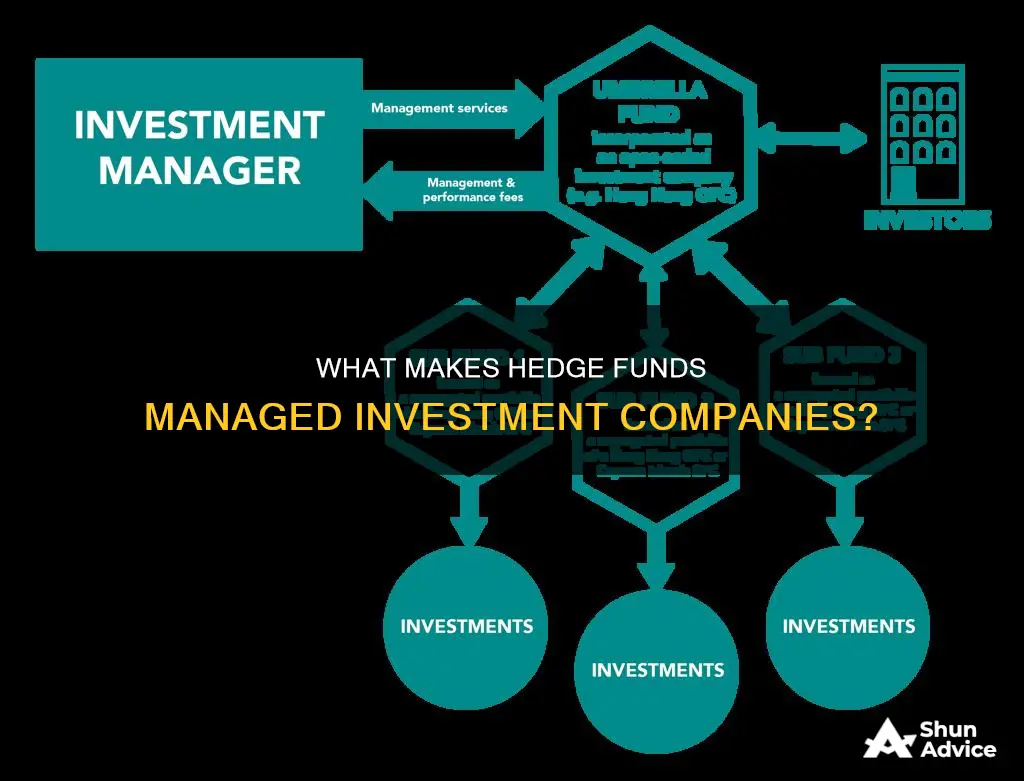
Hedge funds are alternative investment funds that pool money from investors and invest it with the aim of making a profit. They are typically managed by institutional investors who use a wide range of non-traditional investment strategies, with the primary goal of mitigating risk.
Hedge funds are considered riskier than mutual funds, as they take outsized risks in order to achieve outsized gains. They are also less regulated by the government and have much higher minimum investment requirements.
Hedge funds are not subject to the many restrictions that apply to regulated funds, and they can invest in options and derivatives, as well as esoteric investments that mutual funds cannot invest in.
Hedge funds are often structured as limited partnerships, with fund managers taking a standard 2 and 20 fee system, referring to a 2% management fee and a 20% performance fee.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A pool of money that is invested in stocks and other assets |
| Investor type | Wealthy individuals and institutions such as pension funds |
| Investment type | Alternative investments, including derivatives, debt and equity securities, commodities, currencies, real estate |
| Risk | High |
| Returns | Above-average |
| Regulation | Light touch |
| Fees | High |
What You'll Learn
- Hedge funds are lightly regulated and limited to accredited investors, meaning high minimum investments
- Hedge funds use a wider variety of strategies, including short-selling, derivatives, alternative assets, and betting on events like mergers and spin-offs
- Hedge funds charge both management fees and performance fees
- Hedge funds are open-end funds, meaning investors can contribute to or withdraw money from the fund at any time
- Hedge funds are considered alternative investments

Hedge funds are lightly regulated and limited to accredited investors, meaning high minimum investments
Hedge funds are not subject to the many restrictions that apply to regulated funds. They are also distinct from private equity funds and other similar closed-end funds as they generally invest in relatively liquid assets and are usually open-ended. This means they typically allow investors to invest and withdraw capital periodically based on the fund's net asset value.
Hedge funds are considered riskier than other investment options. They use leverage and more complex investment techniques, such as short selling and the use of derivative instruments. Due to the higher risk, hedge funds require investors to have a minimum level of income or assets. Typical investors are institutional investors, such as pension funds and insurance companies, and wealthy individuals. Minimum investments of $100,000 are common, and some funds require $1 million or more.
Hedge funds are also distinct from mutual funds, which are practical, cost-efficient ways to build a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or short-term investments. Mutual funds are available to the general public and the average investor. Hedge funds, on the other hand, normally only accept money from accredited investors who have a certain level of income or net worth.
Hedge funds are loosely regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). They are required to register with the SEC if they have more than $150 million in private funds and manage one or more funds. Funds with assets under management of $500 million or more must file quarterly and report the details of their liabilities and assets.
Strategic Timing for Long-Term Bond Fund Investments
You may want to see also

Hedge funds use a wider variety of strategies, including short-selling, derivatives, alternative assets, and betting on events like mergers and spin-offs
Hedge funds are considered alternative investments and are known for their ability to use leverage and more complex investment techniques. They are also considered distinct from private equity funds and other similar closed-end funds as hedge funds generally invest in relatively liquid assets and are usually open-ended.
Hedge funds use a wide range of strategies, including short-selling, derivatives, alternative assets, and betting on events like mergers and spin-offs.
Short-Selling
Short-selling is a common strategy used by hedge funds, which involves selling borrowed stock with the expectation that the price will fall. Hedge funds will then buy back the stock at a lower price, pocketing the difference as profit. This strategy allows hedge funds to profit from declining stock prices and can provide a hedge against potential losses in long positions.
Derivatives
Hedge funds also make extensive use of derivatives, which are financial contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies. Derivatives can be used to hedge risk, enhance returns, or speculate on future price movements. Examples of derivatives include options, futures, forwards, and swaps.
Alternative Assets
Hedge funds are known for investing in alternative assets, which may include real estate, commodities, private equity, and distressed debt, among others. These types of investments can provide diversification benefits and the potential for higher returns compared to traditional assets.
Betting on Events
Hedge funds often engage in event-driven investing, which involves betting on specific corporate events such as mergers, acquisitions, restructurings, or bankruptcies. For example, a hedge fund may invest in a company that is the target of a potential acquisition, anticipating a boost in the stock price upon the completion of the deal.
Strategies and Risk Management
Hedge funds employ various strategies, including equity-related, event-driven, relative value, opportunistic, and specialist strategies. These strategies involve different levels of risk and potential returns, and hedge fund managers must carefully evaluate and manage these risks.
Overall, hedge funds utilise a diverse range of strategies and investment techniques to generate returns for their investors. While these strategies offer the potential for significant profits, they also come with a higher level of risk compared to more traditional investment approaches.
Starting a Real Estate Fund: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

Hedge funds charge both management fees and performance fees
Hedge funds are considered alternative investments and are actively managed funds that focus on alternative investments that commonly use risky investment strategies. They are not subject to the many restrictions applicable to regulated funds.
The management fee covers the fund's operational expenses, such as salaries, office space, technology, and compliance costs. The fee usually ranges from 1% to 2% of assets under management (AUM), with larger funds often charging lower fees due to economies of scale.
The performance fee, also known as an incentive fee, is a percentage of the fund's profits that is paid to the fund manager. This fee rewards the manager for generating positive returns. Performance fees typically range from 15% to 20% of the fund's profits and are often subject to a high-water mark, meaning the manager only receives the fee if the fund's value exceeds its previous highest level.
The fee structure of hedge funds has come under scrutiny in recent years due to underperformance and high fees. There has been a trend towards lower management and performance fees, with some funds introducing tiered fee structures that lower fees as the fund's AUM grows.
The "2 and 20" fee structure, referring to the 2% management fee and 20% performance fee, has made many hedge fund managers extremely wealthy. However, critics argue that the structure, where managers share in the fund's profits but not in their losses, incentivises fund managers to take greater risks.
Medallion Hedge Fund: A Guide to Investing Wisely
You may want to see also

Hedge funds are open-end funds, meaning investors can contribute to or withdraw money from the fund at any time
The open-ended nature of hedge funds means that they typically allow investors to invest and withdraw capital periodically based on the fund's net asset value. However, it is important to note that hedge funds often have lock-up periods, during which investors cannot withdraw their money. Additionally, withdrawals may only happen at certain intervals, such as quarterly or biannually.
The open-ended structure of hedge funds also means that they do not have to close, allowing investors to contribute or withdraw money at any point in time. This is in contrast to closed-end funds, where the fund will be locked, and capital is tied up for long-term investments.
The open-ended nature of hedge funds is one of the key differences between hedge funds and private equity (PE) funds. Hedge funds invest mostly in public market investments, while PE funds invest in the private markets. Hedge funds also tend to use more uncommon trading techniques, such as derivatives or short selling.
Overall, the open-ended structure of hedge funds provides investors with greater flexibility in terms of contributing and withdrawing capital. However, it is important to consider the specific terms and conditions of each hedge fund, as there may be restrictions on contributions and withdrawals.
Invest in HDFC Property Fund: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Hedge funds are considered alternative investments
Hedge funds are known for their active management approach, where professional fund managers employ a wide range of investment strategies to achieve above-average returns. These strategies may include investing in non-traditional assets, such as derivatives, alternative investments, and real estate. The fund managers' expertise plays a crucial role in the fund's success.
One of the distinctive features of hedge funds is their focus on absolute returns. This means that they aim to generate positive returns regardless of the market conditions. To achieve this, hedge funds utilise various financial instruments and market strategies to limit their exposure to risk, hence the name "hedge" funds. By diversifying their investments and employing hedging techniques, hedge funds aim to reduce the impact of market fluctuations on their portfolio.
Compared to mutual funds, hedge funds have fewer regulatory restrictions and are open only to institutional investors or high-net-worth individuals. They also charge higher fees, typically including a management fee and a performance fee. The management fee covers the fund's operational costs and is usually calculated as a percentage of the fund's net asset value. The performance fee, on the other hand, is intended to incentivise fund managers to generate higher returns and is typically a percentage of the profits made by the fund.
In summary, hedge funds are considered alternative investments due to their unique structure, aggressive investment strategies, focus on absolute returns, and higher fees. They offer the potential for higher returns but also carry a higher level of risk.
Mutual Fund Investing: Cutting Out the Middleman
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A hedge fund is a pool of money from investors that is managed by professional fund managers. Hedge funds are considered alternative investments and are often riskier than other managed funds. They are loosely regulated and employ a wide range of strategies, including the use of leverage and the trading of non-traditional assets, to earn above-average investment returns.
Hedge funds can invest capital anywhere in the market and through a variety of strategies. They are typically managed by institutional investors who use non-traditional investment strategies to mitigate risk and generate returns. Hedge funds often aim for positive or less volatile returns, regardless of market conditions.
Hedge funds make money by charging management fees and performance fees. The management fee is typically around 2% of assets under management, while the performance fee is around 20% of the profits from investing.
Hedge funds and mutual funds differ in terms of investor base, investment strategies, and fee structure. Hedge funds are restricted to institutional investors and limited partners, while mutual funds can raise capital from anyone in the general public. Hedge funds invest in a wider range of assets and employ riskier strategies compared to mutual funds. Additionally, hedge funds charge both management and performance fees, while mutual funds typically only charge management fees.







