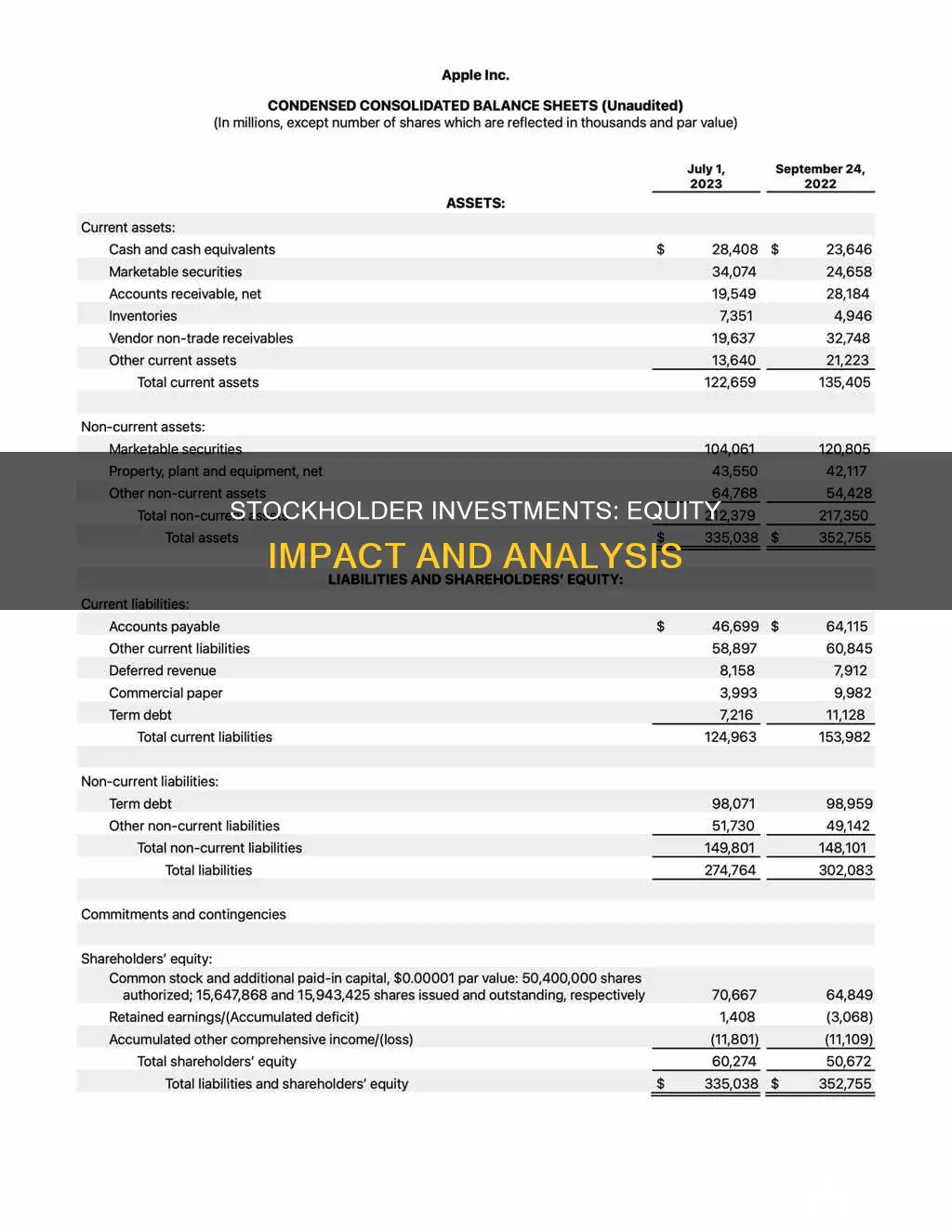
Stockholder equity, also known as shareholder equity, is the amount of financing a company has received by selling stocks. It is calculated by subtracting a company's total liabilities from its total assets. Stockholder equity is influenced by several components, including share capital, retained earnings, and dividend payments. When a company issues new shares of stock, it can lead to an increase in stockholder equity as the revenue generated becomes an asset. However, dividend payments, especially in the form of cash dividends, can result in a reduction of stockholder equity. Therefore, investments by stockholders can impact stockholder equity, either by increasing it through the sale of new shares or decreasing it through dividend payments.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Stockholders' equity is the remaining amount of assets available to shareholders after paying liabilities. |
| Calculation | Stockholders' equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities |
| Impact of Investments | Stockholders' equity increases due to additional stock investments. |
| Impact of Dividends | Cash dividends reduce stockholder equity, while stock dividends do not. |
| Impact of Stock Splits | Stock splits do not impact stockholders' equity as they do not bring in additional revenue. |

Dividend payments
The impact of dividend payments on shareholder equity depends on the type of dividend issued. Cash dividends directly reduce shareholder equity, while stock dividends do not. When a company issues a cash dividend, the dividend amount is deducted from retained earnings, resulting in a straight reduction of shareholder equity. On the other hand, when a company issues a stock dividend, the value of the dividend is transferred from retained earnings to paid-in capital, rearranging the allocation of equity funds without reducing shareholder equity.
Hedging Strategies: Protect Your Portfolio with These Smart Moves
You may want to see also

Share capital
Overall, share capital is a critical metric for understanding a company's financial position and the returns generated for shareholders. It provides insights into the funds available for distribution to shareholders and helps investors make informed decisions about the potential risks and rewards of investing in a particular company.
ERP Modules: Unlocking Investment Management Potential
You may want to see also

Retained earnings
The formula for calculating retained earnings is:
Over time, retained earnings can accumulate and grow larger. Eventually, they may exceed the amount of contributed equity capital and become the main source of stockholders' equity.
Investing in Indian IPOs: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Treasury shares
There are several reasons why companies buy back and hold treasury shares:
- To enhance share value: Reducing the number of shares in the market increases the value of the remaining outstanding shares.
- To avoid hostile acquisitions or takeovers: By limiting the number of floating shares, a company can prevent a hostile corporate entity from acquiring a large number of shares and gaining voting rights.
- To acquire or retain talent: Offering treasury shares as an incentive can help attract or retain talented professionals.
- To raise capital: Holding treasury shares provides a source of potential finance that can be called upon by issuing these shares at a later date.
When a company holds treasury shares, it is entered in the register of shareholders as the owner of those shares, but it cannot exercise any rights associated with those shares, such as voting or receiving dividends.
Group Investment Management: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

Net income
Stockholder equity, also known as shareholders' equity, represents the amount of financing a company has received by selling stocks. It is calculated by subtracting a company's total liabilities from its total assets. Stockholder equity has two main elements: paid-in capital, which is the money collected from selling stock, and retained earnings, which are the profits reinvested in the company.
For example, if a company has $50,000 in net income and decides to pay $10,000 in dividends, the retained earnings and stockholder equity will increase by $40,000. On the other hand, if the company has a net loss, it reduces retained earnings and stockholder equity by the amount of the loss.
A Guide to Investing in the Nasdaq Index from India
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Stockholders' equity is the remaining assets available to shareholders after all liabilities are paid. It is calculated either as a firm's total assets less its total liabilities or as the sum of share capital and retained earnings less treasury shares.
Stockholders' equity comes from two primary sources: the money originally and subsequently invested in the company through share offerings, and the retained earnings (RE) the company accumulates over time through its operations.
Stockholders' equity is influenced by several components: share capital, retained earnings, net income, and dividend payments. Share capital refers to the amounts received by the reporting entity from transactions with its owners. Retained earnings refer to the amounts earned through income that are not distributed as dividends to stockholders but are instead allocated for investment back into the business. Net income increases retained earnings, while dividend payments reduce them.
Stockholders' equity can increase when owners invest in stock or when the business generates net income. It can decrease when dividends are paid out or when the business experiences a net loss.