An investment fund is a financial product that pools capital from multiple investors to purchase a portfolio of various securities, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, and other financial instruments. This strategy allows investors to benefit from the expertise of professional fund managers, who make investment decisions on their behalf. The fund managers' access to market analysis and in-depth research enables them to make informed decisions and aim for higher returns than those offered by traditional investments.
Investment funds are subject to fees, including management fees, administrative expenses, and performance fees, which can impact overall returns. These fees may vary depending on the type of fund and the investment strategy employed.
There are various types of investment funds, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and hedge funds, each with its own investment strategy, risk profile, and management structure. Some funds are actively managed, with fund managers dynamically adjusting their holdings, while others are passively managed, aiming to track a specific benchmark or index.
By participating in investment funds, investors gain access to a diversified portfolio, reducing risk through asset allocation and benefiting from economies of scale. However, it's important to note that investing in any type of fund carries the risk of financial loss, and investors should carefully consider their financial goals and risk tolerance before committing their capital.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A financial product that pools capital from multiple investors to purchase a portfolio of various securities, such as stocks and bonds |
| Purpose | To benefit from the advantages of working as part of a group, such as reducing investment risks, accessing professional investment managers, and achieving economies of scale |
| Management | Managed by a professional portfolio or fund manager who makes investment decisions on behalf of the investors |
| Investment Decisions | Individual investors do not decide how the fund's assets are invested; they choose a fund based on its goals, risks, fees, and other factors |
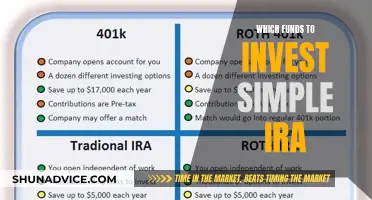
| Types | Mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), money market funds, hedge funds, and more |
| Investor Control | Each investor owns their shares in the fund but does not influence where the money is invested |
| Investor Rights | Investors may lose certain rights connected with individual investments within the fund |
| Objectives | Targeting geographic areas or specific industry sectors |
| Investor Suitability | Investors should consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and the fund's objectives, strategy, performance history, and fee structure |
| Fees | Management fees, administrative expenses, performance fees, transaction fees, and other one-off costs |
What You'll Learn
- Investment funds are a type of financial product that pools capital from multiple investors
- They are managed by professional portfolio managers who make investment decisions
- Investment funds are subject to fees, including management fees and expenses
- There are various types of investment funds, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, and hedge funds
- Investment funds provide investors with a diversified investment portfolio that might help reduce risk

Investment funds are a type of financial product that pools capital from multiple investors
Each investor owns their individual shares in the fund and retains ownership and control of those shares. However, they do not have any influence on where the money in the fund is invested. That decision-making power lies with a professional fund manager, who is responsible for making investment choices based on the fund's objectives and strategy. The manager decides which assets to buy or sell, how many, and when.
Investment funds provide investors with a diversified investment portfolio, which can help to reduce risk and increase returns. By pooling their capital with that of other investors, individuals can gain access to a broader selection of investment opportunities than they might be able to access alone. This includes a wider range of asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions.
There are various types of investment funds, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and hedge funds, each with its own investment strategy and risk profile. Mutual funds, for example, are a popular choice for investors as they offer professional management, diversification, and affordability. ETFs are similar to mutual funds but trade like stocks on exchanges and can be traded throughout the day. Hedge funds, on the other hand, are private and use more aggressive strategies to target higher returns.
While investment funds offer many potential benefits, they also come with risks. These include the potential for financial losses, exposure to market fluctuations, and high management fees. Investors should carefully research and analyse a fund's objectives, strategy, performance history, and fee structure before deciding to invest.
SBI Multicap Fund: A Comprehensive Guide to Investing
You may want to see also

They are managed by professional portfolio managers who make investment decisions
Investment funds are managed by professional portfolio managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors. These portfolio managers are financial professionals who work for wealth management firms, pension funds, foundations, insurance companies, banks, and hedge funds. They are responsible for creating and overseeing an investment strategy that meets the needs and goals of their clients.
Portfolio managers work with a team of analysts and researchers to develop investment strategies. They direct the trades the investment fund or portfolio makes, making final decisions on the securities involved. They meet with analysts who have conducted research on various securities and the institutions that issued them, and based on their recommendations, the portfolio manager decides which securities to buy or sell.
Portfolio managers are investment decision-makers. They devise and implement investment strategies and processes to meet client goals and constraints. They are responsible for constructing and managing portfolios and deciding what and when to buy and sell investments.
Portfolio managers typically begin their careers as financial analysts and work their way up to portfolio manager. They usually hold a bachelor's degree in finance or a related field, and many have a master's degree in finance, business administration, economics, or another quantitative field. They require licensing and certification, such as the chartered financial analyst (CFA) designation.
The role of a portfolio manager is challenging and rewarding. It requires a passion for financial markets, strong analytical and decision-making skills, excellent communication abilities, and adherence to high ethical standards.
Investing in Your 20s: Index Funds for Early Investors
You may want to see also

Investment funds are subject to fees, including management fees and expenses
Investment funds are a type of financial product that pools capital from multiple investors to purchase a portfolio of various securities, such as stocks and bonds. This is usually done with the goal of earning higher returns than those offered by traditional investments.
- Management Fees: These are fees paid to the fund's investment adviser or manager for their services in making investment decisions and managing the fund's portfolio. Management fees are typically calculated as a percentage of the fund's assets under management (AUM) and can vary depending on the type of fund and its investment strategy.
- Administrative Expenses: These include the day-to-day operational costs of running the fund, such as record-keeping, accounting, legal, and custodial fees. These expenses are necessary to ensure compliance with regulations and maintain the smooth functioning of the fund.
- Performance Fees: Some investment funds also charge performance fees, which are usually calculated as a percentage of the profits earned by the fund above a certain threshold. These fees reward the fund manager for strong performance and are intended to align their interests with those of the investors.
- Transaction Costs: Buying and selling securities on behalf of the fund incurs transaction costs, such as brokerage fees and commissions. These costs can vary depending on the volume and frequency of trades.
- Sales Loads: When investors purchase or redeem shares of the fund, they may be charged a sales load, also known as a sales charge. There are front-end sales loads, which are paid when purchasing shares, and back-end or deferred sales loads, which are paid when redeeming shares.
- Distribution Fees: Investment funds may also have distribution fees, also known as 12b-1 fees, which cover the costs of marketing and selling fund shares. These fees are typically paid to brokers and other intermediaries involved in distributing the fund's shares.
It's important for investors to carefully consider the fee structure of an investment fund before committing their capital. While fees are necessary to cover the costs of managing the fund, high fees can eat into investment returns over time. Therefore, it's crucial to weigh the benefits offered by the fund against the fees charged to ensure a favourable outcome for investors.
Apiary Investment Fund: Legit or Scam?
You may want to see also

There are various types of investment funds, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, and hedge funds
Investment funds are a way of investing money with other investors to benefit from the advantages of working as a group, such as reducing investment risks, hiring professional investment managers, and benefiting from economies of scale.
There are various types of investment funds, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and hedge funds. Each has its own investment strategy and risk profile.
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from many investors to build a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other securities. They are professionally managed, and the funds are diversified to spread risk and maximise returns. Mutual funds trade only once a day after the markets close and are designed for longer-term investors.
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are similar to mutual funds in that they pool money from many investors. However, they trade like stocks on exchanges and can be traded at any point during the trading day. ETFs often offer diversification at lower costs than traditional mutual funds.
Hedge funds are private, actively managed investment vehicles that generally use more aggressive strategies to generate higher returns. They are only available to accredited investors due to their high risk and complexity. Hedge funds employ riskier investment strategies, such as short selling, arbitrage, and the use of leverage and derivatives. They also tend to invest in riskier assets, including derivatives such as futures and options.
SS Funds: Where Are Your Contributions Invested?
You may want to see also

Investment funds provide investors with a diversified investment portfolio that might help reduce risk
Investment funds are a type of financial product that pools capital from multiple investors to purchase a portfolio of various securities, such as stocks and bonds. This is usually done with the goal of earning higher returns than those offered by traditional investments.
By investing in an investment fund, investors can benefit from a diversified investment portfolio that might help reduce risk and increase returns.
How Investment Funds Work
Investment funds work by pooling money from multiple investors to purchase a portfolio of securities such as stocks, bonds, commodities, and alternative investments such as real estate and venture capital.
Each investor owns their individual shares in the fund but does not have any influence on where the money in the fund is invested. The fund is managed by a professional fund manager who is responsible for making investment decisions based on the fund's objectives and strategy.
Benefits of Investment Funds
Professional Management
Investment funds are managed by experienced professionals who have access to market analysis and in-depth research to make informed decisions. This can lead to better returns for investors.
Diversification
Investment funds enable investors to spread their money across multiple asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions, reducing the overall risk of their investment portfolio. By holding a variety of investments, the poor performance of any one investment can potentially be offset by the better performance of another, leading to a more consistent overall return.
Flexibility
Investment funds provide investors with a range of options. Investors can choose funds based on their risk tolerance, desired returns, and the type of assets they want to invest in.
Transparency
Investment funds provide investors with full disclosure of their holdings and the fund's historic performance, allowing investors to make informed decisions.
Risks of Investment Funds
Lack of Control
When investing in a fund, investors entrust their money to the fund manager and do not have any control over how and when the money is invested.
Market Risk
Investment funds can be very volatile as they are actively managed and can be affected by market changes. This means that the fund can lose value quickly or take longer to reach its target value.
Lack of Liquidity
Some investment funds are not very liquid and may impose restrictions on when and how investors can redeem their shares.
Fees and Expenses
Investment funds often charge management fees and transaction costs, which can impact the overall returns for investors.
Types of Investment Funds
There are various types of investment funds, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and hedge funds, each with its own investment strategy and risk profile.
Mutual funds pool money from many investors to build a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other securities. They are professionally managed to spread risk and maximise returns.
ETFs are similar to mutual funds but trade like stocks on exchanges and can be traded at any point during the trading day, offering more flexibility to investors.
Hedge funds are private, actively managed investment vehicles that use more aggressive strategies, such as short selling and arbitrage, to generate higher returns. They are only available to accredited investors due to their high risk and complexity.
Investment funds provide investors with a diversified investment portfolio that can help reduce risk and increase returns. However, as with any financial product, there are also risks involved, including the potential for losses, market fluctuations, and fees. When deciding whether to invest in a fund, investors should carefully consider its objectives, strategy, performance history, and fee structure, as well as their own financial goals and risk tolerance.
Emerging Market Funds: Where to Invest and How
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
An investment fund is a financial product that pools capital from multiple investors to purchase a portfolio of various securities, such as stocks and bonds. The fund is managed by a professional who makes investment decisions on behalf of the investors.
Investment funds provide investors with a diversified investment portfolio that might help reduce risk and increase returns. They also offer professional management, flexibility, and access to a wide range of investment opportunities.
Like any other financial product, investment funds carry a number of risks, including the potential for losses, exposure to market fluctuations, and high management fees. They can also be illiquid and impose restrictions on when and how investors can redeem their shares.