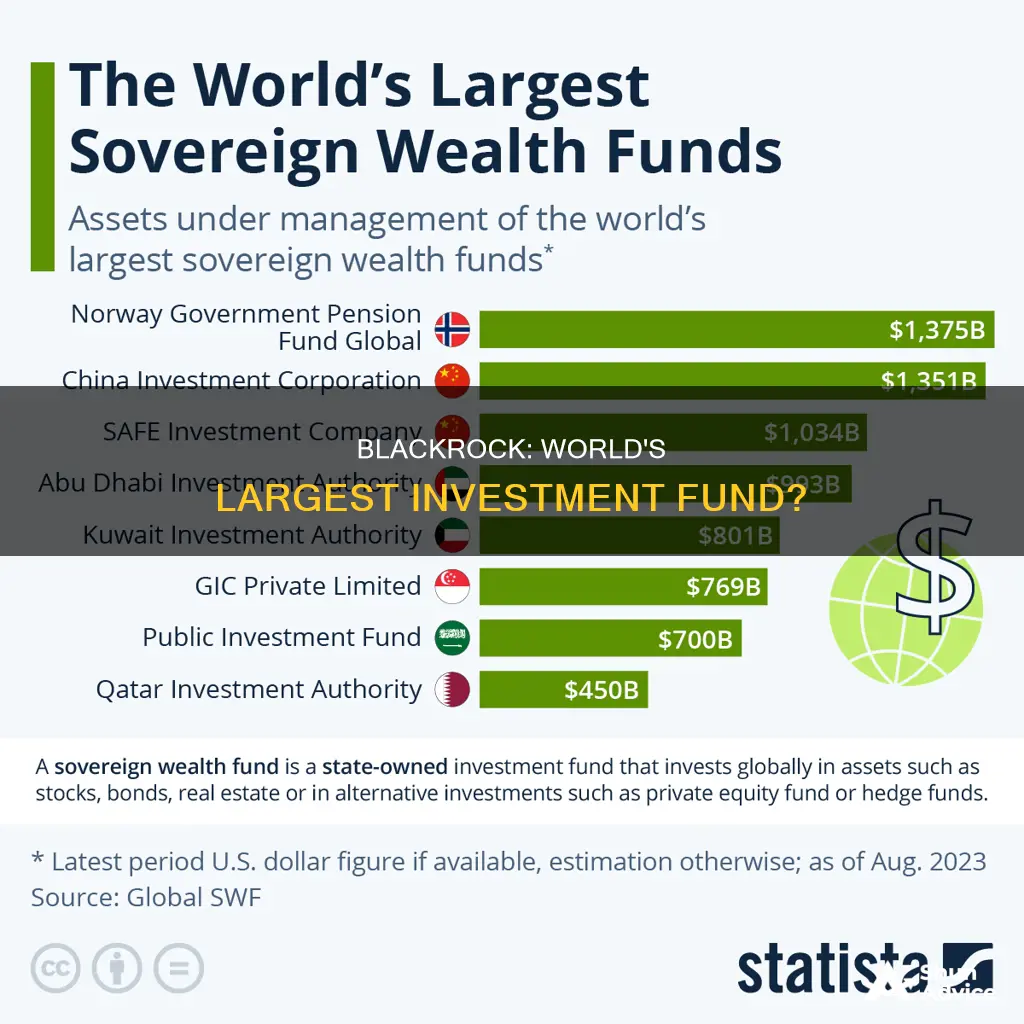
BlackRock, Inc. is an American multinational investment management company and the world's largest asset manager, with US$11.5 trillion in assets under management as of 31 December 2023. The company runs more than 120 mutual funds and an extensive array of exchange-traded funds through its iShares unit. As of June 2024, the largest global equity fund managed by BlackRock was the iShares Core S&P 500 ETF, with net assets under management of approximately 482.8 billion US dollars. BlackRock is also the manager of the second-largest equity mutual fund in the world, the iShares S&P 500 Index Fund - Class G, which held net assets under management of 12.6 billion US dollars as of February 2024.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Global Ranking | World's largest asset manager |
| Total Assets Under Management | $11.5 trillion as of 31 December 2023 |
| Number of Mutual Funds | Over 120 |
| Number of Exchange-Traded Funds | Extensive array |
| Number of Offices | 70 |
| Number of Countries with Offices | 30 |
| Number of Countries with Clients | 100 |
| Location of Headquarters | 50 Hudson Yards, Midtown Manhattan, New York City |
What You'll Learn

BlackRock's iShares Core S&P 500 ETF fund
BlackRock is the world's largest asset manager, with US$11.5 trillion in assets under management as of December 31, 2023. The company manages the iShares group of exchange-traded funds and is considered one of the Big Three index fund managers.
The iShares Core S&P 500 ETF fund is one of the investment options available through BlackRock. This fund seeks to track the investment results of an index composed of large-capitalization U.S. equities. In other words, it aims to mirror the performance of the 500 largest U.S. stocks by market capitalization, as measured by the S&P 500 Index.
This fund is designed to be a core holding in an investor's portfolio, offering exposure to the largest U.S. companies across diverse sectors. It has a low expense ratio of 0.03%, making it a relatively efficient investment choice. As of October 18, 2024, the fund's Net Asset Value (NAV) was $587.41, with a 1-day NAV change of 2.36 (0.40%).
The iShares Core S&P 500 ETF has received recognition, such as the Morningstar Medalist Rating, which awarded the fund a Gold medal for its strong performance and investment strategy. This fund can be traded on the market, providing investors with the flexibility to buy and sell as needed.
BlackRock's iShares Core S&P 500 ETF is a popular choice for investors seeking diversified exposure to large U.S. companies, with the convenience of an exchange-traded fund structure.
Plastic Factory Dreams: Funding Your Small Business Venture
You may want to see also

BlackRock's ESG policies
BlackRock, the world's largest asset manager, has faced criticism for its ESG policies, or lack thereof. The company has been scrutinised for its investments in fossil fuels, the arms industry, and companies that contribute to climate change and human rights violations in China. In response to this criticism, BlackRock has taken some steps to address its ESG practices.
In 2017, BlackRock expanded its environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) projects with new staff and products. They began to draw attention to environmental and diversity issues by sending letters to CEOs and participating in shareholder votes with activist investors or investor networks. In 2018, BlackRock asked Russell 1000 companies to improve gender diversity on their boards of directors if they had fewer than two women. Additionally, in May 2018, after discussions with firearms manufacturers and distributors, BlackRock introduced two new exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that exclude stocks of gun makers and large gun retailers.
However, BlackRock's commitment to ESG has been questioned. In August 2021, a former BlackRock executive who had served as the company's first global chief investment officer for sustainable investing stated that he believed the firm's ESG investing was a "dangerous placebo that harms the public interest." He argued that financial institutions are motivated to engage in ESG investing because of the higher fees associated with ESG products, which increase company profits.
In January 2022, BlackRock's founder and CEO, Larry Fink, defended the company's focus on ESG investing, pushing back against accusations that the company was supporting a "woke" or "politically correct" agenda. Fink stated that the practice of ESG "is not woke." Despite this defence, BlackRock has continued to face criticism from various groups, including US state governments and environmental organisations.
In July 2023, BlackRock announced that it would allow retail investors a proxy vote in its biggest ETF from 2024, in response to claims that the company was trying to push a 'woke agenda' through its pro-ESG activities. This move was seen as an attempt to counter the criticism and provide investors with a say in the company's ESG practices.
Withdraw Funds from American Century Investments: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

BlackRock's ties with the Federal Reserve
BlackRock has been criticised for its close ties with the Federal Reserve during the COVID-19 pandemic. In 2020, the Federal Reserve chose BlackRock to manage two corporate bond-buying programs in response to the pandemic. This included the $500 billion Primary Market Corporate Credit Facility and the Secondary Market Corporate Credit Facility. The Federal Reserve also allowed BlackRock to superintend the $130 billion debt settlement of Bear Stearns and American International Group.
BlackRock's Aladdin software keeps track of investment portfolios for many major financial institutions, and the company has positioned itself as an industry leader in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations in investments. However, it has faced criticism for investing in companies involved in fossil fuels, the arms industry, and human rights violations in China.
In March 2019, an "emergency" bailout plan was developed by BlackRock's ex-central bank team for Fed Chairman Powell as financial markets appeared on the brink of a crisis. Powell then named BlackRock to manage all of the Fed's corporate bond purchase programs, including bonds where BlackRock itself invests. This decision was criticised by a group of NGOs, who wrote to Powell, stating:
> "By giving BlackRock full control of this debt buyout program, the Fed... makes BlackRock even more systemically important to the financial system. Yet BlackRock is not subject to the regulatory scrutiny of even smaller systemically important financial institutions."
In March 2019, the New York Fed hired BlackRock to manage its commercial mortgage-backed securities program and its $750 billion in corporate bonds and ETFs in no-bid contracts. This deal was criticised by financial journalists Pam and Russ Martens, who noted that BlackRock would receive $75 billion in taxpayer money to cover losses on its corporate bond purchases, including its own ETFs.
BlackRock's CEO Larry Fink is said to have a close relationship with Fed Chairman Jerome Powell. Even after Powell gave BlackRock the lucrative no-bid deal, he continued to have BlackRock manage an estimated $25 million of his private securities investments. Public records show that BlackRock doubled the value of Powell's investments from the previous year.
Mutual Fund Tax: What's the Reality?
You may want to see also

BlackRock's investment in China
BlackRock, the world's largest asset manager, has been criticised for its investments in China. In August 2021, BlackRock set up its first mutual fund in China after raising over one billion dollars from 111,000 Chinese investors. This made BlackRock the first foreign-owned company allowed by the Chinese government to operate a wholly-owned business in China's mutual fund industry.
BlackRock's China Fund seeks to maximise total return. The fund invests at least 70% of its total assets in the equity securities of companies domiciled in, or exercising the predominant part of their economic activity in, the People's Republic of China. The fund is subject to currency risk, smaller companies' volatility and liquidity risks, securities lending counterparty risk and currency conversion risk, including Renminbi-denominated classes.
In 2021, BlackRock was scrutinised for its investments in two companies that were blacklisted by the US government for human rights abuses against the Uyghurs in Xinjiang. In one case, BlackRock increased its level of investment after the company's blacklisting. In 2023, the US House of Representatives' Select Committee on the Chinese Communist Party found that BlackRock had channelled $1.9 billion into blacklisted entities. The committee also stated that BlackRock had invested more than $429 million across five funds into Chinese companies that "act directly against the interests of the United States".
BlackRock has defended its investments in China, stating that it complies with all applicable US government laws.
A Guide to Investing in ICICI Liquid Funds
You may want to see also

BlackRock's Aladdin software
BlackRock is the world's largest asset manager, with US$11.5 trillion in assets under management as of 31 December 2023. The company's Aladdin software is a technology platform used by asset managers and owners, including banks, financial institutions, pensions, corporations, insurers, and wealth managers.
Aladdin unifies the investment management process, providing a common data language within an organisation to enable scale, provide insights, and support business transformation. The platform covers alternative investment data management to meet the needs of alternative investment professionals worldwide and across all major alternative asset classes. From fundraising, fund administration, and reporting to data services and analytics, the platform provides capabilities to support decision-making and investment oversight.
Aladdin combines sophisticated risk analytics with quality-controlled data and highly scalable processing capabilities, allowing clients to know what they own across their portfolio, identify opportunities, and make more informed decisions. The software uses around 6,000 computers to analyse global economic data, stock market prices, and numerous other economic factors, including sudden changes in government, weather conditions, and possible disasters.
Aladdin is not a trading software but an analysis system used by BlackRock to evaluate individual investments and help with risk management. It is based on a pool of historical data that uses Monte Carlo simulation to select large, randomly generated samples from the vast number of possible future scenarios. This generates a statistical picture of different scenarios for equities and bonds under different future conditions.
Aladdin was first developed in 1988 on a single workstation from Sun Microsystems. It was initially used in 1994 to analyse the problematic mortgage portfolio of the investment bank Kidder, Peabody & Co, which was considered one of the world's most complex portfolios at the time.
Index Funds: Global Investing Strategies for Diversified Portfolios
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
BlackRock is the world's largest asset manager, with US$11.5 trillion in assets under management as of 31 December 2023.
BlackRock, Inc. is an American multinational investment company founded in 1988. The company is headquartered in New York City and has offices in 30 countries.
BlackRock's sole focus is asset management. The company runs over 120 mutual funds and a wide range of exchange-traded funds through its iShares unit.
BlackRock has made several notable acquisitions, including State Street Research & Management in 2004, Merrill Lynch's Investment Managers division in 2006, and Barclays Global Investors in 2010.
BlackRock has been expanding its environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives and has also been appointed by the Federal Reserve to manage corporate bond-buying programs in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.