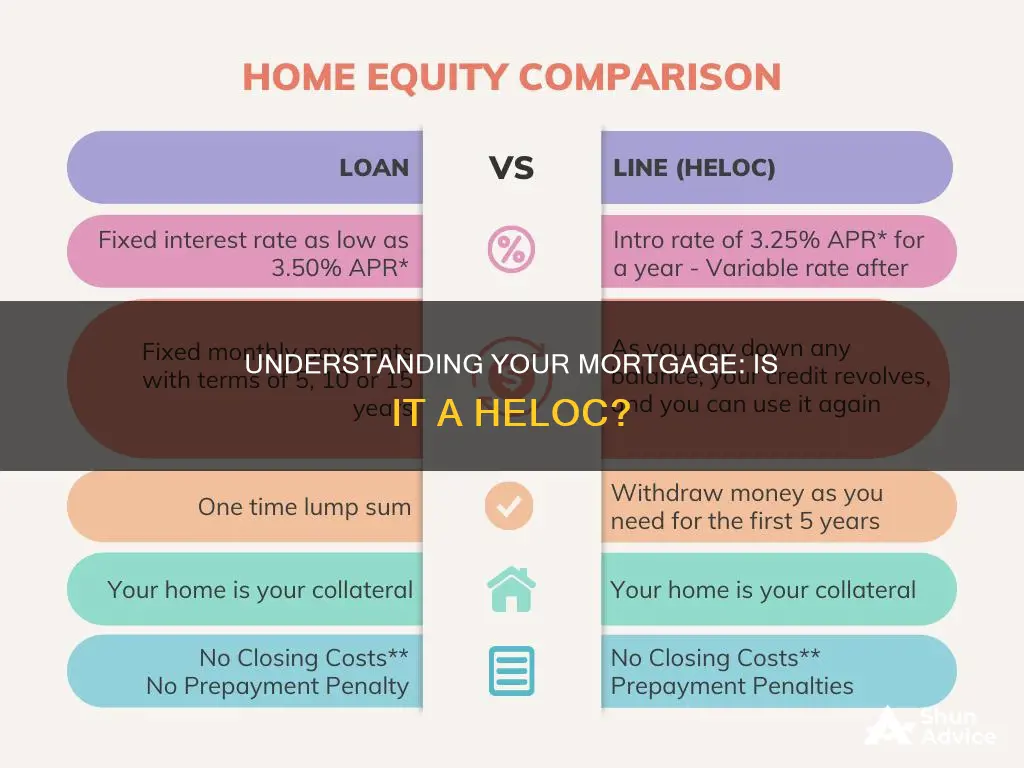
A Home Equity Line of Credit, or HELOC, is a type of second mortgage that allows you to borrow against the available equity in your home. In other words, it is a line of credit borrowed against the value of your home minus the amount you still owe on your mortgage. HELOCs are similar to credit cards in that they are revolving credit lines that you can use and pay down as needed. However, unlike credit cards, HELOCs are intended for large expenses rather than minor ones. They also have lower interest rates than credit cards and personal loans but higher than mortgage loan rates.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A home equity line of credit (HELOC) is a type of second mortgage that lets you borrow against your home equity. |
| How it works | Much like a credit card, a HELOC is a revolving credit line that you pay down, and you only pay interest on the portion of the line you use. |
| Qualification criteria | To qualify for a HELOC, you need to have available equity in your home, meaning that the amount you owe on your home must be less than the value of your home. A lender generally looks at your credit score and history, employment history, monthly income, and monthly debts. |
| Interest rate | Most HELOCs have variable interest rates, which means the rate can fluctuate up or down. However, it is possible to get a HELOC with a fixed rate. |
| Repayment | A HELOC has two phases: the draw period and the repayment period. During the draw period, you can borrow money as needed and make minimum or interest-only payments. In the repayment period, you can no longer borrow money and will pay back the principal and interest. |
| Costs | Closing costs, which are often between 2% and 5% of the loan amount. Some lenders also charge annual fees, which can be around $50 per year. |
| Comparison with mortgage | A HELOC is a second mortgage that gives you access to cash based on the value of your home. Mortgages are used to buy a home or property, while HELOCs are used to tap into existing home equity for other expenses. HELOCs typically have higher interest rates than mortgages. |
What You'll Learn

HELOCs are a type of second mortgage
A HELOC, or Home Equity Line of Credit, is a type of second mortgage. It is a line of credit secured by your home that gives you a revolving credit line to use for large expenses or to consolidate higher-interest-rate debt on other loans. A HELOC is a loan borrowed against the available equity of your home. Your home's equity is the difference between the appraised value of your home and your current mortgage balance.
To qualify for a HELOC, you need to have available equity in your home, meaning that the amount you owe on your home must be less than the value of your home. A lender will also look at your credit score and history, employment history, monthly income, and monthly debts. The interest rate on a HELOC is typically lower than other forms of credit, and the interest you pay may be tax-deductible, although you should consult a tax advisor.
A HELOC has two phases: the draw period and the repayment period. During the draw period, you can borrow money as needed, and monthly payments generally cover only the interest. In the repayment period, you can no longer borrow money and will pay back the principal and interest. A HELOC is a type of second mortgage because it is a loan secured by your home's equity while keeping your first mortgage intact.
Finding Your Mortgage Number: A Simple Guide to Locating It
You may want to see also

HELOCs have two phases: the draw period and the repayment period
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is a second mortgage that gives you access to cash based on the value of your home. It is a line of credit secured by your home that gives you a revolving credit line to use for large expenses. HELOCs have two phases: the draw period and the repayment period.
The draw period is the initial phase of a HELOC, during which you can withdraw funds, up to your credit limit. The draw period typically lasts up to 10 years. During this time, you’re usually only required to pay interest on what you borrow. The draw period is the first period of the line of credit which you can typically access by writing a check, transferring funds through online banking, or via your mobile banking app. You can borrow as little or as much as you need throughout your draw period up to the credit limit you establish at closing.
At the end of the draw period, you’ll begin the repayment period, where you can no longer borrow money and will pay back the principal and interest. The repayment period may last up to 20 years. During the repayment period, monthly payments (including principal and interest) will start, and they may more than double when compared to the draw period.
The interest rate on a HELOC is often lower than other forms of credit, and the interest you pay may be tax-deductible. However, because most HELOCs have an adjustable rate, it’s possible your payments could exceed what you’d originally planned. If you can’t pay back what you’ve withdrawn, the lender could foreclose on your home.
Who Holds Your Mortgage? A Guide to Finding Out
You may want to see also

HELOCs have variable interest rates
A home equity line of credit, or HELOC, is a second mortgage that gives you access to cash based on the value of your home. It is a line of credit secured by your home that gives you a revolving credit line to use for large expenses or to consolidate higher-interest-rate debt on other loans. The interest rate on a HELOC is typically lower than the rate on a credit card or personal loan, and closer to a mortgage rate.
HELOCs usually have variable interest rates, which means that the interest rate on your HELOC will adjust as baseline interest rates go up or down. The interest rate on a HELOC is based on an underlying index rate, which is a benchmark rate that reflects the general economy. Lenders then add a markup, called a margin, to the index rate to calculate the interest rate offered to the borrower. For example, if the prime rate is 7.75% and the lender charges a 1% margin, the HELOC interest rate would be 8.5%. This rate will change as the prime rate does, and could be as often as once per month.
Most HELOCs have variable interest rates, but there are some exceptions. Some lenders offer HELOCs with an initial fixed rate for a limited period of time, which can provide the stability of predictable monthly payments. The fixed-rate portion of the HELOC can be locked in for terms ranging from five years to 30 years, during which time the loan is paid back like a typical mortgage. However, the fixed-rate variety might impose parameters on borrowing that you won’t have with a variable-rate HELOC.
Before taking out a HELOC, it is important to consider the risks and have a repayment plan in place. Because most HELOCs have an adjustable rate, it is possible that your payments could exceed what you had originally planned. If you can’t pay back what you’ve withdrawn, the lender could foreclose on your home.
Understanding Mortgage Basics: Holding Your Dream Home
You may want to see also

HELOCs can be used for large expenses
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is a revolving line of credit that you can tap as needed, similar to a credit card. It is a type of second mortgage that lets you borrow against your home equity. It is a secured loan, with your home used as collateral, allowing lenders to charge lower interest rates.
HELOCs are a good option for large expenses as they offer quick access to funds, with the ability to borrow as much as you need, up to a predetermined credit limit. They also often have lower interest rates than other common types of loans, and the interest may be tax-deductible. However, it is important to note that HELOCs are tied to your home, so failure to pay off the loan could result in foreclosure.
Who Owns Your Mortgage Now? Find Out
You may want to see also

HELOCs can be used to consolidate higher-interest-rate debt
A home equity line of credit, or HELOC, is a type of second mortgage that allows you to borrow against the equity in your home. It is a revolving line of credit, much like a credit card, that you can tap into as needed and then pay back over time. The interest rate on a HELOC is typically lower than that of a credit card or personal loan but may be higher than a traditional mortgage.
One of the key benefits of a HELOC is that it can be used to consolidate higher-interest-rate debt. This means that you can use the funds from the HELOC to pay off multiple existing debts, such as credit cards, car loans, medical debts, or other high-interest loans. By consolidating these debts into a single HELOC, you can simplify your finances by having only one monthly payment to keep track of, potentially lowering your monthly payments and reducing the overall interest you pay.
The interest rate on a HELOC is often lower than that of other types of debt, such as credit cards or personal loans, because the loan is secured by your home as collateral. This means that if you fail to repay the HELOC, your lender can take possession of your home and sell it to recover their loss. As such, it is important to carefully consider your financial situation and ability to make payments before using a HELOC for debt consolidation.
In addition to the potential for lower interest rates, another advantage of using a HELOC for debt consolidation is the flexibility it offers. With a HELOC, you can borrow as much or as little as you need during the draw period, which typically lasts for 5 to 10 years. This can be particularly useful if you need extended access to cash or if you are unsure of the exact amount you will need to borrow. However, it is important to note that most HELOCs have variable interest rates, which means your monthly payments may fluctuate over time.
While consolidating higher-interest-rate debt with a HELOC can have its benefits, it is important to carefully weigh the risks. In addition to the possibility of losing your home if you cannot make payments, there are also other costs associated with HELOCs, such as closing costs and annual fees. Additionally, the interest rates on HELOCs can be unpredictable due to their variable nature, making it difficult to forecast your monthly payments accurately. Therefore, it is crucial to consider your financial situation, shop around for the best rates, and ensure you understand the terms and conditions before deciding if a HELOC is the right choice for consolidating your debt.
Finding Your Mortgage: Record Number Search Simplified
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
HELOC stands for Home Equity Line of Credit. It is a type of second mortgage that allows you to borrow against the available equity in your home.
Mortgages are used to buy a home or property, whereas HELOCs allow you to borrow against the existing equity in your home. Mortgages usually have lower interest rates than HELOCs.
Lenders will typically look at your credit score and history, employment history, monthly income, monthly debts, and the value of your home. You will need a debt-to-income ratio that's 40% or less and a credit score of 620 or higher.
HELOCs offer flexibility as you can access your line of credit and pay back what you use. They often have lower interest rates than other common types of loans, and the interest may be tax-deductible.
HELOCs have variable interest rates, so your payments can exceed what you originally planned. If you can't pay back what you've withdrawn, the lender could foreclose on your home.