Interest expense is a critical financial metric that can significantly impact a company's overall financial health and performance. It represents the cost of borrowing money and is a key component of a company's income statement. When considering whether interest expense is an investing activity, it's essential to understand the nature of investing activities and their impact on a company's financial statements. Investing activities typically involve the acquisition or disposal of long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, or the purchase and sale of marketable securities. These activities are crucial for a company's long-term growth and stability. However, interest expense, which is a cost associated with borrowing, is not directly related to these investing activities. Instead, it is a financing activity, as it reflects the cost of capital and the company's financial leverage. Understanding the distinction between interest expense and investing activities is essential for investors and financial analysts to accurately assess a company's financial health and make informed decisions.
What You'll Learn
- Definition of Interest Expense: The cost of borrowing money, typically paid to creditors
- Impact on Cash Flow: Interest expense reduces cash flow, affecting investing activities
- Capital Structure: High interest expenses can indicate a reliance on debt financing
- Investor Perception: Investors analyze interest expenses to assess financial health and stability
- Regulatory Compliance: Interest expenses must be reported in financial statements to meet regulations

Definition of Interest Expense: The cost of borrowing money, typically paid to creditors
Interest expense is a fundamental concept in accounting and finance, representing the cost incurred by a company for borrowing money. It is a critical component of a company's financial statements and is often a significant expense for businesses, especially those with substantial debt. When a company borrows funds, whether through loans, bonds, or other financial instruments, it is obligated to pay back the principal amount plus interest over time. This interest expense is a direct result of the company's borrowing activities and is a regular outflow of cash or cash equivalents.
In simple terms, interest expense is the price a company pays for the use of someone else's money. It is calculated as a percentage of the borrowed amount and is typically paid periodically, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the terms of the loan or debt agreement. The interest rate, which determines the amount of interest to be paid, can be fixed or variable, depending on the nature of the debt.
For investors and creditors, understanding interest expense is crucial as it directly impacts a company's financial health and stability. High interest expenses can strain a company's cash flow, especially if it has a large debt burden. This may lead to challenges in meeting financial obligations, affecting the company's ability to invest in growth opportunities or maintain its operations. On the other hand, managing interest expenses effectively can contribute to a company's financial stability and long-term success.
In the context of a company's financial activities, interest expense is not considered an investing activity. Investing activities primarily involve the purchase and sale of long-term assets, investments, and other financial items related to the company's long-term financial strategy. Interest expense, however, is an operating activity, as it is directly related to the company's day-to-day operations and the management of its short-term financial obligations. It represents the cost of funding the company's ongoing business activities and is a recurring expense that businesses must manage to ensure financial viability.
In summary, interest expense is the cost of borrowing money, typically paid to creditors, and it is an essential aspect of a company's financial management. While it is not an investing activity, it is a critical component of a company's financial performance and stability, especially in the context of debt management and cash flow. Understanding interest expense is vital for businesses, investors, and creditors alike to make informed financial decisions and assess the overall financial health of a company.
Navigating the Megarive: Strategies for Investing in a Rising Interest Rate Environment
You may want to see also

Impact on Cash Flow: Interest expense reduces cash flow, affecting investing activities
Interest expense is a critical component of a company's financial operations and can significantly impact its cash flow, especially when it comes to investing activities. When a company incurs interest expense, it represents the cost of borrowing money, typically through loans, bonds, or other debt instruments. This expense is a necessary outflow of cash, reducing the company's available funds for various purposes, including investment.
The impact on cash flow is twofold. Firstly, interest expense directly reduces the company's net income, which is a key indicator of its profitability. This reduction in net income means that the company has less cash available for reinvestment into its business or for other strategic initiatives. Secondly, the outflow of cash to service debt obligations can limit the company's ability to allocate funds towards long-term investments, expansion projects, or research and development.
In the context of investing activities, interest expense can have a substantial effect on a company's financial decisions. Investing activities often involve the purchase or sale of long-term assets, investments in securities, or other capital expenditures. When a company has a substantial interest expense, it may need to allocate a larger portion of its cash flow to debt servicing, leaving fewer resources for strategic investments. This can result in missed opportunities to acquire new assets, expand market share, or diversify the business portfolio.
For instance, consider a company that generates a significant portion of its revenue from a single product line. If this company has a high interest expense due to substantial debt, it might struggle to invest in research and development for new products, potentially losing market competitiveness over time. Alternatively, a company with a well-managed debt structure and lower interest expenses may have more flexibility to invest in innovative projects, thereby enhancing its long-term growth prospects.
Understanding the relationship between interest expense and cash flow is essential for businesses to make informed financial decisions. Effective management of debt and interest expenses can help companies optimize their cash flow, ensuring they have the financial resources to support their investing activities and overall business strategy. This may involve negotiating better loan terms, exploring alternative financing options, or implementing cost-saving measures to reduce the overall interest burden.
Understanding Interest Accrual: A Guide to Semiannual Investment Growth
You may want to see also

Capital Structure: High interest expenses can indicate a reliance on debt financing
High interest expenses can be a significant indicator of a company's capital structure and its financial health. When a company incurs substantial interest costs, it often suggests a heavy reliance on debt financing. This reliance on debt can have both positive and negative implications for the business.
On the positive side, debt financing can provide companies with the necessary capital to fund growth, expansion, or strategic initiatives. It allows businesses to leverage their assets and potentially generate higher returns on investment. However, the high interest expenses associated with this debt can also be a cause for concern.
A company with a high interest expense may be indicating that it is using debt as a primary source of funding. While debt can be a powerful tool for growth, excessive reliance on it can lead to financial vulnerability. High interest expenses reduce the company's cash flow, impacting its ability to invest in other areas, such as research and development, marketing, or operational improvements. This can result in a cycle of increased debt and higher interest payments, making it challenging for the company to maintain a healthy financial position.
Additionally, high interest expenses can signal that the company is facing challenges in managing its cash flow. Effective cash flow management is crucial for any business, as it ensures the ability to meet short-term obligations and invest in long-term growth. If interest expenses are a significant portion of the company's cash outflow, it may indicate that the business is struggling to generate sufficient cash from its operations to cover these costs.
In the context of capital structure, a high interest expense can be a red flag for investors and analysts. It may suggest that the company is taking on too much risk by relying heavily on debt. This could potentially lead to financial distress if the company's ability to generate revenue and cash flow is not sufficient to cover the debt servicing requirements. Therefore, understanding and managing interest expenses is crucial for maintaining a balanced and sustainable capital structure.
Unraveling the Magic: How Investments Generate Interest
You may want to see also

Investor Perception: Investors analyze interest expenses to assess financial health and stability
Investors play a crucial role in evaluating the financial health and stability of companies, and their analysis often extends to various financial metrics, including interest expenses. When assessing a company's financial performance, investors scrutinize interest expenses as a key indicator of its financial stability and overall health. This is particularly important in understanding the company's ability to manage its debt and the potential impact on its long-term viability.
Interest expenses represent the cost of borrowing for a company, and it is a recurring financial obligation. Investors analyze these expenses to gauge the company's financial leverage and its capacity to service its debt. High interest expenses relative to revenue or earnings can signal potential financial distress, especially if the company struggles to generate sufficient cash flow to cover these costs. This analysis is vital for investors as it helps them make informed decisions about the company's creditworthiness and the potential risks associated with its debt.
In the context of financial stability, investors consider interest expenses as a critical component of a company's cash flow statement. They evaluate how the company manages its debt payments and whether it can consistently meet its financial obligations. A company with a well-managed interest expense structure, where expenses are stable or decreasing over time, is often perceived as more financially stable and less prone to default. This perception can significantly influence investors' decisions regarding investments, especially in industries with high-interest rates or significant debt.
Moreover, investors also consider the interest coverage ratio, which compares a company's earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) to its interest expenses. A higher interest coverage ratio indicates that the company's earnings are sufficient to cover its interest payments, suggesting a healthier financial position. This metric is a valuable tool for investors to assess the company's ability to manage its debt and make informed judgments about its long-term financial health.
In summary, investors analyze interest expenses as a critical aspect of their financial assessment process. By evaluating these expenses, investors can gain insights into a company's financial stability, debt management capabilities, and overall financial health. This analysis is essential for making informed investment decisions and managing the associated risks effectively. Understanding interest expenses is a fundamental step in investors' due diligence, ensuring they make well-informed choices in the complex world of finance.
Maximize Your Returns: Strategies for 10% Investment Interest
You may want to see also

Regulatory Compliance: Interest expenses must be reported in financial statements to meet regulations
Interest expenses are a critical component of financial reporting and play a significant role in meeting regulatory compliance. When it comes to financial statements, the reporting of interest expenses is a mandatory requirement to ensure transparency and accuracy in financial reporting. This is especially important for companies to provide a clear picture of their financial health and performance to stakeholders, investors, and regulatory bodies.
The primary reason for this reporting is to provide a comprehensive view of a company's financial obligations and costs. Interest expenses represent the cost of borrowing and using debt financing. By including these expenses in financial statements, companies can accurately reflect the true cost of their operations and the impact of debt on their financial position. This information is vital for investors and creditors to assess the company's ability to manage its debt and make informed decisions.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States, have established guidelines and standards that mandate the disclosure of interest expenses. These regulations ensure that financial statements are prepared and presented consistently and fairly. For example, the SEC requires companies to disclose interest expenses in their income statements, providing a clear breakdown of interest costs associated with various sources of debt. This level of transparency allows investors to analyze the company's financial leverage and assess the potential risks and rewards of investing in the company.
Furthermore, regulatory compliance regarding interest expenses extends beyond the income statement. Financial statements also require the disclosure of interest expenses in the notes to the financial statements. This section provides additional details and explanations, ensuring that users of the financial statements can fully understand the components of the company's financial performance. It includes information about the nature of the debt, interest rates, and any significant changes or trends in interest expenses over time.
In summary, regulatory compliance dictates that interest expenses must be reported in financial statements to ensure transparency and accuracy. This reporting requirement allows companies to provide a comprehensive view of their financial obligations, costs, and the impact of debt on their operations. By adhering to these regulations, companies can maintain trust with stakeholders and investors, ensuring that their financial statements are reliable and informative.
Interest Rates and Investment: A Surprising Curve
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
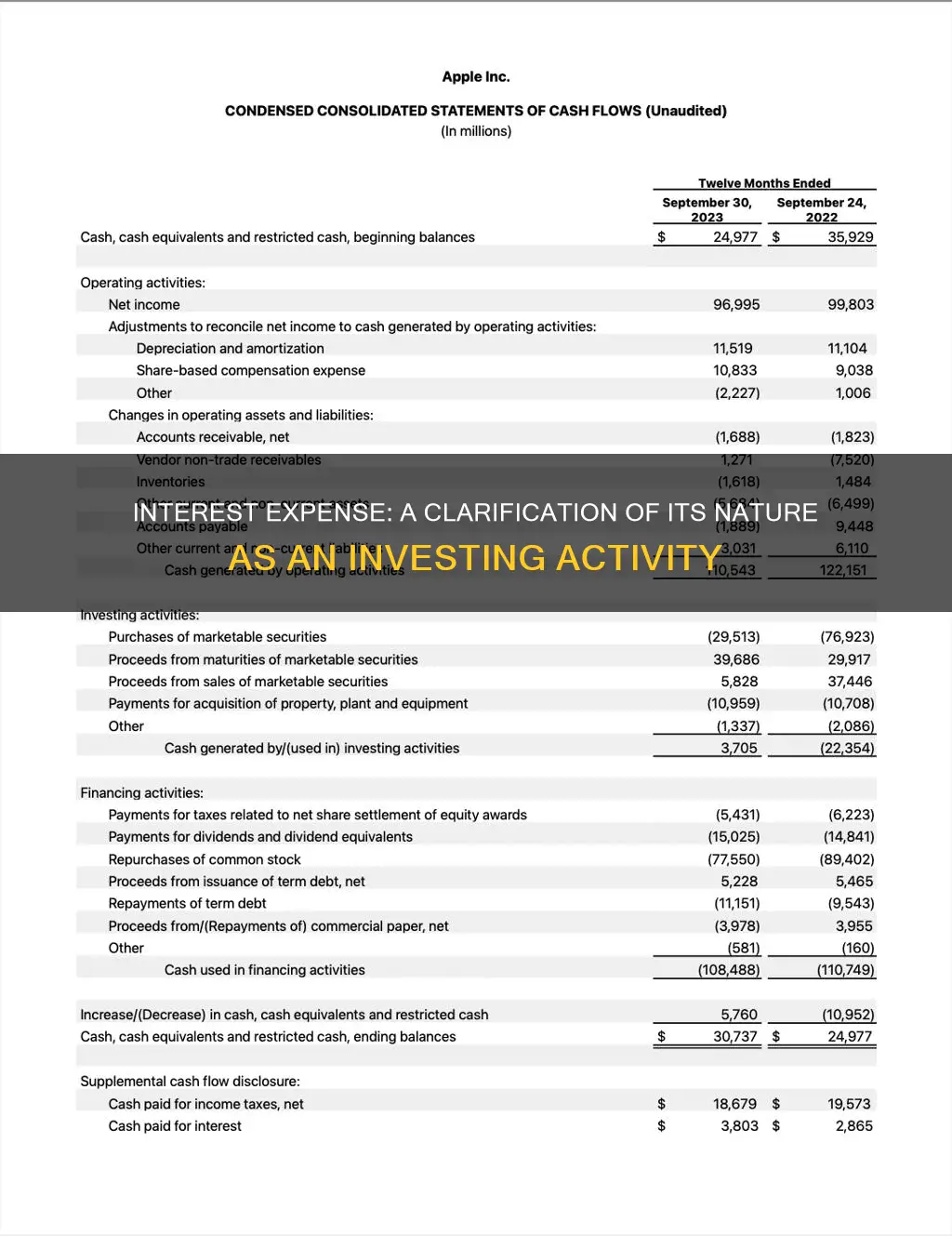
No, interest expense is not classified as an investing activity. Interest expense is a financing activity, which involves the cost of borrowing funds and is typically reported under the financing section of a company's financial statements. It represents the interest paid or accrued on debt, such as loans, bonds, or other forms of long-term debt.
Investing activities are related to the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, as well as other long-term investments. These activities involve the use of cash and are reflected in the cash flow statement under the investing section. Interest expense, on the other hand, is a periodic cost associated with borrowing and is not directly related to the purchase or sale of assets.
Yes, the classification of an activity can sometimes be complex and may depend on the specific context. For instance, if a company incurs interest expense related to a specific investing project or asset, it might be considered an investing activity. However, in general, interest expense is more commonly associated with financing activities and the management of debt.
While interest expense is primarily a financing activity, there can be exceptions. For example, if a company has a significant amount of interest expense related to a specific investment or project, it might be classified as an investing activity. Additionally, in some industries or accounting standards, the classification of interest expense may vary, so it's important to consider the specific guidelines and context of the company's financial reporting.