A minimum variance portfolio is an investment strategy that uses diversification to minimise risk and maximise profits. It is a low-risk portfolio that holds individual, volatile securities that are not correlated with one another. This means that the portfolio as a whole is viewed as less risky. The minimum variance portfolio formula is: Minimum Variance Portfolio = W12σ12 + W22σ22 + 2W1W2Cov1,2. W1 is the first asset's portfolio weight, W2 is the second asset's portfolio weight, σ1 is the first asset's standard deviation, σ2 is the second asset's standard deviation, and Cov1,2 is the covariance of the two assets.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A well-diversified portfolio of individually risky assets, which are hedged when traded together, resulting in the lowest possible risk for the rate of expected return. |
| Type of Investment | Low-risk |
| Investment Risk | Each investment in a minimum variance portfolio is risky if traded individually, but when traded in the portfolio, the risk is hedged. |
| Investment Correlation | Investments with low to negative correlation to each other. |
| Investment Examples | Stocks and bonds. |
| Formula | Minimum Variance Portfolio = W12σ12 + W22σ22 + 2W1W2Cov1,2 |
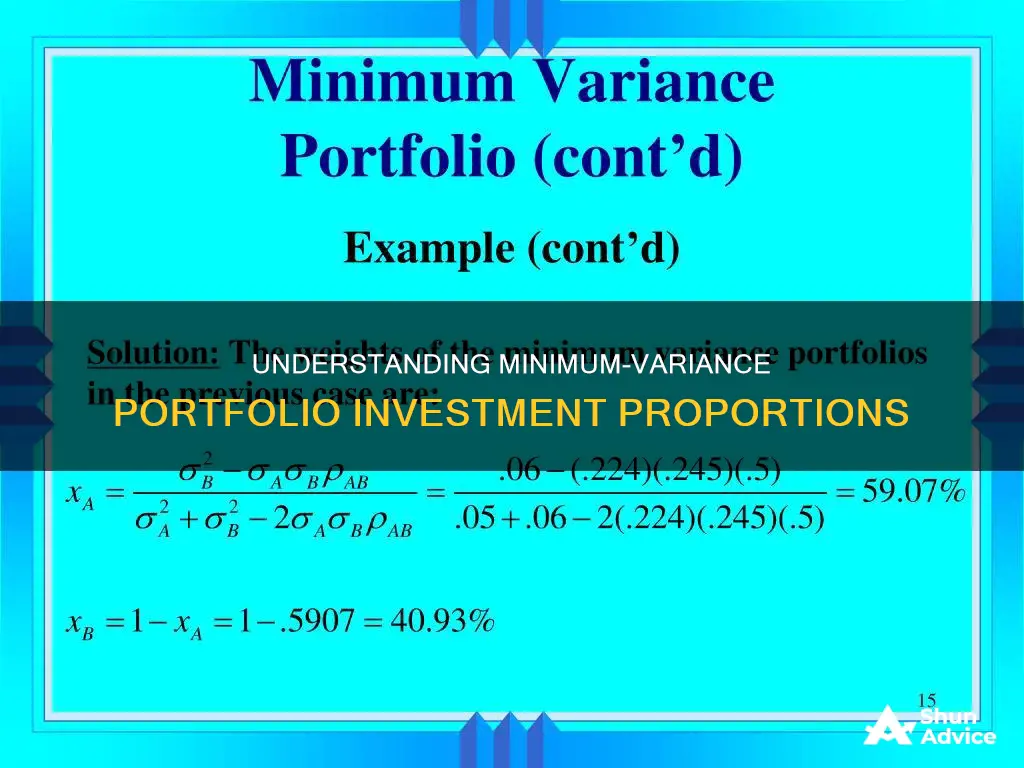
| Example Calculation | Louis has a portfolio of two stocks. One is worth $45,000, and the other is worth $90,000. The first stock has a standard deviation of 18%, the second stock has a standard deviation of 9%, and the correlation between the stocks is 0.72. The portfolio weightage of the first and second stocks is 33.3% and 66.7%, respectively. The minimum variance is calculated as: (33.3%^2 x 18%^2) + (66.7%^2 x 9%^2) + (2 x 33.3% x 18% x 66.7% x 9% x 0.72) = 0.012 or 1.2%. |
What You'll Learn

Minimum-variance portfolios are well-diversified
In a minimum-variance portfolio, high-risk stocks complement each other but do not correlate. This means that if one sector is experiencing a downturn, it will not affect the entire portfolio. For example, if an investor holds a portfolio of 30 different technology stocks, and the tech sector takes a hit, the investor will lose a lot of money. However, if the investor possesses a 30-stock portfolio covering a range of industries, bonds, and real estate, the impact of any one sector experiencing a downturn will be minimised.
The minimum-variance approach combines diversification with hedging. Hedging is an investment strategy that protects traders against potential losses due to unforeseen price fluctuations. To hedge risks, investors hold stock in one financial market and then take another position in a different market to offset potential losses caused by the first position.
The minimum-variance portfolio formula is as follows:
Minimum Variance Portfolio = W12σ12 + W22σ22 + 2W1W2Cov1,2
Where:
- W1 = the portfolio weight of the first asset
- W2 = the portfolio weight of the second asset
- Σ1 = the standard deviation of the first asset
- Σ2 = the standard deviation of the second asset
- Cov1,2 = the covariance of the two assets, expressed as p (1,2) σ1σ2
- P (1,2) = the correlation coefficient between the two assets
Minimum-variance portfolios are based on the idea that portfolio variance can be reduced by choosing asset classes with low or negative correlation. This idea comes from modern portfolio theory, which was developed by Harry Markowitz in 1952. Markowitz stated that portfolio variance could be minimised if stocks are selected using negative correlation.
Understanding the Domestic Saving-Investment Imbalance
You may want to see also

They consist of individually risky assets
A minimum variance portfolio is a well-diversified portfolio that consists of individually risky assets. These assets are hedged when traded together, resulting in the lowest possible risk for the expected rate of return. In other words, each investment in a minimum variance portfolio is risky if traded individually, but when traded together in a portfolio, the risk is hedged.
The term originates from the Markowitz Portfolio Theory, which suggests that volatility can be used to replace risk and, therefore, less volatility variance correlates with less investment risk. According to this theory, choosing asset classes with low to negative correlation, such as stocks and bonds, can lead to a reduction in portfolio variance.
For example, an investor holding a portfolio of 30 different technology stocks will have a high correlation, whereas an investor with a 30-stock portfolio covering a range of industries, bonds, and real estate will have a lower correlation.
In the minimum variance approach, investors combine diversification with hedging. Hedging is an investment strategy that protects traders against potential losses due to unforeseen price fluctuations. To hedge risks, investors hold stock in one financial market and then take another position in a different market to offset potential losses caused by the first position.
The minimum variance portfolio formula is as follows:
Minimum Variance Portfolio = W12σ12 + W22σ22 + 2W1W2Cov1,2
Where:
- W1 is the first asset's portfolio weight
- W2 is the second asset's portfolio weight
- Σ1 is the first asset's standard deviation
- Σ2 is the second asset's standard deviation
- Cov1,2 is the covariance of the two assets, expressed as p (1,2) σ1σ2
- P (1,2) represents the correlation coefficient between the two assets
Smart Saving and Investing Strategies for Your Kids' Future
You may want to see also

These risky assets are hedged when traded together
A minimum variance portfolio is a well-diversified portfolio that consists of risky assets that are hedged when traded together, resulting in the lowest possible risk for the expected return. This is based on the Markowitz Portfolio Theory, which suggests that volatility can be used to replace risk, and therefore, less volatility variance correlates with less investment risk.
In a minimum variance portfolio, investors combine diversification with hedging. Hedging is an investment strategy that protects traders against potential losses due to unforeseen price fluctuations. To hedge risks, investors hold stock in one financial market and then take another position in a different market to offset potential losses caused by the first position. This is done by investing in stocks, derivatives, swaps, options, futures contracts, and ETFs.
The minimum variance portfolio formula is as follows:
Minimum Variance Portfolio = W12σ12 + W22σ22 + 2W1W2Cov1,2
Where:
- W1 is the first asset's portfolio weight
- W2 is the second asset's portfolio weight
- Σ1 is the first asset's standard deviation
- Σ2 is the second asset's standard deviation
- Cov1,2 is the covariance of the two assets, expressed as p (1,2) σ1σ2
- P (1,2) is the correlation coefficient between the two assets
For example, let's say Louis has a portfolio of two stocks. One is worth $45,000, and the other is worth $90,000. The first stock has a standard deviation of 18%, and the second stock has a standard deviation of 9%. If the correlation between the stocks is 0.72, the portfolio weightage of the first and second stocks is 33.3% and 66.7%, respectively.
To calculate the minimum variance, we apply the given values to the formula:
Minimum Variance = (33.3%^2 x 18%^2) + (66.7%^2 x 9%^2) + (2 x 33.3% x 18% x 66.7% x 9% x 0.72) = 0.012 or 1.2%
Thus, Louis's portfolio exhibits a variance of 1.2%.
The minimum variance portfolio approach is based on the variance percentage and is a simple method. In contrast, a tangency portfolio relies on the Sharpe ratio and is a complex process. The advantages of a minimum variance portfolio include resistance to systematic risk, aiding in understanding different sectors, suitability for both long-term wealth creation and short-term profits, and the ability to fit a variety of financial instruments. However, it tends to overlook potential risks, does not guarantee good returns, and does not account for associated costs like broker commissions and taxes.
Hedging Strategies: Protect Your Portfolio with These Smart Moves
You may want to see also

The result is the lowest possible risk for the expected return
A minimum variance portfolio is an investment strategy that uses diversification to minimise risk and maximise profits. The investor combines stock holdings so that the price volatility of the entire portfolio is reduced. This is done by investing in high-risk stocks that complement each other but are not correlated. In other words, the stocks are picked from a variety of sectors so that a loss in one sector does not affect the entire portfolio.
The minimum variance portfolio is based on the Markowitz Portfolio Theory, which suggests that volatility can be used to replace risk and, therefore, less volatility variance correlates with less investment risk. The theory also states that portfolio variance can be minimised if stocks are selected using negative correlation. If the correlation between assets within a portfolio is less, the variance is also less.
The minimum variance portfolio formula is as follows:
Minimum Variance Portfolio = W12σ12 + W22σ22 + 2W1W2Cov1,2
Where:
- W1 = the portfolio weight of the first asset
- W2 = the portfolio weight of the second asset
- Σ1 = the standard deviation of the first asset
- Σ2 = the standard deviation of the second asset
- Cov1,2 = the covariance of the two assets, expressed as p (1,2) σ1σ2
- P (1,2) = the correlation coefficient between the two assets
The minimum variance portfolio is a well-diversified portfolio that consists of individually risky assets, which are hedged when traded together, resulting in the lowest possible risk for the expected return.
Savings-to-Investment Ratio: A Window to Your Financial Health
You may want to see also

The portfolio is influenced by modern portfolio theory
The minimum-variance portfolio is a strategy that uses diversification to minimise risk and maximise profits. It is influenced by modern portfolio theory (MPT), which was introduced by Harry Markowitz in 1952. MPT is a mathematical framework for assembling a portfolio of assets that maximises expected returns for a given level of risk.
MPT assumes that investors are risk-averse and that they will prefer a less risky portfolio when given two portfolios with the same expected returns. It also assumes that investors are non-satiated and will choose the highest expected return when presented with securities with the same standard deviation.
MPT focuses on diversification, arguing that owning different kinds of financial assets is less risky than owning only one type. It suggests that investors can achieve optimal results by choosing a mix of low-risk and high-risk investments based on their individual tolerance for risk.
MPT uses statistical measures such as variance and correlation to evaluate a portfolio's risk and return. It also introduces the concept of the efficient frontier, which is a plot of all possible combinations of assets, with the portfolio's risk on the x-axis and the expected return on the y-axis. The efficient frontier connects the most efficient portfolios, offering the best possible expected return for a given level of risk.
MPT has been criticised for evaluating portfolios based on variance rather than downside risk. The post-modern portfolio theory (PMPT) was developed to address this issue by minimising downside risk instead of variance.
Savings and Investments: Smart Money Strategies for Beginners
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A minimum-variance portfolio is a low-risk portfolio that holds individual, volatile securities that are not correlated with one another. It is a well-diversified portfolio that consists of individually risky assets, which are hedged when traded together, resulting in the lowest possible risk for the rate of expected return.
In a minimum-variance portfolio, investors combine diversification with hedging. Hedging is an investment strategy that protects traders against potential losses due to unforeseen price fluctuations. To hedge risks, investors hold stock in one financial market and then take another position in a different market to offset potential losses caused by the first position.
The portfolio becomes resistant to systematic risk. As a result, underperforming and high-risk assets can be scrutinized and replaced. Diversification helps investors understand different sectors and this strategy suits both long-term wealth creation and short-term profits.