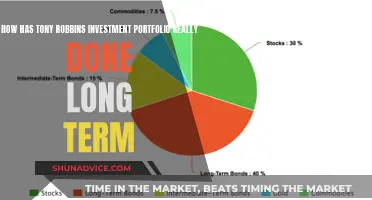
Understanding the classification of investments as short-term or long-term is crucial for financial planning and decision-making. This distinction is essential for investors and financial professionals to assess the liquidity, risk, and potential returns of different investment options. Short-term investments typically refer to assets that can be easily converted into cash within a year or less, such as stocks, bonds, or money market funds. In contrast, long-term investments are those held for an extended period, often years or even decades, and may include real estate, mutual funds, or retirement accounts. The classification of investments into these categories helps investors manage their portfolios effectively, balance risk and return, and align their investment strategies with their financial goals and time horizons.
What You'll Learn
- Liquidity: Investments that can be quickly converted to cash without significant loss are considered short-term
- Holding Period: Short-term investments are typically held for less than one year, while long-term are held for over a year
- Tax Implications: Short-term capital gains are taxed at higher rates than long-term gains
- Market Volatility: Short-term investments are more susceptible to market fluctuations and short-term trends
- Investment Strategy: Short-term strategies focus on quick returns, while long-term strategies aim for steady growth over time

Liquidity: Investments that can be quickly converted to cash without significant loss are considered short-term
Liquidity is a critical factor in distinguishing between short-term and long-term investments. It refers to the ease and speed with which an investment can be converted into cash without incurring a substantial loss. Short-term investments are those that can be readily liquidated, providing quick access to funds. This characteristic is essential for investors who prioritize flexibility and the ability to respond to financial needs or opportunities promptly.
In the context of short-term investments, liquidity is a key differentiator. These investments are typically held for a brief period, often less than a year. Examples include money market funds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and treasury bills. Money market funds, for instance, invest in highly liquid assets like short-term government securities, ensuring that investors can withdraw their funds quickly without significant penalties or losses. CDs, on the other hand, offer a fixed rate of interest for a specified period, providing a predictable return while maintaining liquidity through early withdrawal options.
The concept of liquidity is closely tied to risk and return. Short-term investments generally offer lower returns compared to long-term investments due to their lower risk profile. Since these investments can be easily converted to cash, investors are less exposed to market fluctuations and potential losses over extended periods. This makes short-term investments an attractive option for risk-averse investors or those seeking a more conservative approach to their portfolios.
Understanding liquidity is crucial for investors to make informed decisions about their investment strategies. It allows them to assess the accessibility and flexibility of their investments. For instance, a well-diversified portfolio might include a mix of short-term and long-term investments, balancing liquidity with potential growth. This approach enables investors to meet their financial goals while managing risk effectively.
In summary, liquidity is a defining characteristic of short-term investments, allowing investors to access their funds quickly without significant losses. This feature is particularly valuable for those seeking financial flexibility and a more conservative investment strategy. By considering liquidity, investors can construct portfolios that align with their risk tolerance and financial objectives.
Understanding Short-Term Investments: Strategies for Quick Financial Growth
You may want to see also

Holding Period: Short-term investments are typically held for less than one year, while long-term are held for over a year
The concept of holding periods is a fundamental aspect of investment classification, particularly when distinguishing between short-term and long-term investments. This classification is crucial for investors as it helps them understand the potential risks and rewards associated with different types of investments.
Short-term investments are characterized by their relatively brief holding periods, typically lasting less than one year. These investments are often made with a focus on liquidity and capital preservation. Investors may choose short-term investments for their quick access to funds, as they can be easily converted into cash without incurring significant losses. Examples of short-term investments include money market funds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and treasury bills. These assets are considered low-risk, providing a safe haven for investors seeking short-term gains or quick access to their capital.
In contrast, long-term investments are held for an extended period, generally over a year. This classification is more suitable for investors who are willing to commit their capital for an extended duration, often with the goal of achieving higher returns. Long-term investments are typically associated with higher risk but also offer the potential for substantial gains. Stocks, bonds, real estate, and certain mutual funds are common examples of long-term investments. These assets are often chosen for their ability to grow over time, providing investors with capital appreciation and potential dividends or interest payments.
The holding period is a critical factor in investment strategies, as it influences the tax treatment and reporting requirements. In many jurisdictions, short-term capital gains are taxed at a higher rate than long-term gains, encouraging investors to hold investments for the long term. Additionally, short-term investments may be more suitable for risk-averse investors who prioritize capital safety, while long-term investments cater to those seeking growth and potential wealth accumulation.
Understanding the distinction between short-term and long-term investments is essential for investors to make informed decisions. It allows them to align their investment choices with their financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizons. By recognizing the characteristics of each holding period, investors can navigate the investment landscape more effectively and build a well-diversified portfolio.
Unlocking Retirement Wealth: IRA's Long-Term Investment Potential
You may want to see also

Tax Implications: Short-term capital gains are taxed at higher rates than long-term gains
Understanding the tax implications of short-term and long-term investments is crucial for investors, as it can significantly impact their overall financial strategy. When it comes to capital gains, the duration of the investment plays a pivotal role in determining the tax treatment. Short-term capital gains, which are profits realized from the sale of assets held for a short period, typically one year or less, are generally taxed at a higher rate compared to long-term gains. This is an essential distinction for investors to grasp, as it can influence their decision-making process.
The tax rates for short-term capital gains are often more aggressive, reflecting the idea that these gains are considered more speculative and less tied to long-term investment strategies. In many jurisdictions, short-term gains are treated as ordinary income, meaning they are taxed at the same rates as regular income. This can result in a higher tax burden for investors, especially those in higher income tax brackets. For instance, in the United States, short-term capital gains are currently taxed at the ordinary income tax rate, which can vary depending on the individual's income level.
On the other hand, long-term capital gains, which are profits from assets held for more than a year, are typically taxed at lower rates. This preferential treatment encourages investors to adopt a long-term investment horizon, promoting a more stable and thoughtful approach to wealth accumulation. The reduced tax rate on long-term gains is a significant incentive for investors, as it can lead to substantial savings over time. For example, in the US, long-term capital gains are currently taxed at 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on the taxpayer's income, providing a substantial tax break for long-term investors.
The difference in tax rates between short-term and long-term gains can have a substantial impact on an investor's net returns. For short-term investments, the higher tax rate may eat into a significant portion of the profit, leaving investors with a smaller net gain or even a loss. Conversely, long-term investments benefit from the reduced tax rate, allowing investors to retain a larger portion of their profits. This distinction is particularly important for investors who frequently buy and sell assets, as it can influence their overall investment strategy and risk tolerance.
In summary, the tax implications of short-term and long-term investments are a critical aspect of investment planning. Short-term capital gains are taxed at higher rates, often treated as ordinary income, which can be a significant consideration for investors. In contrast, long-term gains benefit from lower tax rates, encouraging a more patient and strategic investment approach. Understanding these tax differences is essential for investors to optimize their financial strategies and make informed decisions regarding their investment portfolios.
Ethereum's Long-Term Potential: A Wise Investment Choice?
You may want to see also

Market Volatility: Short-term investments are more susceptible to market fluctuations and short-term trends
Market volatility is a critical concept to understand when differentiating between short-term and long-term investments. Short-term investments are inherently more vulnerable to market fluctuations and short-term trends compared to long-term investments. This is primarily due to the nature of short-term investments, which are typically defined as assets that can be quickly converted into cash or sold without significant loss of value. As a result, they are more responsive to immediate market changes, such as daily price movements or short-term economic shifts.
In the short-term investment landscape, market volatility can lead to rapid price swings. For instance, a stock's price might fluctuate significantly in a single day due to various factors like news, earnings reports, or market sentiment. These short-term price movements can create opportunities for quick gains or losses, making short-term investments more attractive to traders seeking to capitalize on short-term trends. However, this increased volatility also means that short-term investments are more susceptible to market panic or herd behavior, where investors might make impulsive decisions based on short-term market conditions.
Long-term investments, on the other hand, are designed to withstand market volatility over an extended period. These investments are typically held for several years or even decades, allowing investors to smooth out the impact of short-term market fluctuations. Long-term investments often include assets like real estate, bonds, or carefully selected stocks that are expected to grow in value over time, regardless of short-term market volatility. By maintaining a long-term perspective, investors can focus on the underlying fundamentals of the investment rather than daily price movements.
Understanding market volatility is crucial for investors as it influences their investment strategies and risk tolerance. Short-term investors often employ techniques like day trading or swing trading, which involve rapid buying and selling of assets to capitalize on short-term price movements. In contrast, long-term investors typically adopt a buy-and-hold strategy, diversifying their portfolios to minimize the impact of short-term market volatility. This approach allows them to benefit from the long-term growth potential of their investments while reducing the risk associated with short-term market fluctuations.
In summary, market volatility plays a significant role in distinguishing between short-term and long-term investments. Short-term investments are more sensitive to market fluctuations and short-term trends, making them suitable for active traders seeking quick gains. Long-term investments, however, are designed to weather market volatility over an extended period, providing a more stable and patient approach to wealth accumulation. Recognizing the impact of market volatility is essential for investors to make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and risk preferences.
Long-Term Investments: Financing or Investing? Unlocking the Strategy
You may want to see also

Investment Strategy: Short-term strategies focus on quick returns, while long-term strategies aim for steady growth over time
When it comes to investment strategies, understanding the difference between short-term and long-term approaches is crucial for investors. Short-term strategies are designed to generate quick returns within a relatively short period, typically ranging from a few months to a couple of years. These strategies often involve more frequent buying and selling of assets, aiming to capitalize on short-term market fluctuations and trends. The primary goal is to take advantage of price movements and secure profits in a relatively short timeframe.
In contrast, long-term investment strategies focus on steady growth and compound appreciation over an extended period, often spanning several years or even decades. This approach emphasizes patience and a buy-and-hold strategy, allowing investors to weather short-term market volatility and benefit from the long-term upward trend of the markets. Long-term investors typically hold a diverse range of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds, and aim to build wealth by reinvesting dividends and capital gains.
Short-term strategies often involve active trading, where investors frequently buy and sell securities to take advantage of market opportunities. This approach requires a keen understanding of market dynamics, technical analysis, and the ability to make quick decisions. Short-term traders often use various tools like stop-loss orders and leverage to manage risk and maximize returns. However, this strategy can be more complex and may require a higher level of market knowledge and discipline.
On the other hand, long-term investment strategies are more passive and require less frequent intervention. Investors typically construct a well-diversified portfolio and hold it for an extended period, allowing the power of compounding to work in their favor. This approach is particularly effective in asset classes like real estate, where long-term ownership can lead to significant appreciation and rental income. Long-term investors often focus on fundamental analysis, studying company financials and industry trends to identify undervalued assets.
In summary, the key distinction between short-term and long-term investment strategies lies in their time horizons and objectives. Short-term strategies prioritize quick returns and active trading, while long-term strategies emphasize steady growth and a buy-and-hold approach. Understanding these differences is essential for investors to align their investment choices with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Mastering Short-Term Put Options: A Beginner's Guide to Profitable Trading
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Short-term investments are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or sold within a short period, typically one year or less. These investments are considered highly liquid and are often used to meet short-term financial goals or to take advantage of immediate investment opportunities. Examples include money market funds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and short-term government bonds.
Long-term investments are those that are held for an extended period, usually beyond one year. They are typically less liquid and may take longer to sell or convert into cash. Long-term investments are often chosen for their potential to generate higher returns over time and are a key component of retirement planning and wealth accumulation strategies. Stocks, real estate, and certain mutual funds are common examples of long-term investments.
The classification of an investment as short-term or long-term often depends on the investor's financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Generally, investments that can be easily liquidated and provide a relatively quick return are considered short-term. In contrast, long-term investments are those that are held for an extended period, allowing investors to benefit from potential capital appreciation and dividend growth. It's important to note that these classifications can vary based on individual circumstances and the specific investment vehicles involved.