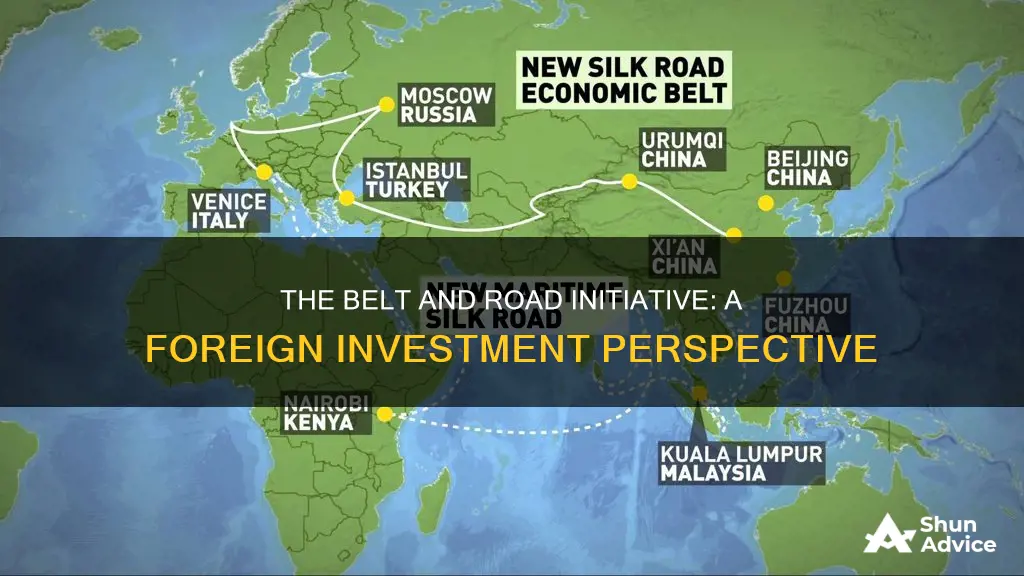
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a massive global infrastructure development and investment program, has sparked debates about its nature and impact. One key question that arises is whether the BRI can be considered a form of foreign direct investment (FDI). This paragraph aims to explore this intriguing topic, examining the characteristics of the BRI and its potential classification as FDI. By analyzing the initiative's structure, funding mechanisms, and investment patterns, we can gain insights into how the BRI might fit into the broader category of FDI and its implications for international trade and economic cooperation.
What You'll Learn
- Economic Impact: The initiative's influence on global trade and economic growth
- Infrastructure Development: How it funds and builds transportation and energy networks
- Political Relations: The role of the initiative in fostering diplomatic ties
- Environmental Considerations: Potential environmental consequences and sustainability practices
- Debt Sustainability: Risks and strategies to manage debt from BRI projects

Economic Impact: The initiative's influence on global trade and economic growth
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has been a significant driver of global economic activity, particularly in the context of foreign direct investment (FDI). The initiative, proposed by China in 2013, aims to enhance connectivity and cooperation across Eurasia, Africa, and beyond through a network of land-based and maritime trade routes. This massive infrastructure development project has the potential to reshape global trade patterns and stimulate economic growth in participating countries.
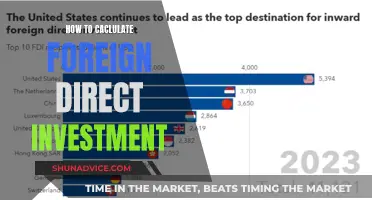
One of the primary economic impacts of the BRI is the facilitation of increased FDI flows. By improving transportation and communication infrastructure, the initiative reduces the cost of doing business and enhances market access for businesses and investors. This improved connectivity enables foreign investors to tap into new markets, especially in developing countries along the BRI corridors. As a result, FDI has been directed towards various sectors, including energy, transportation, telecommunications, and manufacturing, fostering economic diversification and industrialization in these regions.
The initiative's focus on infrastructure development has led to a surge in investment in transportation networks, energy projects, and industrial zones. For instance, China has invested heavily in port infrastructure in countries like Sri Lanka, Pakistan, and Greece, creating new trade hubs and improving maritime connectivity. These investments not only create jobs and boost local economies but also attract further FDI, creating a positive feedback loop. The development of industrial parks and special economic zones along the BRI routes further encourages foreign companies to set up regional headquarters, regional distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities, thereby increasing the overall FDI inflow.
Moreover, the BRI has fostered economic growth by promoting intra-regional trade and regional value chains. By connecting markets and reducing trade barriers, the initiative facilitates the movement of goods and services, encouraging the development of regional supply chains. This integration of markets has led to increased trade volumes and improved terms of trade for many participating countries. As a result, local businesses and industries have expanded their operations, and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have gained access to larger markets, fostering economic diversification and reducing reliance on traditional export markets.
In conclusion, the Belt and Road Initiative has had a profound economic impact by significantly influencing global trade and economic growth. Through its infrastructure development and connectivity enhancements, the BRI has attracted substantial FDI, particularly in infrastructure, energy, and manufacturing sectors. The initiative's focus on regional integration has also led to increased intra-regional trade and the development of regional value chains, further stimulating economic activity. As the BRI continues to evolve, its potential to shape global economic landscapes and foster international cooperation remains a key area of interest for economists and policymakers alike.
Corporate Cash Investment Strategies: Maximizing Returns, Minimizing Risk
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: How it funds and builds transportation and energy networks
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a massive global infrastructure development project proposed by the Chinese government, aiming to enhance connectivity and cooperation across Eurasia. While the BRI primarily focuses on transportation and energy infrastructure, it also has significant implications for foreign direct investment (FDI). The initiative's scale and scope have sparked debates about its nature as a form of FDI.
Infrastructure development is a critical aspect of the BRI, aiming to improve transportation and energy networks across participating countries. These projects often involve substantial investments in roads, railways, ports, and power generation facilities. The funding for these initiatives can come from various sources, including government budgets, international financial institutions, and private investors. One of the key strategies is to attract foreign investment, which can take the form of FDI.
Foreign direct investment in infrastructure projects under the BRI can take several forms. Firstly, Chinese companies may invest directly in foreign infrastructure projects, either independently or in partnership with local firms. This direct investment can involve the transfer of capital, technology, and expertise to the host country. Secondly, the Chinese government and state-owned enterprises (SOEs) can provide loans and grants to support infrastructure development, often through specialized financial institutions like the China Export-Import Bank. These financial mechanisms enable the construction and operation of large-scale projects.
Additionally, the BRI encourages public-private partnerships (PPPs), where private companies collaborate with governments to develop and manage infrastructure assets. This approach leverages the strengths of both sectors, with private companies bringing expertise in project management and financing, while governments provide regulatory support and long-term stability. PPPs have been instrumental in funding and executing transportation and energy projects, ensuring efficient resource allocation and risk mitigation.
In summary, the Belt and Road Initiative's infrastructure development component plays a crucial role in attracting foreign direct investment. Through direct investments, financial support, and public-private partnerships, the BRI facilitates the construction of transportation and energy networks across Eurasia. This approach not only enhances connectivity but also contributes to the economic growth and development of participating countries. Understanding the funding mechanisms and investment strategies employed by the BRI is essential for assessing its impact and potential benefits.
Unlocking Global Opportunities: A Guide to Foreign Investment Registration
You may want to see also

Political Relations: The role of the initiative in fostering diplomatic ties
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has significantly impacted global political relations, serving as a powerful tool to strengthen diplomatic ties between participating countries. This initiative, proposed by China in 2013, aims to enhance connectivity and cooperation across Eurasia, Africa, and beyond. By focusing on infrastructure development, the BRI has created a platform for nations to engage in mutually beneficial partnerships, fostering a sense of camaraderie and shared progress.
One of the key aspects of the BRI's influence on political relations is the promotion of economic interdependence. As countries invest in and develop infrastructure projects together, they become increasingly reliant on each other's resources, expertise, and markets. This interdependence often translates into stronger diplomatic ties, as nations are more inclined to support each other's interests and resolve conflicts through dialogue and cooperation. For example, the BRI has facilitated increased trade between China and Central Asian countries, leading to improved diplomatic relations and joint efforts to address regional challenges.
Furthermore, the initiative has encouraged the exchange of cultural and educational programs, which play a vital role in building trust and understanding between nations. Cultural exchanges, language training, and educational collaborations fostered through the BRI contribute to a more profound appreciation of each other's cultures and histories, breaking down barriers and fostering goodwill. This cultural diplomacy aspect of the initiative is essential in developing long-lasting political relationships.
The BRI also provides a framework for resolving disputes and promoting peace. By engaging in joint infrastructure projects, countries learn to navigate challenges and disagreements in a constructive manner. This collaborative approach to problem-solving encourages nations to seek diplomatic solutions rather than resorting to confrontation. As a result, the initiative has the potential to reduce tensions and create a more stable international environment, especially in regions where political relations have been strained.
In summary, the Belt and Road Initiative's impact on political relations is profound and multifaceted. It encourages economic interdependence, cultural exchange, and peaceful dispute resolution, all of which contribute to stronger diplomatic ties. As the initiative continues to gain momentum, its role in fostering international cooperation and understanding will likely become even more significant, shaping the future of global political interactions.
Bloomberg Terminals: Investment Bankers' Best Friend
You may want to see also

Environmental Considerations: Potential environmental consequences and sustainability practices
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a massive global infrastructure development program, has sparked both enthusiasm and concern regarding its environmental implications. As the initiative expands across continents, it is crucial to examine the potential environmental consequences and the role of sustainability practices in mitigating these impacts.
One of the primary environmental considerations is the impact on ecosystems and biodiversity. The BRI involves extensive construction activities, including the development of roads, railways, and energy infrastructure. These projects can lead to habitat destruction, fragmentation, and the displacement of wildlife. For example, the construction of new highways might disrupt migratory patterns of birds and mammals, while the establishment of hydropower plants could affect aquatic ecosystems. To address these concerns, environmental impact assessments should be conducted before project initiation, identifying and mitigating potential risks to biodiversity. Implementing strict environmental regulations and standards for construction and operation can help minimize ecological damage.
Water resources are another critical aspect of environmental sustainability. The BRI's infrastructure projects, such as dams and water diversion schemes, can significantly alter natural water flows and impact aquatic ecosystems. These changes may lead to water scarcity, affecting local communities and agriculture. Sustainable water management practices are essential to ensure the long-term availability of water resources. This includes implementing efficient irrigation systems, promoting water recycling and reuse, and adopting water-saving technologies in construction processes.
Furthermore, the BRI's focus on energy infrastructure development raises concerns about air and water pollution. The construction and operation of power plants, particularly those using fossil fuels, can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and local air pollution. To mitigate these effects, the initiative should prioritize the adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, and encourage the implementation of stringent emission control measures. Additionally, proper waste management systems should be in place to prevent soil and water contamination.
Sustainability practices also involve the use of environmentally friendly materials and construction methods. The BRI can promote the adoption of green building standards, which emphasize energy efficiency, water conservation, and the use of sustainable materials. This approach can reduce the environmental footprint of infrastructure projects and set a positive example for future developments.
In summary, the environmental considerations of the Belt and Road Initiative are multifaceted, requiring careful planning and implementation of sustainable practices. By addressing biodiversity, water resource management, pollution control, and the adoption of green technologies, the initiative can strive to minimize its ecological impact and contribute to global sustainability goals. It is essential for all stakeholders involved to prioritize environmental responsibility to ensure the long-term success and sustainability of the BRI.
Foreign Investment's Impact on the Monetary Base: A Comprehensive Analysis
You may want to see also

Debt Sustainability: Risks and strategies to manage debt from BRI projects
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a massive global infrastructure development and investment program, and its potential impact on debt sustainability is a critical aspect that requires careful consideration. As the BRI involves significant financial commitments from various countries, understanding the risks and implementing effective strategies to manage debt is essential to ensure long-term economic stability.
One of the primary risks associated with BRI projects is the potential for debt distress, especially in countries with limited financial resources. These projects often require substantial upfront investments, and if not managed properly, they can lead to a rapid accumulation of debt. The high costs of infrastructure development, combined with the potential for over-investment in certain sectors, can strain a country's ability to service its debt. For instance, countries may take on substantial loans for large-scale infrastructure projects, such as ports, railways, or power plants, which, if not utilized efficiently or maintained effectively, could result in long-term financial burdens.
To mitigate these risks, several strategies can be employed. Firstly, comprehensive debt management frameworks should be established. This includes regular debt monitoring and analysis, ensuring that borrowing is aligned with a country's economic growth prospects and capacity to repay. Countries should also focus on diversifying their funding sources, reducing reliance on a single lender or type of loan. By spreading debt across multiple creditors and loan types, the risk of a single default event causing widespread financial distress is minimized.
Another crucial strategy is to enhance transparency and accountability. This involves providing clear and accessible information about the terms and conditions of BRI-related loans, ensuring that borrowers and lenders are well-informed. Regular audits and independent assessments of project implementation and financial management can help identify potential issues early on. Additionally, fostering a culture of dialogue and cooperation between borrowers, lenders, and international financial institutions can facilitate the early resolution of debt-related challenges.
Furthermore, countries should prioritize sustainable development practices. This means ensuring that BRI projects are environmentally and socially sustainable, contributing to long-term economic growth and resilience. By integrating sustainable development goals into project planning and execution, countries can attract more favorable loan terms and reduce the risk of debt distress. This approach also ensures that the benefits of the projects are widely shared, reducing the likelihood of social unrest and political instability, which can further exacerbate debt management issues.
In conclusion, managing debt associated with BRI projects requires a proactive and comprehensive approach. By implementing robust debt management practices, promoting transparency, and embracing sustainable development, countries can mitigate the risks of debt distress. Effective strategies will ensure that the BRI's infrastructure development goals are achieved while maintaining economic stability and fostering a positive investment environment.
Mastering Foreign Currency Investment: A Guide to Global Financial Growth
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), also known as the One Belt One Road (OBOR) initiative, is a global infrastructure development strategy proposed by the Chinese government in 2013. It aims to enhance connectivity and cooperation between Eurasian countries through investments in transport, energy, and other infrastructure projects.
The BRI is often associated with FDI as it involves significant foreign investments in various sectors across participating countries. Chinese companies and state-owned enterprises (SOEs) are major investors, but the initiative also encourages foreign businesses to participate, fostering international trade and investment.
While the BRI primarily focuses on infrastructure development, it can be seen as a strategic investment and a form of FDI. Chinese companies invest in projects, often with a long-term perspective, which can lead to increased economic cooperation and integration among the countries involved.
The BRI offers numerous opportunities for FDI, including access to new markets, improved infrastructure, and potential cost savings. However, challenges include political and regulatory risks, language and cultural barriers, and concerns about debt sustainability for some recipient countries. Balancing these factors is crucial for successful FDI projects under the BRI framework.