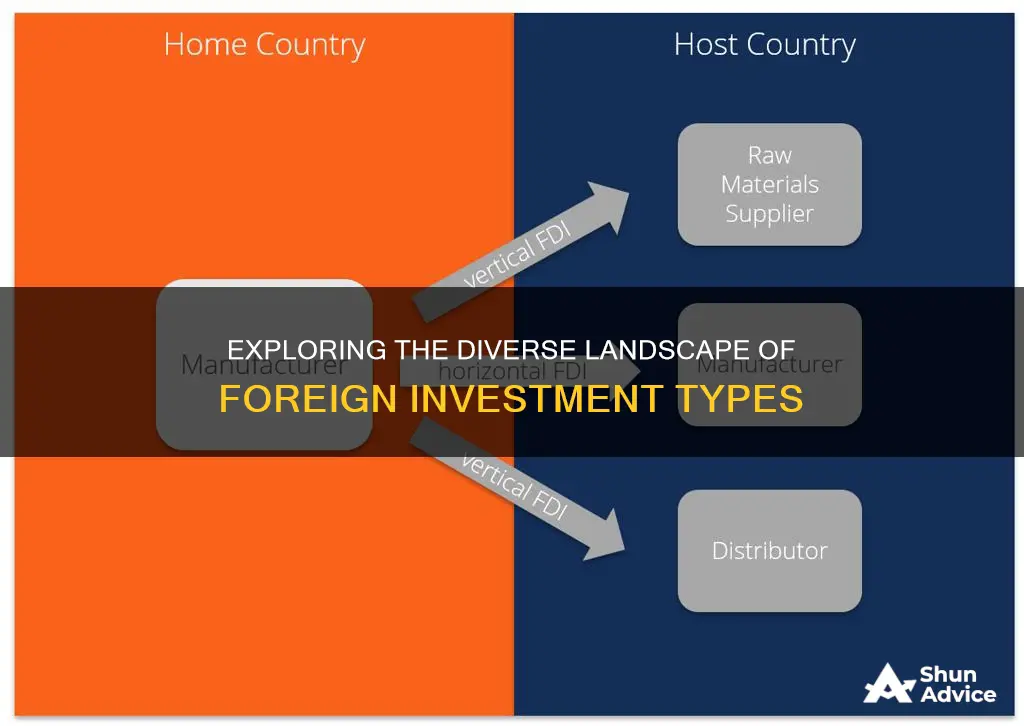
Foreign investment is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various strategies and approaches, each with its own unique characteristics and implications. Understanding the different types of foreign investment is crucial for businesses and investors seeking to navigate the global market effectively. From direct investments in foreign assets to portfolio investments in foreign securities, the spectrum of foreign investment is broad and diverse. This paragraph aims to explore and clarify the various types of foreign investment, providing a comprehensive overview to guide readers in their international business ventures.
What You'll Learn
- Direct Investment: When a company or individual acquires a controlling interest in a foreign business
- Portfolio Investment: Involves buying and selling securities in foreign markets without establishing a business presence
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): A significant investment made to control an enterprise operating in another country
- Portfolio Investment in Real Estate: Purchasing property or land in a foreign country for investment purposes
- Cross-Border Mergers and Acquisitions: Companies merging or acquiring businesses in other countries to expand globally

Direct Investment: When a company or individual acquires a controlling interest in a foreign business
Direct investment is a powerful strategy for businesses and individuals seeking to expand their global footprint and gain a competitive edge in international markets. This type of investment involves acquiring a significant stake, often a controlling interest, in a foreign company or enterprise. By doing so, investors gain a substantial say in the management and operations of the target company, allowing for a more comprehensive and integrated approach to market entry.
In the context of direct investment, the investor becomes a major shareholder, typically holding more than 50% of the shares or an equivalent voting power. This level of ownership provides the investor with the authority to influence strategic decisions, appoint key executives, and shape the overall direction of the foreign business. It is a more hands-on approach compared to other investment methods, as it requires active involvement and a long-term commitment to the host country's market.
One of the key advantages of direct investment is the ability to establish a local presence and build a strong connection with the target market. Investors can adapt their products, services, and business models to suit the local needs and preferences, fostering a deeper understanding of the cultural and economic landscape. This can lead to more effective marketing, improved customer satisfaction, and a stronger competitive position in the host country.
Direct investment also offers the opportunity to tap into new markets, access resources, and leverage the host country's infrastructure and talent pool. Investors can benefit from the local expertise and networks, potentially reducing the time and cost associated with market entry. Moreover, with a controlling interest, investors can make strategic decisions swiftly, ensuring a more agile and responsive business operation.
However, direct investment is not without its challenges. It requires a comprehensive understanding of the host country's legal, cultural, and economic environment. Investors must navigate complex regulations, potential language barriers, and varying business practices. Due diligence is essential to identify and mitigate risks, ensuring a successful and sustainable investment. This may include legal and financial assessments, market research, and the establishment of a robust local team to support the investment.
Choosing the Right Investment Firm: Factors to Consider
You may want to see also

Portfolio Investment: Involves buying and selling securities in foreign markets without establishing a business presence
Portfolio investment is a strategic approach to foreign investment, primarily focused on the buying and selling of securities in foreign markets. This type of investment is characterized by its short-term nature, aiming to capitalize on market opportunities and price fluctuations rather than long-term business operations. Investors engaging in portfolio investment typically seek to diversify their portfolios by accessing international markets, thereby reducing risk and potentially increasing returns.
The process involves a meticulous analysis of foreign securities, such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives, to identify attractive investment opportunities. Investors can choose to invest in individual securities or opt for more diversified approaches, such as mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), which offer exposure to a broader range of assets. This strategy allows investors to gain exposure to foreign markets without the need to set up a physical business presence, making it an attractive option for those seeking international diversification.
One of the key advantages of portfolio investment is the ability to quickly adapt to changing market conditions. Investors can make rapid decisions based on market trends and news, taking advantage of short-term price movements. This agility is particularly beneficial in volatile markets, where quick responses can lead to significant gains. Additionally, portfolio investment often requires lower capital outlays compared to other forms of foreign investment, making it accessible to a wider range of investors.
However, it is essential to approach portfolio investment with caution. The foreign exchange market, which is integral to this strategy, can be highly volatile and subject to rapid fluctuations. Investors must carefully consider the risks associated with currency exchange rates, political instability, and economic changes in the countries they invest in. Due diligence and ongoing research are crucial to making informed decisions and managing potential risks.
In summary, portfolio investment is a dynamic and accessible approach to foreign investment, allowing investors to participate in global markets without the complexities of establishing a business presence. By carefully selecting securities and staying informed about market dynamics, investors can navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by international markets, potentially achieving their financial goals while managing risk effectively.
Investment Cash: Revenue or Not?
You may want to see also

Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): A significant investment made to control an enterprise operating in another country
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is a powerful tool for businesses and governments seeking to expand their global reach and gain a competitive edge in international markets. It involves a significant investment made by an individual or company in a foreign country, with the primary goal of acquiring a lasting interest in a business or enterprise. This type of investment is a strategic move that can bring numerous benefits, including access to new markets, resources, and talent, as well as the potential for long-term growth and profitability.
FDI is a complex process that requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. When a company decides to invest directly in a foreign market, it typically involves a substantial financial commitment and a long-term strategic vision. The investor aims to establish a presence in the host country, often by acquiring a significant stake in an existing business or by setting up a new operation. This could include mergers and acquisitions, greenfield investments (building a new facility), or joint ventures with local companies. The key aspect is gaining control over the enterprise, which provides the investor with the ability to influence decision-making and shape the company's future.
There are several motivations behind FDI. Firstly, it allows companies to diversify their operations and reduce risks associated with relying solely on domestic markets. By entering a new market, businesses can tap into untapped consumer bases, access raw materials or resources, and benefit from different regulatory environments. For instance, a technology firm might invest in a foreign country to establish a research and development center, leveraging the local talent pool and potentially gaining a competitive edge through innovation. Secondly, FDI can facilitate knowledge transfer and technology sharing, as investors bring their expertise and best practices to the host country.
The process of FDI often involves thorough research and due diligence. Investors must carefully select the target country, considering factors such as political stability, economic policies, infrastructure, and the overall business environment. They may also need to navigate legal and regulatory frameworks, which can vary significantly across different nations. Additionally, cultural and linguistic barriers might require strategic planning to ensure effective communication and integration with the local business landscape.
In summary, Foreign Direct Investment is a significant financial commitment that enables businesses to expand globally and gain control over foreign enterprises. It offers a range of benefits, including market access, resource acquisition, and knowledge transfer. FDI is a strategic move that requires careful planning, considering various economic, political, and cultural factors to ensure a successful and sustainable presence in the host country. Understanding the motivations and processes behind FDI is essential for businesses aiming to make informed decisions in the global marketplace.
Investment Bankers' Toolbox: Models and Methods
You may want to see also

Portfolio Investment in Real Estate: Purchasing property or land in a foreign country for investment purposes
Portfolio investment in real estate is a strategic approach for diversifying one's investment portfolio and can be an attractive option for investors seeking to expand their horizons globally. This type of investment involves acquiring property or land in a foreign country with the primary goal of generating returns through rental income, property appreciation, or future development. Here's an overview of this investment strategy:
Benefits and Considerations:
- Diversification: Real estate investment abroad offers a unique way to diversify your portfolio. By entering new markets, investors can reduce the overall risk associated with their investments. This is particularly appealing to those with a long-term investment perspective, as it can provide a hedge against economic fluctuations in their home country.
- Return Potential: Real estate markets worldwide offer varying levels of growth and rental income potential. Purchasing property in an emerging market might yield higher returns over time, especially if the market is experiencing rapid development and urbanization. However, it's essential to conduct thorough research to understand the local market dynamics and potential risks.
- Long-Term Strategy: This investment is often a long-term play. It may take time to see significant returns, especially when considering the initial costs of purchasing property and the potential for rental income to grow steadily over the years. Investors should be prepared for a longer-term commitment and have a clear understanding of their investment goals.
Steps and Research:
- Market Analysis: Begin by researching the real estate market in the desired country. Study factors such as local laws, property taxes, rental regulations, and the overall economic climate. Understanding the market dynamics will help you make informed decisions about the type of property to invest in and the potential for growth.
- Location Selection: Choose the right location is crucial. Consider factors like proximity to local amenities, transportation, and employment hubs. Properties in prime locations often command higher rental rates and have better long-term value.
- Legal and Financial Considerations: Navigating foreign real estate investment requires an understanding of legal and financial aspects. Seek professional advice on the legal process of purchasing property, including any necessary visas or residency permits. Also, be aware of currency exchange rates and potential tax implications to ensure your investment remains profitable.
Investment Types:
- Residential Properties: Investing in houses or apartments for rental income is a common strategy. This can provide a steady cash flow and, over time, potential for significant equity buildup.
- Commercial Real Estate: Office spaces, retail stores, or industrial properties can be attractive investments for those seeking higher rental yields. These properties often cater to businesses and can provide long-term leases, offering stability and potential for growth.
- Land Development: For more experienced investors, purchasing land with development potential can be lucrative. This strategy involves acquiring land and then developing it according to local regulations, which can result in substantial returns.
In summary, portfolio investment in real estate abroad offers a unique opportunity to diversify and grow your wealth. It requires careful research, an understanding of local markets, and a long-term investment mindset. By following these steps and staying informed, investors can make well-calculated decisions, potentially reaping the rewards of successful international real estate ventures.
Life Insurance: An Investment Vehicle for Your Future
You may want to see also

Cross-Border Mergers and Acquisitions: Companies merging or acquiring businesses in other countries to expand globally
Cross-border mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are a significant strategy for companies aiming to expand their global footprint and gain a competitive edge in international markets. This type of investment involves one company acquiring or merging with a business in a different country, often to enter new markets, diversify its operations, or gain access to resources and expertise. The process can be complex and requires careful planning and consideration of various legal, cultural, and economic factors.
When a company engages in a cross-border M&A, it typically aims to achieve several objectives. Firstly, it seeks to establish a physical presence in a new market, allowing it to directly serve local customers and compete with established local businesses. This is particularly important for industries where consumer proximity and personalized services are crucial, such as retail, hospitality, or professional services. By acquiring a local business, the parent company can quickly gain a foothold in the new market and build a customer base.
Secondly, cross-border M&A can provide access to unique resources and capabilities. Target companies may possess specialized knowledge, intellectual property, or skilled personnel that the acquiring company lacks. For instance, a technology firm might acquire a smaller software developer in a foreign country to gain access to their innovative technology and talented workforce, thereby enhancing its own product offerings and competitive advantage. This strategic move can lead to improved efficiency, innovation, and market position.
Furthermore, this type of investment allows companies to diversify their revenue streams and reduce risk. By expanding into new markets, businesses can mitigate the impact of economic fluctuations in their home country. For example, a company heavily reliant on domestic sales might acquire a foreign competitor to gain a stronger position in an international market, ensuring a more stable and diverse revenue portfolio. This strategic move can also lead to economies of scale, as the combined operations of the two companies may result in reduced costs per unit of production or service delivery.
However, cross-border M&A is not without its challenges. Cultural and legal differences between countries can present significant obstacles. Companies must navigate varying business practices, regulations, and tax systems, ensuring compliance and effective integration. The process often requires extensive due diligence to assess the target company's financial health, legal standing, and potential risks. Effective communication and a clear understanding of the local market are essential to ensure a successful integration and long-term sustainability.
In summary, cross-border mergers and acquisitions are a powerful tool for companies seeking global expansion. It enables them to establish a physical presence in new markets, access unique resources, and diversify their operations. While it presents challenges, careful planning, cultural sensitivity, and a comprehensive understanding of the target market can lead to successful and mutually beneficial outcomes. This strategy continues to be a driving force in the global business landscape, fostering international trade and economic integration.
Civil Suit-Proof Investments: What You Can't Touch
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are several types of foreign investment, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes. These can be broadly categorized into direct investment, portfolio investment, and other investment. Direct investment involves establishing a presence in a foreign country, such as mergers and acquisitions or building foreign affiliates. Portfolio investment includes buying and selling equity securities and debt instruments in foreign markets. Other investment encompasses a wide range of activities like financial derivatives, insurance, and real estate.
Absolutely! Direct investment is when a company or individual invests in a foreign business, often by acquiring a controlling interest or establishing a subsidiary. This type of investment is more hands-on and involves active management and integration into the host country's economy. Portfolio investment, on the other hand, is more passive and involves buying and selling securities like stocks and bonds in foreign markets. It is a more liquid form of investment and is often used by investors seeking diversification and potential capital gains.
Yes, other investment can include financial derivatives, insurance, and real estate. Financial derivatives are complex financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset. Insurance companies may invest in foreign markets to diversify their portfolios and manage risk. Real estate investment can involve purchasing properties or developing projects in foreign countries, offering both rental income and potential capital appreciation.
Each type of foreign investment has the potential to influence the host country's economy in different ways. Direct investment can bring significant capital inflows, create jobs, and transfer technology and expertise. It can also lead to increased competition and improve productivity. Portfolio investment can inject capital into the market, potentially stimulating economic growth and providing liquidity to the financial system. Other investment categories may have more indirect effects, such as stabilizing exchange rates or providing insurance coverage for local businesses.
Yes, many countries have specific regulations and restrictions in place to manage foreign investment. These rules can vary widely and may include restrictions on ownership percentages, sectoral limitations, or requirements for local partnerships. Governments often implement these measures to protect domestic industries, ensure technology transfer, or maintain control over strategic assets. It is essential for investors to research and understand the legal and regulatory environment of the target country before making any investment decisions.