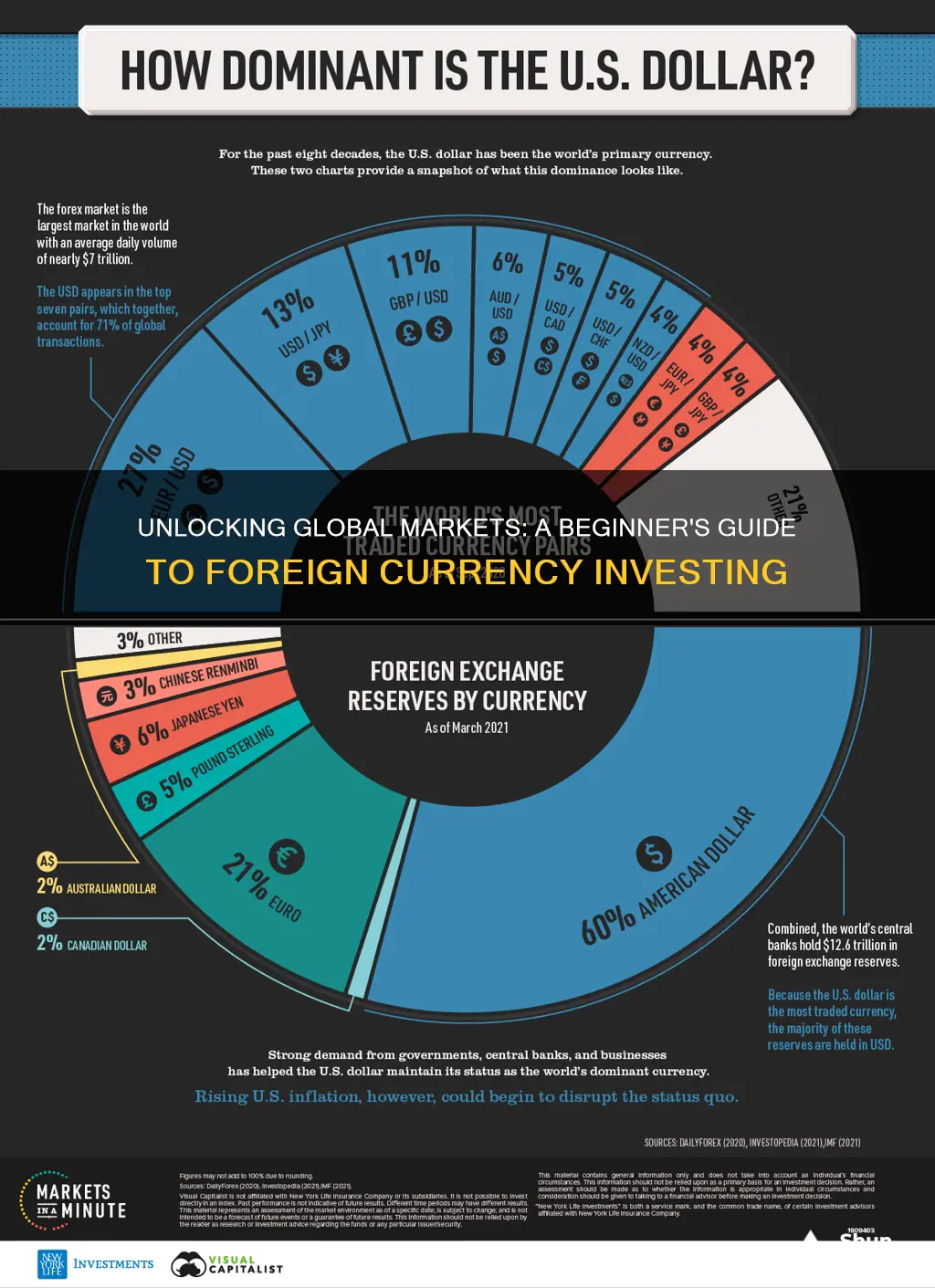
Foreign currency investing is a strategy that allows individuals to speculate on the fluctuations of different currencies in the global market. It involves buying and selling currencies in the foreign exchange market, which is the largest and most liquid financial market globally. This type of investment can be complex and risky, as currency values can be influenced by various economic, political, and social factors. Understanding the mechanics of currency trading, the role of central banks, and the impact of global events on currency values is essential for anyone considering this investment avenue. This paragraph sets the stage for a detailed exploration of the process and considerations involved in foreign currency investing.
What You'll Learn
- Exchange Rates: Fluctuations impact investment returns and risk
- Currency Pairs: Trading involves buying one currency and selling another
- Market Forces: Supply and demand drive currency values
- Economic Indicators: Data like GDP and inflation affect currency strength
- Portfolio Diversification: Foreign currency investments add diversity to investment portfolios

Exchange Rates: Fluctuations impact investment returns and risk
Foreign currency investing involves purchasing assets denominated in a foreign currency, and understanding exchange rates is crucial for investors. Exchange rates represent the value of one country's currency in relation to another, and they fluctuate constantly due to various economic and geopolitical factors. These fluctuations have a significant impact on the returns and risk associated with foreign currency investments.
When investing in foreign currencies, investors aim to profit from the exchange rate movements. For instance, if an investor buys a foreign currency and the exchange rate appreciates against their domestic currency, they can realize a gain. However, the volatility of exchange rates introduces both opportunities and risks. A sudden and significant change in the exchange rate can lead to substantial gains or losses for investors. For example, if an investor holds a foreign currency investment and the exchange rate depreciates, their investment value will decrease, resulting in a loss.
The impact of exchange rate fluctuations is particularly important for investors in foreign direct investments (FDIs) and international bonds. FDIs involve purchasing assets in a foreign country, such as real estate or companies, and the value of these investments is directly linked to the exchange rate. If the host country's currency strengthens against the investor's domestic currency, the value of the FDI will increase, providing a favorable return. Conversely, a weakening host country currency can erode the value of the investment. Similarly, international bond investors must consider exchange rates to assess the true return on their investments, as the interest payments and principal repayments are often in a different currency.
To navigate these risks, investors employ various strategies. One approach is to use currency hedging, which involves protecting the investment against exchange rate fluctuations. This can be done through forward contracts, options, or currency swaps, allowing investors to lock in an exchange rate and minimize potential losses. Additionally, investors may diversify their portfolios across multiple currencies to reduce the impact of any single exchange rate movement.
In summary, exchange rate fluctuations are a critical aspect of foreign currency investing, affecting investment returns and risk. Investors must closely monitor exchange rates and consider implementing hedging strategies to manage potential losses. Understanding the dynamics of exchange rates is essential for making informed investment decisions in the foreign currency market.
School Loan vs. Investment Loan: Which Debt Should You Tackle First?
You may want to see also

Currency Pairs: Trading involves buying one currency and selling another
Foreign currency trading, or forex trading, is a complex and dynamic market that involves the buying and selling of currencies from around the world. At its core, the forex market is a global network of financial institutions, banks, and traders who exchange one currency for another, creating a vast and ever-changing marketplace. One of the fundamental concepts in forex trading is the idea of currency pairs.
When engaging in forex trading, participants are essentially buying one currency and simultaneously selling another. This is where the term 'currency pair' comes into play. A currency pair consists of two currencies, each represented by a unique three-letter code, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen). The first currency in the pair is known as the 'base currency,' while the second is the 'quote or counter currency.' The trader's goal is to predict whether the value of the base currency will increase or decrease relative to the quote currency.
Trading currency pairs involves making a prediction about the future exchange rate between the two currencies. Traders analyze various factors, such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment, to determine whether a currency pair will appreciate or depreciate. For example, if a trader believes that the US economy will strengthen, they might anticipate the US Dollar (USD) to appreciate against other currencies, including the Euro (EUR). In this scenario, the trader would buy USD/EUR, expecting the value of the USD to increase relative to the EUR.
The process of trading currency pairs involves opening a position, which means buying or selling the currency pair. If a trader expects the value of the base currency to rise, they go long, buying the currency pair. Conversely, if they anticipate a decline, they go short, selling the currency pair. Traders can also use leverage, which allows them to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, but this also increases the risk.
Managing risk is crucial in forex trading. Traders employ various strategies to minimize potential losses, such as setting stop-loss orders to limit potential downside and taking profits at predetermined levels. Additionally, understanding the concept of pips, which represent the smallest price change in a currency pair, is essential for calculating profits and losses. Each pip movement in a currency pair represents a one-unit change in the value of the quote currency.
In summary, currency pairs are the building blocks of forex trading, where traders buy one currency and sell another, anticipating price movements. Successful forex trading requires a deep understanding of market dynamics, risk management, and the ability to make informed decisions based on economic and geopolitical factors. It is a highly competitive and rewarding market for those who can navigate its complexities.
Angel Investors: Unlocking the Dream of Home Ownership
You may want to see also

Market Forces: Supply and demand drive currency values
The foreign currency market is a dynamic and complex arena where the principles of supply and demand play a pivotal role in determining currency values. This market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and is influenced by a myriad of factors, both economic and geopolitical. At its core, the relationship between supply and demand dictates the price of currencies, much like it does for any other commodity or asset.
In the context of foreign currency investing, supply and demand dynamics are shaped by the global economy's intricate web of interactions. When a country's economy is strong, it typically has a higher demand for its currency from foreign investors seeking to capitalize on its economic stability. This increased demand can lead to a rise in the currency's value relative to other currencies. Conversely, if a country's economy is struggling, investors may be less inclined to hold its currency, causing its value to depreciate.
The supply side of the equation is equally crucial. Currencies are supplied through various channels, including trade, investment, and financial transactions. For instance, a country's exports increase the supply of its currency in the global market as foreign buyers need to purchase the local currency to pay for the goods. Similarly, foreign direct investment (FDI) can significantly impact the supply of a currency, as investors bring in capital that needs to be exchanged into the local currency.
Market forces also come into play when central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market. These interventions can either increase or decrease the supply of a currency, thereby influencing its value. For example, a central bank might buy its own currency to strengthen its value or sell it to weaken it, often as a tool to manage inflation or stabilize the economy. Such actions can have a profound impact on the market, especially in the short term.
Understanding these market forces is essential for investors looking to navigate the foreign currency market successfully. It requires a keen eye for economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. Investors must stay informed about global economic trends, as these can significantly affect currency values. Additionally, keeping an eye on central bank policies and international trade agreements is crucial, as these can create shifts in supply and demand, impacting currency prices.
Bullion Basics: Unlocking Gold Investment Strategies for Beginners
You may want to see also

Economic Indicators: Data like GDP and inflation affect currency strength
Economic indicators play a crucial role in the foreign currency market, as they provide valuable insights into a country's economic health and stability. Two of the most important indicators are Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and inflation, which can significantly impact the strength and value of a currency.
GDP is a key measure of a country's economic performance and represents the total value of goods and services produced within its borders over a specific period. A country with a high GDP growth rate is often considered more economically robust and attractive to investors. Investors tend to favor currencies of countries with strong GDP growth as it indicates a thriving economy, higher demand for goods and services, and potentially higher returns on investment. For instance, if Country A's GDP growth rate is consistently higher than Country B's, investors might be more inclined to invest in Country A's currency, assuming all other factors are equal.
Inflation, on the other hand, measures the rate at which prices for goods and services are rising. It is an essential indicator of a country's economic stability and purchasing power. High inflation can erode the value of a currency over time, making it less attractive to investors. When inflation is high, the purchasing power of a country's currency decreases, meaning that the same amount of money can buy fewer goods and services. This can lead to a decrease in demand for that currency, causing its value to weaken. Conversely, low inflation or deflation (a decrease in prices) can make a currency more appealing, as it suggests a stable economy and potentially stronger purchasing power in the long term.
The relationship between economic indicators and currency strength is often direct and proportional. As GDP growth increases, it generally leads to higher demand for the country's currency, causing its value to appreciate. Similarly, low inflation or deflation can strengthen a currency by maintaining its purchasing power. However, it's important to note that these indicators are just a part of a larger economic picture. Other factors, such as interest rates, employment data, and political stability, also influence currency movements.
Investors and traders closely monitor these economic indicators to make informed decisions about foreign currency investments. By analyzing GDP growth and inflation rates, they can assess the potential risks and rewards associated with different currencies. Understanding these indicators is essential for anyone looking to navigate the complex world of foreign currency investing, as they provide a foundation for evaluating a country's economic health and its currency's strength in the global market.
Fitness Investment: What's the Priority?
You may want to see also

Portfolio Diversification: Foreign currency investments add diversity to investment portfolios
Foreign currency investments play a crucial role in portfolio diversification, offering investors a means to spread their risk and potentially enhance returns. By incorporating foreign currencies into an investment strategy, individuals can achieve a more balanced and resilient portfolio, especially when combined with other asset classes. This approach is particularly relevant in today's globalized economy, where international trade and financial markets are increasingly interconnected.
The primary benefit of foreign currency investments is the opportunity to diversify across different markets and economies. By holding a portion of their portfolio in foreign currencies, investors can reduce the overall risk associated with their investments. For instance, if an investor's portfolio is heavily weighted towards a single country or region, a downturn in that specific market could significantly impact the overall performance. However, by allocating funds to various foreign currencies, the potential negative effects of a single market's decline are mitigated, as the performance of other currencies can offset the losses.
This diversification strategy is especially valuable for risk-averse investors who seek to minimize potential losses. It allows them to maintain a degree of stability in their portfolio, even during turbulent economic times. For example, during a global financial crisis, certain currencies might perform well due to their country's economic resilience, while others may suffer. By holding a diverse range of currencies, investors can benefit from the strength of some currencies while minimizing the impact of the weaker ones.
In addition to risk reduction, foreign currency investments can also provide an opportunity for capital appreciation. Exchange rates are constantly fluctuating, influenced by various economic and geopolitical factors. Investors can take advantage of these rate movements by buying and selling currencies at opportune times. This strategy requires a keen understanding of market trends and economic indicators, but it can result in significant gains when executed successfully.
Furthermore, foreign currency investments can offer a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation. In countries with high inflation rates, the value of the local currency may decrease over time. By investing in foreign currencies, investors can protect their purchasing power and potentially benefit from the weaker currency's depreciation against a stronger one. This aspect is particularly important for long-term investors seeking to preserve and grow their wealth.
In summary, foreign currency investments are a powerful tool for portfolio diversification, enabling investors to spread risk, enhance potential returns, and protect against economic downturns. By allocating a portion of their portfolio to foreign currencies, investors can achieve a more balanced and resilient investment strategy, taking advantage of global market opportunities while managing risks effectively.
UK Investors: Who and How Many?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Foreign currency investing involves purchasing and trading currencies from different countries, aiming to profit from the fluctuations in their exchange rates. It is a speculative activity where investors buy one currency and sell another, hoping to make a profit from the price movements.
Exchange rates play a crucial role in foreign currency investing. These rates determine the value of one currency relative to another and can fluctuate based on various economic factors. Investors analyze these rates to identify potential opportunities, such as buying a currency that is expected to strengthen against a weaker one.
Foreign currency investing carries several risks. Firstly, currency values can be highly volatile, leading to significant price swings. Secondly, the leverage often used in this market can amplify both profits and losses. Additionally, geopolitical events and economic policies can impact currency values, making it a complex and uncertain investment environment.
Successful foreign currency investing often involves a combination of technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and risk management. Investors may use technical indicators to identify trading patterns and potential entry/exit points. Fundamental analysis helps assess economic factors like interest rates, inflation, and political stability that can influence currency values. Effective risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders and diversifying the portfolio, are also essential.