Dividends are a distribution of a company's earnings to its shareholders, and they can be issued as cash payments or shares of stock. Dividends are generally paid quarterly, but they can also be paid semi-annually or annually. To determine whether equity investees' investments have paid dividends, investors can research financial news sites, such as Investopedia's Markets Today page, or utilise the screening tools provided by stock brokerages. Additionally, information about dividend payments can be found on the Securities and Exchange Commission's website and through specialty providers. By law, publicly traded companies must report all dividend payments on Form 1099, which can be accessed through the EDGAR system on the SEC's website.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Dividend definition | A distribution of a company's earnings to its shareholders |
| Dividend payments | Often paid quarterly, but can also be paid monthly, semi-annually, annually, or non-recurrently |
| Dividend amounts | Decided by the board of directors based on the company's most recent earnings |
| Dividend types | Cash, additional shares, special dividends, preferred dividends, dividend reinvestment programs (DRIPs) |
| Dividend eligibility | Common stock shareholders of dividend-paying companies are eligible as long as they own the stock before the ex-dividend date |
| Dividend taxation | All dividends are taxable, but qualified dividends (held for at least 60 days) are taxed at capital gains rates |
| Dividend and stock price | A stock's share price will change to reflect a dividend payment |
| Dividend and company finances | Dividends are considered an indication of a company's financial well-being; a reduction in dividends may signal trouble |
| Dividend and company influence | The equity method of accounting is used when an investor has significant influence (generally 20% or more ownership) over the investee company |
| Dividend and investment value | Net income increases investment value, while loss and dividend payouts decrease it |
What You'll Learn

Dividends decrease investment asset balance but increase cash flow
Dividends are a distribution of a company's profits to its shareholders. They are a reward for their investment. Companies are not required to issue dividends, but many pride themselves on paying consistent or constantly increasing dividends each year. Dividends can be paid in cash or by issuing additional shares of stock.
Cash dividends affect the cash and shareholder equity on the balance sheet. Both retained earnings and cash are reduced by the total value of the dividend. This means that dividends decrease investment asset balance.
However, dividends also increase cash flow. Cash flow is the rate at which money passes through a company, and it is an excellent indicator of a company's financial health. Dividends are paid from the company's cash flow, so they are considered a liability rather than an asset. Dividends are only paid when there is enough profit to cover the payout. Therefore, dividends are an outflow of cash, and they increase cash flow.
Stock dividends, on the other hand, have no impact on the cash position of a company. They only impact the shareholders' equity section of the balance sheet.
Savings and Investment: Finding Equilibrium Balance
You may want to see also

Dividends are paid out of net income/earnings
Dividends are a distribution of a company's earnings to its shareholders. They are paid out of net income or net earnings, which is a reflection of a company's profit. Net income is calculated by taking a company's revenue and subtracting all costs associated with doing business.
Dividends are not considered an expense and do not affect a company's net income or profit. Instead, they impact the shareholders' equity section of the balance sheet. Dividends are not recorded as an expense on a company's income statement because they are not an operating expense, which are the costs to run the day-to-day business.
Dividends can be issued as cash payments, shares of stock, or other property. When a company declares dividends, it gives investors a certain dollar amount for every share of its stock. This is done to reward investors and make the stock seem more attractive.
Dividends represent a portion of a company's net income. However, they do not cause net income to go down. Instead, dividends are just one example of what a company might choose to do with its net income. For example, a company can choose to reinvest its net income in the business or share its proceeds with investors through dividends.
To calculate the total dividends paid in any given period, one can look at net income and the change in retained earnings. Retained earnings are calculated by taking the cumulative net income and subtracting the cumulative dividends paid to shareholders. Therefore, the amount paid out in dividends is equal to net income minus the change in retained earnings for any period of time.
A Beginner's Guide to Investing in India's Top ETFs
You may want to see also

Dividends are paid per share of stock
A company's DPS is often derived using the dividend paid in the most recent quarter, which is also used to calculate the dividend yield. DPS is an important measure for investors because the amount a firm pays out in dividends directly translates to income for the shareholder. It is the most straightforward figure an investor can use to calculate their dividend payments from owning shares of a stock over time.
A consistent increase in DPS over time can also give investors confidence that the company's management believes that its growth in earnings can be sustained. A rising DPS is a sign of strong performance and indicates that a company's management thinks its earnings growth is sustainable.
Dividends are generally paid quarterly, with the amount decided by the board of directors based on the company's most recent earnings. Dividends may be paid in cash or additional shares. When a company announces a dividend, it also announces the payment date on which the dividend will be paid into the shareholders' accounts.
The dividend yield of a stock is the dividend amount paid per share and is expressed as a percentage of the company's share price, such as 2.5%. For example, if a company's board of directors decides to issue an annual 5% dividend per share, and the company's shares are worth $100, the dividend is $5. If the dividends are issued every quarter, each distribution is $1.25.
Dividends are typically paid according to how many shares an investor owns. For example, if an investor owns 100 shares of a company that is trading at $1 per share and paying a dividend of 25%, they would be paid $25.
What Keeps an Investment Managing Director Up at Night?
You may want to see also

Dividends can be paid in cash or as shares of stock
Dividends are a distribution of a company's earnings paid to its shareholders. They are decided by the company's board of directors and are a way to return wealth to shareholders. Dividends can be paid out in cash or as shares of stock.
Cash Dividends
Cash dividends are paid out as cash, either by check or electronic transfer. They provide investors with regular income but also come with tax consequences. The company's share price tends to drop by roughly the same amount as the dividend, and the receiver of a cash dividend must pay tax on the value of the distribution.
Stock Dividends
Stock dividends are paid out as additional shares in the company. They are usually not taxed and increase the shareholder's stake in the company. Stock dividends are often chosen when a company has limited liquid cash. They also give shareholders the choice to keep or sell the shares. However, stock dividends may signal financial instability or limited cash reserves.
Calculating Dividends
Dividends are typically paid according to the number of shares held. For example, if a company is trading at $1 per share and pays a dividend of 25%, an investor with 100 shares would be paid $25.
Building a Solid Investment Portfolio with a $2,000 Foundation
You may want to see also

Dividends are approved by shareholders and paid on a set schedule
Dividends are a way for companies to share a portion of their profits with their shareholders. They are issued as a reward for their shareholders' investment in the company and are usually paid out of the company's net profits. Dividends can be issued as cash payments or as shares of stock.
Dividends are approved by the shareholders by voting rights and must also be approved by the company's board of directors. The board decides on the amount to be paid out in dividends based on the company's financial performance, future growth plans, and overall business strategy. The board must also set a record date to determine which stockholders are entitled to receive the dividend.
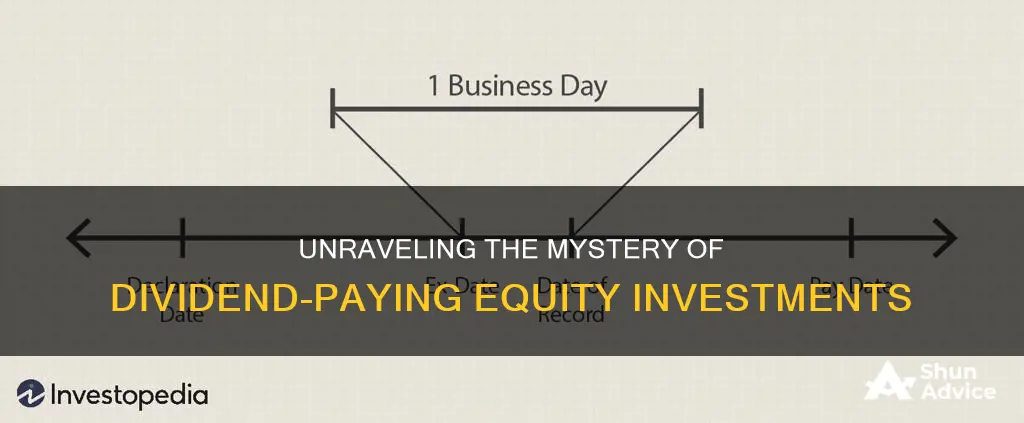
There are several key dates to keep in mind when it comes to dividend payments. The first is the declaration date, when the company officially announces its intention to pay a dividend, including the dividend amount, payment date, and other relevant details. The ex-dividend date is the cutoff day for eligibility to receive the dividend. If you purchase shares on or after this date, you will not receive the upcoming dividend. The record date is when the company officially determines which shareholders are eligible to receive the dividend. Finally, the payment date is when the dividend is actually paid out to shareholders, either in cash or additional shares.
Dividends are typically distributed to shareholders on a set schedule, which is decided by the board. They may be paid monthly, quarterly, or annually. For example, Walmart Inc. and Unilever make regular quarterly dividend payments. Companies can also issue non-recurring special dividends, either individually or in addition to a scheduled dividend.
Investment Networks: Financial Risk Management Strategies
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Dividend-paying companies are usually more established and prefer to distribute profits to shareholders instead of reinvesting them in the business. You can find out if a company pays dividends by checking financial news sites, such as CNBC, Morningstar, The Wall Street Journal, and Investopedia, or by checking the company's financial statements.
A company's share price will change to reflect a dividend payment. For example, if a company's share price is $60 and it declares a $2 dividend, the share price may increase to $62 once the news becomes public. On the ex-dividend date, the share price is adjusted and trading begins at the new price, excluding the dividend.
The dividend yield of a stock is the dividend amount paid per share, expressed as a percentage of the company's share price. For example, if a company's shares are worth $100 and it issues an annual 5% dividend per share, the dividend is $5. If the dividends are issued quarterly, each distribution is $1.25.







