Lower interest rates can cause increased investment and spending. In the US, the Federal Reserve Board, or the Fed, adjusts interest rates to keep prices and demand for goods and services steady. Lower interest rates mean consumers spend more, and businesses increase production of goods and create new jobs. Lower interest rates also make it cheaper for businesses to borrow money for new projects. However, an overheated economy can eventually cause shortages of products and labour, which causes inflation. To prevent this, the Fed may begin to gradually raise interest rates.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Effect on consumers | Lower interest rates mean more spending |
| Effect on businesses | Lower interest rates mean increased production of goods and the creation of new jobs |
| Effect on the economy | Lowering interest rates is the Fed's most powerful tool to increase investment spending in the U.S. and to attempt to steer the country clear of recessions |
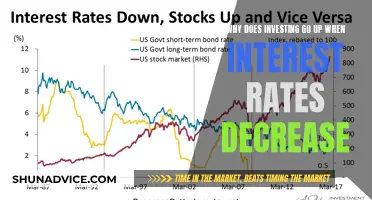
| Effect on the stock market | Interest rate fluctuations have a substantial effect on the stock market |
| Effect on inflation | Lower interest rates can eventually cause shortages of products and labour, which causes inflation |
What You'll Learn
- Lower interest rates increase business investment by making it cheaper to borrow money for new projects
- Lower interest rates for consumers mean more spending
- Lower interest rates for businesses mean increased production of goods
- Lower interest rates can lead to an overheated economy, which can cause shortages of products and labour, leading to inflation
- The Fed may lower interest rates during an economic downturn to encourage additional investment spending

Lower interest rates increase business investment by making it cheaper to borrow money for new projects
However, an overheated economy can eventually cause shortages of products and labour, which causes inflation. To prevent this, the Fed may begin to gradually raise interest rates. It gets more expensive to borrow money, so both businesses and consumers step back their spending, hopefully just enough to keep a healthy economy going.
During an economic downturn, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage additional investment spending. When the economy is growing too fast, the Fed may increase interest rates slightly to keep inflation at bay. Business rates vary as well, depending on the soundness of the company and its ability to offer collateral for a loan.
Interest Rates: Impact on Savings and Investments
You may want to see also

Lower interest rates for consumers mean more spending
Lower interest rates are also good for businesses, as they can borrow money more cheaply for new projects, which increases investment spending. This can lead to increased production of goods, and the creation of new jobs for the people who produce, sell, and deliver the goods.
However, an overheated economy can eventually cause shortages of products and labour, which causes inflation. To prevent this, the Fed may begin to gradually raise interest rates, which makes it more expensive to borrow money. Both businesses and consumers will then step back their spending, hopefully just enough to keep a healthy economy going.
Interest rate fluctuations have a substantial effect on the stock market, inflation, and the economy as a whole. Lowering interest rates is the Fed's most powerful tool to increase investment spending in the U.S. and to attempt to steer the country clear of recessions.
Interest Rates: Investment Discouragement or Encouragement?
You may want to see also

Lower interest rates for businesses mean increased production of goods
The Fed may lower interest rates during an economic downturn to encourage investment spending. This can lead to an overheated economy, which can cause shortages of products and labour, and eventually inflation. To prevent this, the Fed may begin to gradually raise interest rates, making it more expensive to borrow money. This causes both businesses and consumers to step back their spending.
The Fed uses monetary policy to keep the economy stable, and interest rate fluctuations have a substantial effect on the stock market, inflation, and the economy as a whole. There are many interest rates at any given time, with consumers paying different rates for credit card debt, a home mortgage, and a new car.
Why Investment Homes Have Higher Interest Rates Than Second Homes
You may want to see also

Lower interest rates can lead to an overheated economy, which can cause shortages of products and labour, leading to inflation
Lowering interest rates is a key part of national monetary policy. In the US, the Federal Reserve Board, or the Fed, adjusts interest rates to keep prices and demand for goods and services steady. Lowering interest rates makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money for new projects, which increases investment spending. Lower interest rates for consumers mean more spending, too.
However, this can lead to an overheated economy, which can eventually cause shortages of products and labour. This causes inflation. To prevent inflation, the Fed may begin to gradually raise interest rates. It gets more expensive to borrow money, so both businesses and consumers step back their spending, hopefully just enough to keep a healthy economy going.
Daily Compound Interest: A Guide to Investing and Earning More
You may want to see also

The Fed may lower interest rates during an economic downturn to encourage additional investment spending
Lowering interest rates is a key part of national monetary policy. In the US, the Federal Reserve Board, usually referred to as the Fed, adjusts interest rates to keep prices and demand for goods and services steady.
Lower interest rates mean consumers spend more. For businesses, it means increased production of goods, and the creation of new jobs for the people who produce, sell, and deliver the goods. Lower interest rates also increase business investment by making it cheaper to borrow money for new projects.
However, the Fed has a delicate balancing act to perform. An overheated economy can eventually cause shortages of products and labour, which causes inflation. To prevent inflation, the Fed may begin to gradually raise interest rates. It gets more expensive to borrow money, and both businesses and consumers step back their spending, hopefully just enough to keep a healthy economy going.
The Fed uses monetary policy to keep the economy stable. Interest rate fluctuations have a substantial effect on the stock market, inflation, and the economy as a whole. Lowering interest rates is the Fed's most powerful tool to increase investment spending in the US and to attempt to steer the country clear of recessions. During an economic downturn, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage additional investment spending.
Low Interest Rates: Friend or Foe of Investment?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, lower interest rates increase investment spending. Lower interest rates for consumers mean more spending, and lower interest rates for businesses mean increased production of goods, and the creation of new jobs for the people who produce, sell, and deliver the goods.
Lower interest rates make it cheaper for businesses to borrow money for new projects, which encourages investment spending.
Interest rates are decreased to boost the economy and to steer clear of recessions.