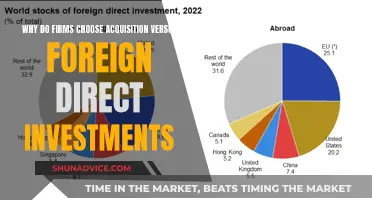
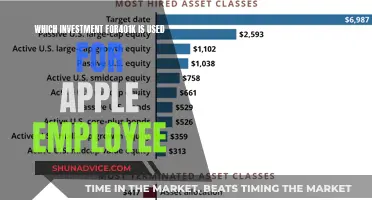
In today's globalized economy, universities are increasingly investing in foreign equities to diversify their portfolios and maximize returns. This strategy involves allocating a portion of their endowment funds to international markets, which can offer higher potential yields compared to domestic investments. However, it also comes with increased risks due to varying economic conditions, political instability, and currency fluctuations. This paragraph will explore the various factors that universities consider when investing in foreign equities, including market research, risk management strategies, and the potential benefits of international diversification.
What You'll Learn
- Regulatory Frameworks: Governments set rules for foreign equity investments by universities, ensuring compliance and transparency
- Risk Management: Institutions employ strategies to mitigate risks associated with international stock markets
- Diversification: Spreading investments across various countries and sectors to reduce volatility and enhance returns
- Market Analysis: Universities study global economic trends, political stability, and industry performance to make informed investment decisions
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical investing practices, including environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, are considered in foreign equity portfolios

Regulatory Frameworks: Governments set rules for foreign equity investments by universities, ensuring compliance and transparency
The investment practices of universities, particularly their engagement in foreign equity markets, are subject to a complex web of regulatory frameworks designed to ensure transparency, compliance, and ethical standards. Governments worldwide have recognized the importance of overseeing these activities due to their potential impact on the economy, national security, and the financial well-being of students and alumni. These regulatory measures aim to strike a balance between fostering international collaboration and safeguarding the interests of the institutions and their stakeholders.
One key aspect of this regulatory approach is the establishment of guidelines and reporting requirements. Governments often mandate that universities disclose their foreign equity investments, including the types of assets held, their valuation, and the reasons for these investments. Such transparency allows regulatory bodies to monitor the portfolio's performance and identify any potential risks or conflicts of interest. For instance, a university's investment in a foreign company might be scrutinized to ensure it aligns with the institution's mission and does not compromise its academic integrity.
Regulatory frameworks also typically involve setting thresholds for foreign equity investments. Governments may define limits on the proportion of a university's investment portfolio that can be allocated to foreign securities. These thresholds are designed to prevent excessive risk exposure and ensure that the university's financial stability is not unduly affected by international market fluctuations. By setting these limits, authorities aim to encourage a diversified investment strategy while mitigating potential risks.
In addition to disclosure and threshold requirements, governments often implement due diligence processes for foreign equity investments. This includes thorough background checks on the companies in which universities invest, assessing their financial health, business practices, and potential risks. Due diligence ensures that universities make informed decisions and minimizes the chances of investing in entities with questionable activities or poor governance. Such measures are crucial in maintaining the reputation and integrity of the educational institution.
Furthermore, regulatory bodies may establish oversight committees or advisory panels comprising experts and stakeholders to review and provide guidance on foreign equity investments. These committees can offer recommendations on investment strategies, risk management, and compliance with relevant laws. By involving external experts, governments can ensure that the regulatory framework remains effective and adaptable to the evolving nature of university investments. This collaborative approach fosters a culture of compliance and encourages universities to adopt best practices in their foreign equity investments.
Registered Investment Advisors: Your Money's Best Friend
You may want to see also

Risk Management: Institutions employ strategies to mitigate risks associated with international stock markets
In the realm of international investing, universities and other institutions often find themselves at the crossroads of global financial markets. The decision to invest in foreign equities can offer diversification benefits and potentially higher returns, but it also introduces unique risks that demand careful management. Risk management in this context is a critical aspect of institutional investing, ensuring that the potential rewards are not overshadowed by the inherent dangers.
One of the primary strategies employed by institutions is portfolio diversification. By allocating assets across various international markets, institutions can reduce the impact of any single market's volatility. This approach involves a meticulous selection process, where each foreign market is chosen based on its historical performance, economic stability, and potential for growth. Diversification aims to create a balanced portfolio, minimizing the risk associated with any one investment while maximizing the potential for overall portfolio appreciation.
Institutions also utilize advanced risk assessment tools and models to identify and quantify potential risks. These tools analyze historical data, market trends, and geopolitical factors to provide insights into the likelihood and potential impact of various risks. For instance, a comprehensive risk assessment might consider currency fluctuations, political instability, and economic sanctions, helping institutions make informed decisions about their investment strategies.
Another critical aspect of risk management is the implementation of strict investment policies and guidelines. Institutions often establish parameters for their foreign equity investments, including maximum allowable concentrations in specific countries or sectors. These policies ensure that the investment strategy remains aligned with the institution's risk tolerance and financial objectives. Regular reviews and updates to these policies are essential to adapt to changing market conditions and global events.
Additionally, institutions may employ hedging techniques to protect their investments. Hedging involves using financial instruments like derivatives to offset potential losses. For instance, institutions can use currency swaps to manage currency risk or options contracts to protect against sudden market downturns. These hedging strategies provide a safety net, allowing institutions to maintain their investment positions while minimizing the impact of adverse events.
In summary, managing the risks associated with international stock markets is a multifaceted process. Institutions employ a combination of diversification, advanced risk assessment, strict investment policies, and hedging techniques to navigate the complexities of foreign equity investments. By implementing these strategies, universities and other institutions can make informed decisions, ensuring that their foreign equity investments contribute to their financial goals while mitigating potential pitfalls.
Foreign Investments: Counting Financial Flows and Their Impact
You may want to see also

Diversification: Spreading investments across various countries and sectors to reduce volatility and enhance returns
Diversification is a fundamental strategy for managing investment risk and optimizing returns, especially when it comes to investing in foreign equities. It involves spreading your investments across a wide range of countries, industries, and asset classes to ensure that your portfolio is not overly exposed to any single market or sector. This approach is particularly crucial for universities and other institutional investors with large foreign equity holdings, as it can help mitigate the impact of geopolitical risks and economic fluctuations.
The primary goal of diversification is to reduce the volatility of your investment portfolio. By allocating capital to multiple countries and sectors, you can lower the potential impact of negative events in any one region or industry. For instance, if a particular country's economy experiences a downturn, the overall effect on your portfolio will be less severe due to the presence of investments in other markets. This strategy is especially important for universities, as they often have substantial financial resources that need to be protected and grown over the long term.
When it comes to foreign equity investments, diversification can be achieved through various means. One common method is to invest in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds that track specific regions or sectors. These funds provide instant diversification, as they hold a basket of securities from multiple countries or industries. For example, a university might invest in an ETF that focuses on emerging market equities, which would expose them to a diverse range of companies across various countries. This approach allows for a more efficient allocation of resources and provides access to markets that individual stocks might not offer.
Another strategy is to directly invest in individual foreign companies across different sectors and countries. This requires a more in-depth analysis and research, as it involves understanding the specific market dynamics and risks associated with each investment. By carefully selecting companies with strong fundamentals and growth potential, universities can build a diversified portfolio that benefits from the global economic expansion. However, this approach demands a higher level of expertise and resources to monitor and manage the investments effectively.
In addition to geographic and sectoral diversification, universities should also consider investing in different asset classes. This could include a mix of large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks, as well as investments in bonds and other fixed-income securities. By diversifying across asset classes, universities can further reduce risk and potentially capture a broader range of market opportunities. This comprehensive approach to diversification ensures that the investment strategy is robust and adaptable to changing market conditions.
Quicken for Investment Tracking: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Market Analysis: Universities study global economic trends, political stability, and industry performance to make informed investment decisions
Universities, as large institutional investors, play a significant role in the global financial markets, particularly when it comes to foreign equity investments. Their investment decisions are not made arbitrarily but are backed by extensive market analysis and research. This analysis is crucial as it helps universities navigate the complexities of the international financial landscape, which is often characterized by diverse economic conditions, varying political climates, and industry-specific performance metrics.
The primary focus of this market analysis is to identify and assess the risks and opportunities associated with different countries and sectors. Economic trends are a key consideration, as they provide insights into the overall health and growth prospects of a region. For instance, a university might study historical GDP growth rates, inflation trends, and economic policies to predict future economic performance. This analysis is vital for making informed decisions about where to allocate capital, especially in foreign markets.
Political stability is another critical factor in this analysis. Political risks can significantly impact the performance of foreign investments. A university's investment team would examine political landscapes, including governance structures, regulatory frameworks, and historical data on political events and their economic consequences. Understanding the political environment helps in assessing the potential for policy changes that could affect the value of investments.
Industry performance is also a key aspect of market analysis for universities. They would study industry-specific trends, competitive landscapes, and growth prospects. This includes analyzing revenue growth, market share, and the impact of technological advancements on various sectors. For example, a university might focus on the technology sector, studying the performance of tech startups in different countries, their funding sources, and the regulatory environment surrounding tech innovation.
Additionally, universities often employ sophisticated data analytics and modeling techniques to support their investment decisions. They may use econometric models to predict economic outcomes, risk assessment models to evaluate political and industry-specific risks, and portfolio optimization tools to allocate assets across different markets and sectors. This comprehensive approach ensures that their investment strategies are well-informed and aligned with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
In summary, the market analysis process for universities investing in foreign equities is a meticulous and data-driven approach. It involves a deep understanding of global economic trends, political stability, and industry performance, all of which are essential for making strategic investment choices. This analysis is a critical component of their investment strategy, helping them navigate the complexities of the international financial markets and achieve their long-term financial objectives.
Morris Invest: The Cash-Only Strategy Explained
You may want to see also

Ethical Considerations: Ethical investing practices, including environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, are considered in foreign equity portfolios
The concept of ethical investing has gained significant traction in recent years, and universities are increasingly incorporating these principles into their investment strategies, especially when it comes to foreign equity portfolios. This approach involves considering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors as integral components of the investment decision-making process. By integrating ESG criteria, universities can ensure that their foreign equity investments align with their values and contribute to positive global change.
Environmental factors play a crucial role in ethical investing. When investing in foreign equities, universities should assess the environmental impact of the companies they are considering. This includes evaluating the companies' carbon footprint, resource consumption, and adherence to sustainable practices. For instance, investing in renewable energy companies or those committed to reducing pollution can contribute to a greener economy. By promoting and supporting environmentally responsible businesses, universities can influence global practices and encourage sustainable development.
Social considerations are another essential aspect of ethical investing. Universities should examine the social implications of their investments, focusing on labor practices, human rights, and community engagement. This involves assessing companies' treatment of employees, including fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for workers' rights. Additionally, universities might prioritize investments in companies that actively promote diversity, equity, and inclusion, ensuring that their financial support contributes to a more equitable society.
Governance factors are also integral to ethical investing practices. Effective corporate governance is essential for responsible business conduct. Universities should evaluate the quality of corporate governance in foreign companies, including board structure, executive compensation, and transparency in financial reporting. By investing in companies with strong governance practices, universities can support transparent and accountable business operations, reducing the risk of corruption and unethical behavior.
Incorporating ESG factors into foreign equity portfolios allows universities to make informed investment decisions that align with their ethical values. This approach enables them to influence global markets positively while also managing risks associated with environmental degradation, social injustice, and poor governance. By integrating these considerations, universities can contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future, ensuring that their investment practices are not only financially sound but also socially responsible.
Tips for Investing: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Universities often invest in foreign equities as part of their endowments to diversify their asset portfolios and potentially gain higher returns. By allocating a portion of their funds to international markets, they aim to reduce risk and increase the overall growth of their investments.
Investment decisions are typically made by a university's investment committee or a dedicated financial team. They conduct thorough research and analysis, considering factors such as market trends, economic indicators, political stability, and the potential for long-term growth in the respective countries. The committee may also seek advice from external financial advisors.
Yes, universities must adhere to various regulations and guidelines set by financial authorities and governing bodies. These rules often include restrictions on the types of investments, reporting requirements, and guidelines for risk management. For instance, some countries may have restrictions on foreign ownership or specific tax regulations that universities need to navigate.
Investing in foreign equities carries several risks, including political instability, currency fluctuations, and varying regulatory environments. Universities must carefully assess these risks and implement appropriate strategies to mitigate them. This may involve diversifying across multiple countries, regularly reviewing investments, and having contingency plans in place to protect the university's financial interests.