maximizing Output from Your Investments
You may want to see also

They are fixed portfolios of securities
Unit Investment Trusts (UITs) are a type of investment company that offers investors a fixed portfolio of securities, generally consisting of stocks and bonds. These portfolios are made up of a fixed number of securities or units, which are bought and held with little to no changes over the life of the UIT.
The fixed nature of UITs means that investors know exactly what they are investing in for the duration of their investment. The portfolio is not actively traded, and securities are only bought or sold in response to changes in the underlying investments, such as a corporate merger or bankruptcy.
The two main types of UIT portfolios are stock (equity) trusts and bond (fixed-income) trusts. Stock trusts are designed to provide capital appreciation, dividend income, or both, and they issue as many units (shares) as necessary for a set period before closing their primary offering. Bond trusts, on the other hand, issue a set number of units and, once all are sold, close their primary offering period.
Both types of UITs have a stated date for termination, which is specified at the time of creation and is often based on the investments held in the portfolio. For example, a bond portfolio might have a mix of five-, ten-, and twenty-year bonds, and the portfolio would be set to terminate when the longest-term bonds reach maturity.
The fixed portfolio nature of UITs provides investors with a level of predictability and transparency, as they know the exact securities held and the timeline managed. However, it also means that investors have little control over the investments made by the trust, and poor performers may be retained without the option to trade away or change strategy.
Illiquid Investments: Which Portfolio Has the Least Liquidity?
You may want to see also

They are redeemable units
Unit Investment Trusts (UITs) are redeemable units. This means that the UIT will buy back an investor's units at their approximate net asset value (NAV). In other words, investors can sell their holdings back to the issuing investment company at any time. These redemptions will be paid based on the current underlying value of the holdings.
Many UIT sponsors will also maintain a secondary market, which allows investors to buy and sell UIT units at the market price. Investors can redeem mutual fund shares or UIT units at net asset value (NAV) to the fund or trust either directly or with the help of an investment advisor. The NAV is defined as the total value of the portfolio divided by the number of shares or units outstanding, and it is calculated each business day.
It is important to note that UITs are not actively traded, meaning securities are not bought or sold unless there is a change in the underlying investment, such as a corporate merger or bankruptcy. This is because UITs have a fixed portfolio of securities and a set investment strategy. As a result, investors have little control over the investments made by the trust.
Maximizing Your Investment Portfolio: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

They are not actively traded
Unit Investment Trusts (UITs) are not actively traded. This means that, unlike mutual funds, the securities within a UIT are not bought or sold unless there is a change in the underlying investment, such as a corporate merger or bankruptcy.
A UIT is created for a specific length of time and is a fixed portfolio. Its securities will not be sold or bought except in certain limited situations. For example, if a company is filing for bankruptcy or a sale is required due to a merger.
The portfolio of a UIT is constructed by professional investment managers but is not actively traded. So, after it is created, it remains intact until it is dissolved and assets are returned to investors.
A UIT typically issues redeemable units, which means that the UIT will buy back an investor's units at their approximate net asset value (NAV). Many UIT sponsors will also maintain a secondary market, which allows investors to buy and sell UIT units at the market price.
Investors favour bond UITs over stock UITs because bond UITs are more predictable and less likely to suffer losses. Stocks are sold in the UIT at expiry, which doesn't allow the investor to recoup any losses.
Crafting an Effective Investment Portfolio Presentation
You may want to see also

They have a predetermined expiration date
Unit Investment Trusts (UITs) have a predetermined expiration date. They are created for a specific length of time and are not actively traded. This means that the securities in the portfolio are generally fixed and are not bought or sold unless there is a change in the underlying investment, such as a corporate merger or bankruptcy.
The expiration date of a UIT is usually based on the investments held in its portfolio. For example, a portfolio that holds bonds may have a mix of five-, ten-, and twenty-year bonds. In this case, the portfolio would be set to terminate when the twenty-year bonds reach maturity.
At termination, the remaining investment portfolio securities are sold, and the proceeds are paid to the investors. This is known as the UIT's net assets.
The predetermined expiration date of UITs makes them function similarly to bonds or similar debt securities. This feature is attractive to investors as it provides a level of predictability and transparency to their investments.
Savings and Investments: Strategies for Effective Money Allocation
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A UIT is an investment company that offers investors a fixed portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities for a specific period.
A UIT pools money from multiple investors to purchase a fixed portfolio of securities. Once the trust is created, investors purchase units that represent a proportional ownership interest in the underlying assets. The trust is then managed, and income is distributed over the life of the assets.
UITs provide investors with access to a diversified portfolio of securities, reducing the risk of losses due to the underperformance of a single security. They also offer greater transparency into holdings and investment strategies, lower fees, and more predictable performance compared to actively managed funds.
Investors have limited control over the investments made by the trust, and poor-performing securities may be retained. UITs may also offer less diversification than other types of investments and are designed to be long-term holdings, making them illiquid for investors who need quick access to their funds.
Unlike mutual funds, UITs have a stated expiration date and are not actively traded. UITs also have a fixed portfolio of securities, providing more predictable performance. However, investors may lose money if the underlying investments underperform and are not traded.







