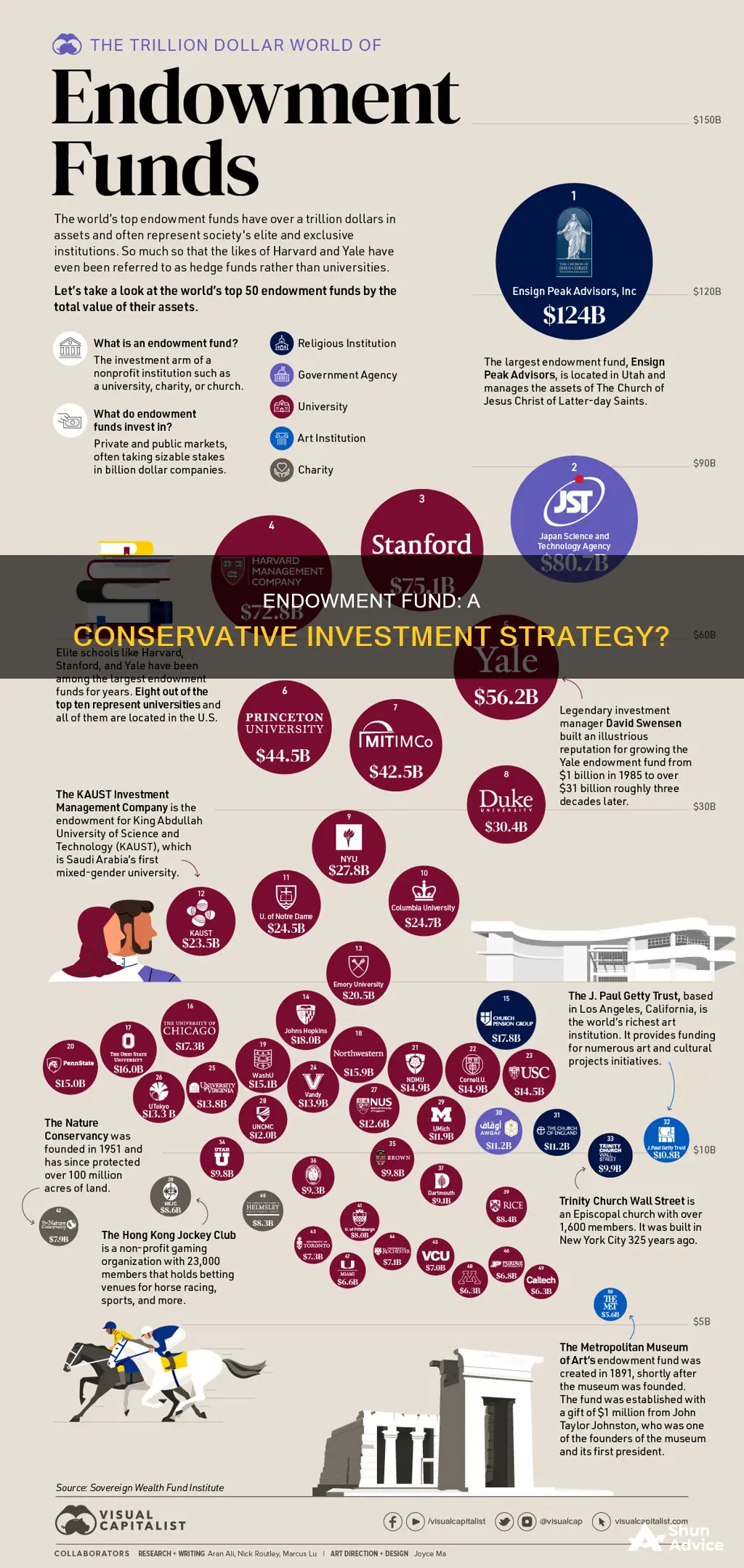
Endowment funds are a type of investment portfolio that is funded by donations. They are typically used to fund charitable and nonprofit institutions such as churches, hospitals, universities, and cultural facilities. The funds are usually set up as trusts, which are independent of the organisations they support. The principal value of the fund is kept intact, while the investment income is used to fund the operations of the beneficiary organisation. This means that endowment funds can be held permanently, allowing donors to support causes they care about indefinitely. Endowment funds are subject to various rules and policies, including investment policies, withdrawal policies, and usage policies, which are designed to ensure the fund's longevity and that the money is spent in line with the donor's intentions.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To generate revenue for charitable activities |
| Beneficiaries | Nonprofit organizations |
| Principal value | Intact |
| Investment earnings | Distributable dollars |
| Permanence | Can be held permanently |
| Donations | Tax-deductible |
| Donors | Institutions and individuals |
| Donations | Cash and non-cash assets |
| Investment strategies | Increase the fund's impact and create sustainable growth |
| Endowment fund policies | Investment policy, withdrawal policy, usage policy |
| Endowment fund types | Restricted, term, quasi, unrestricted |
What You'll Learn
- Endowment funds are established to fund charitable and nonprofit institutions such as churches, hospitals and universities
- Endowment funds are governed by investment, withdrawal and usage policies
- Endowment funds are typically structured with intact principals and investment income available for use
- Endowment funds are initially invested by donors for certain charitable purposes
- Endowment funds are not exclusive to educational institutions

Endowment funds are established to fund charitable and nonprofit institutions such as churches, hospitals and universities
Endowment funds are a way to generate long-term financial support for charitable and nonprofit institutions such as churches, hospitals, universities, and other organisations. They are established with donations, which are then invested to generate revenue for these institutions. The principal value of the fund is kept intact, while the earnings are used for charitable grants.
Endowment funds are typically structured as trusts, which keep them independent of the organisations they support. They consist of cash, equities, bonds, and other types of securities that can generate investment income. The beneficiary of an endowment fund is always a non-profit organisation, and donations to these funds are tax-deductible.
Endowment funds are governed by three main policies: an investment policy, a withdrawal policy, and a usage policy. The investment policy outlines the types of investments that can be made and the level of risk that can be taken. The withdrawal policy establishes the amount that can be taken out of the fund at each period or instalment, and the usage policy defines the fund's purpose.
There are four main types of endowment funds: restricted, unrestricted, quasi, and term. Restricted endowment funds are the most common and have specific guidelines on how the fund's distributions can be used. Unrestricted endowment funds have no limitations on how the money is used, and quasi-endowment funds (also known as board-designated funds) are used like endowments but without the legal definition of one. Term endowment funds are established for a specific period or until a certain event occurs.
Invest in Amazon: A Guide to Using Mutual Funds
You may want to see also

Endowment funds are governed by investment, withdrawal and usage policies
The investment policy outlines the types of investments that can be made and the level of risk that can be taken. Endowment funds typically have a lower risk level than other investment funds. The withdrawal policy sets out the amount that can be taken from the fund at each period or instalment, usually with an annual withdrawal limit. The usage policy defines the purpose of the fund and ensures that grants are used effectively and properly.
In addition to these three main policies, endowment funds may also have rules around how the money can be used and how much can be withdrawn at one time. These rules are set by the organisation's leadership and aim to ensure the fund's longevity. For example, a fund might limit withdrawals to 5% of the total amount annually.
Endowment funds are an important tool for nonprofits to achieve financial stability and support their long-term initiatives. However, they also come with certain drawbacks, such as restricted fund use and investment risks. It is important for organisations to carefully manage their endowment funds to ensure they are used effectively and in alignment with their objectives.
Best Index Funds to Invest in: A NerdWallet Guide
You may want to see also

Endowment funds are typically structured with intact principals and investment income available for use
Endowment funds are established to fund charitable and nonprofit institutions such as churches, hospitals, universities, and community initiatives. The funds are generated from donations, which are tax-deductible. The principal amount of the endowment fund is derived from these donations and is not typically available for daily use by the organizations. Instead, the principal is invested to generate income, which can then be used to further the organization's charitable activities and initiatives.
The major difference between an endowment fund and a typical investment fund is the beneficiary. While a typical investment fund benefits individual investors, an endowment fund benefits a non-profit organization. Endowment funds are usually established as trusts, keeping them independent of the organizations they support. This structure allows for the preservation of the principal amount while generating income for the organization's use.
Endowment funds are subject to various policies that govern their management and usage. These include investment policies, which outline allowable investments and manager restrictions to meet return targets. Withdrawal policies establish the amount that can be withdrawn from the fund at regular intervals or as needed by the organization. Finally, usage policies define the purpose of the fund and ensure that grants are aligned with this purpose.
Overall, the structure of endowment funds, with their intact principals and investment income, provides a sustainable source of funding for charitable organizations, enabling them to carry out their missions and initiatives over the long term.
Researching Investment Funds: A Guide to Getting Started
You may want to see also

Endowment funds are initially invested by donors for certain charitable purposes
Endowment funds are usually established as trusts, which keep them independent of the organizations that they support. They consist of cash, equities, bonds, and other types of securities that can generate investment income. The major difference between an endowment fund and a typical investment fund is that the beneficiary of an endowment fund is a non-profit organization instead of individual investors.
Endowment funds are often subject to three types of policies: investment, withdrawal, and usage policies. Investment policies outline the types of investments that the fund manager is allowed to make and the associated risk level. Withdrawal policies limit the amount of money that can be withdrawn from the fund within each period, usually capped at a certain percentage of the total amount. Usage policies determine the purposes for which the fund can be used, such as scholarships, scientific research, public services, and other charitable activities.
There are several types of endowment funds, including restricted, unrestricted, quasi, and term endowments. Restricted endowments have specific guidelines on how the fund's distributions can be used. Unrestricted endowments, on the other hand, do not limit the purpose of usage, allowing the recipient to spend the money as needed. Quasi-endowments, also known as "board-designated funds," function like endowments but offer more flexibility in funding decisions. Term endowments are established for a specific period or until a certain event occurs, providing temporary financial support.
Invest in Mutual Funds: Quick and Easy Ways
You may want to see also

Endowment funds are not exclusive to educational institutions
While endowment funds are often associated with educational institutions, they are not exclusive to this sector. Endowment funds are also used by a variety of other organisations, including:
- Churches
- Hospitals
- Nonprofit charities
- Community foundations
Endowment funds are established to fund charitable and nonprofit institutions, and donations to these funds are tax-deductible. The funds are typically structured with intact principals, and the investment income is available for use. The principal value of an endowment fund is usually kept intact, while the investment earnings can be used for charitable grants or other specific purposes.
Nonprofit organisations such as charities, hospitals, and community foundations establish endowment funds to secure sustained financial support for their activities. Donors contribute to these funds to support specific causes or the organisation's overall mission. Nonprofit endowments may focus on various areas, including community development, the environment, education, or social services.
Endowment funds can be categorised into different types, including restricted, term, unrestricted, and quasi-endowments, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes. These funds are governed by policies that outline investment strategies, withdrawal limitations, and usage guidelines.
Overall, while endowment funds are commonly linked to educational institutions, they are utilised by a diverse range of organisations to support their charitable and nonprofit endeavours.
Mutual Funds Philippines: Best Time to Invest
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
An endowment fund is a pool of assets established by a nonprofit, such as a charity, church, hospital, service group, educational institution or cultural facility. It's a way for monetary donations to develop into long-term financial support for mission-related activities.
Organisations use endowment funds to pool financial resources from donations and invest them. The donations typically form the principal investment balance, with the nonprofit then using a small portion of that to pay for its initiatives.
Endowment funds can provide long-term financial support and stability for nonprofits, and may attract supporters by demonstrating a commitment to financial sustainability. However, they can also be restrictive in terms of fund usage and are subject to market fluctuations and inflation risk.