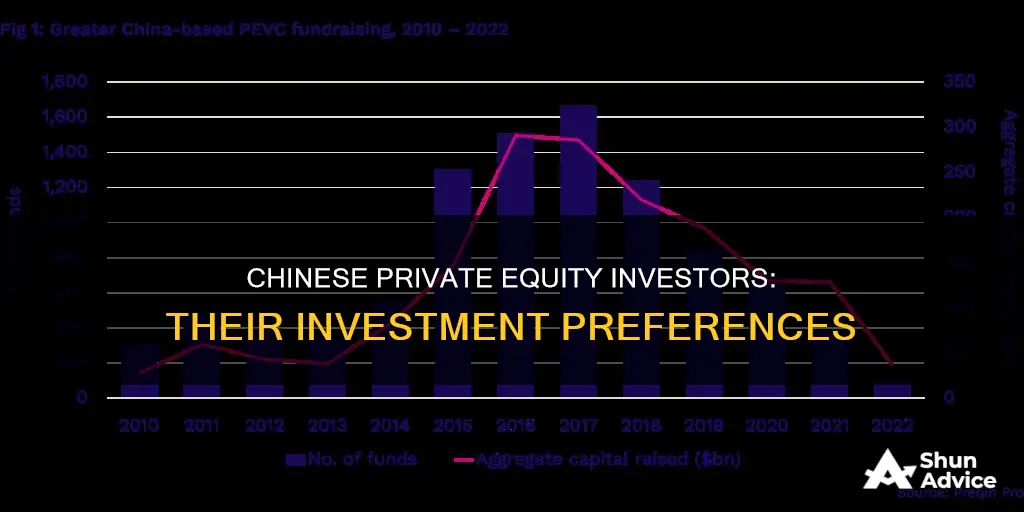
China's private equity market is one of the world's emerging markets, and despite complications on the political and economic fronts, it has remained active. However, it is facing increasing limitations due to the downfall of stock valuation and foreign investor reluctance. The market is hyper-local, with private equity firms focusing on local funds and local professionals who can easily connect with local businesses. Technology, healthcare, manufacturing, cleantech, consumer, energy, real estate, and financial services are among the industries that Chinese private equity investors like to invest in.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Industry Focus | Technology, healthcare, manufacturing, cleantech, consumer, energy, real estate, financial services |
| Deal Types | Growth deals, leveraged buyouts |
| Investment Strategies | Pan-Asia investing, industry-specific focus |
| Top Firms | Blackstone, Boyu Capital, BPEA EQT, Carlyle, CDH Investments, CITIC Capital, FountainVest, General Atlantic, GLP China, Hillhouse, Hony Capital, Hopu, KKR, Qiming Ventures, Sequoia, TPG, Vivo Capital, Warburg Pincus |
| Investment Sources | Local funds, international funds |
| Investment Location | China, overseas |
What You'll Learn

Technology, especially IT, internet and semiconductors
Chinese Internet and technology firms are capturing a growing share of global private equity and venture investment. In 2018, global investors poured an estimated $81 billion into Chinese start-ups, accounting for 32% of invested global venture capital. This surge in investment has seen Greater China produce unicorns at a faster pace than the US, with Internet and technology deals making up roughly 85% of Greater China's PE investment growth over the past eight years.
The Chinese consumer's obsession with technology and convenience has been a significant driver of this trend. Chinese Internet users are quick to adopt new apps for online entertainment, payments, and education and travel services. This has resulted in a cutthroat competitive environment among the country's burgeoning Internet and tech companies, leading to a demanding corporate culture with grueling work hours.
The intense competition has also fueled the rapid growth of Chinese tech companies, as they expand outside their core products and services and acquire companies in diverse sectors such as financial services, gaming, education, healthcare, and artificial intelligence.
However, there are signs that China's new economy may be overheating, with asset values soaring and the potential for a speculative bubble to burst. Despite these risks, China's new economy is expected to bounce back from any crash due to its long-term potential.
The influx of investors has led to a saturation of the market for smaller deals, prompting a shift towards larger investments. The average deal size in 2018 rose to $213 million, up from $30 million in 2013.
While the US government's restrictions on outbound technology investment and AI, semiconductor, and quantum computing companies in "countries of concern" have impacted tech sector deals, alternative sources of capital from the Middle East and China's local funds are stepping up to fill the gap.
Overall, the technology sector, particularly IT, internet, and semiconductors, remains a key focus for Chinese private equity investors, driven by consumer demand, competitive dynamics, and the potential for rapid growth and expansion.
Workplace Savings and Investment Plans: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Healthcare
China's healthcare sector is attracting a lot of interest from private equity investors. The country's healthcare market is ripe for expansion, with rising incomes and an ageing population driving demand for quality medical services.
Private equity firms and hedge funds are investing heavily in China's healthcare industry, particularly in private hospitals and drug makers. The healthcare sector in China is predicted to become a US$1 trillion a year business by 2020, according to McKinsey & Company.
China's population of individuals aged 60 or older is set to increase by 90% to 240 million by 2020, according to the World Health Organisation. This ageing population, coupled with the one-child policy introduced in 1979 and officially phased out in 2015, means that the burden of caring for ageing parents will fall heavily on younger generations. As a result, there will be a greater demand for healthcare services, and private hospitals are expected to attract large amounts of capital in the coming years.
There is ample access to money for investment in China's healthcare sector, with fund-raising on a steep growth trajectory. The total amount of cash available through private equity/venture capital funds reached $40 billion in 2017, up from $4 billion in 2014. The number of funds has increased, and the average size of the funds has also ballooned.
Private equity investment in healthcare is not limited to China, however. Private investment in U.S. healthcare has grown significantly over the past decade, with investors keen to enter a large, rapidly growing, and recession-proof market with historically high returns. Private equity and venture capital firms are investing in health technology startups, addiction treatment facilities, and physician practices, among other areas. In 2018, the number of private equity deals in U.S. healthcare reached almost 800, with a total value of more than $100 billion.
NRIs: Understanding the Portfolio Investment Scheme
You may want to see also

Manufacturing
Chinese private equity firms, particularly local funds, are crucial in driving investments in the manufacturing sector. They have a strong focus on local enterprises and play a vital role in connecting with local business people and facilitating deals. This emphasis on local networks and relationships is a distinctive feature of China's private equity landscape.
International private equity firms also participate in the manufacturing sector, although their involvement may vary. Some international firms, such as Sequoia, have established USD and RMB funds in China, demonstrating their commitment to the market. However, domestic firms often have the upper hand due to their deeper connections and political involvement with the Chinese Communist Party.
The manufacturing industry in China attracts private equity investments across a range of sub-sectors. This includes investments in high-end manufacturing, which involves advanced technologies and innovative processes. Private equity investors seek opportunities in manufacturing companies with long-term growth potential, sustainable competitive advantages, and strong management teams.
The Chinese government also plays a significant role in the private equity market, being the leading investor in the country. Government-linked investments are particularly common in sectors like mining, construction, and real estate, where the state has a more dominant role.
Overall, the manufacturing sector in China presents attractive investment opportunities for private equity investors, both domestic and international. The sector's dynamism and diversity offer a range of options for investors seeking long-term growth and sustainable returns.
Maximizing Cloud Investment: Azure Cost Management Strategies
You may want to see also

Cleantech
China's cleantech sector has grown rapidly over the past decade, and the country is now the world's largest manufacturer of silicon solar PV and a dominant force in wind turbine manufacturing. It is also a significant end market for wind, solar thermal and solar PV.
Chinese investors in the cleantech sector are becoming increasingly sophisticated, looking beyond cheap deals and splashy technology to seek out good technology matches, complementary strategies and intangible value. They are also patient, driving a hard bargain.
The Chinese cleantech market is diverse, with most outbound investments executed via state-owned entities, but private firms are increasingly investing overseas, especially in cleantech.
Chinese investors are also active at the edges of cleantech, with favourite targets including LEDs, building energy management, smart grids and energy storage.
System-wide financial reforms are opening the doors for Chinese investors, including private equity and venture capital, to invest in global markets.
Some of the top private equity firms in China include Blackstone, Boyu Capital, Carlyle, CITIC Capital, and Warburg Pincus.
Equity-Indexed Annuities: Investment or Insurance Product?
You may want to see also

Real estate
Chinese private equity investors have shown a strong interest in real estate, both domestically and internationally. In a bid to revive the country's real estate sector, China has encouraged foreign investment in this area. This has led to the establishment of property-focused private equity investment funds, with qualified managers allowed to set up funds dedicated to residential and commercial property.
Chinese investment firms have been particularly active in this regard, acquiring stakes in property companies and real estate projects worldwide. For example, Chinese investment firm Fosun Property Holdings acquired a stake in the French property firm Paris Realty Fund (Paref) for $48 million. Paref Group operates in commercial and residential investments and management on behalf of third parties, with a significant portfolio of assets.
Chinese investors have also targeted iconic properties, such as the famous UK pub, The Plough at Cadsden, near the UK Prime Minister's countryside residence, acquired by SinoFortone Group for $2.5 million. Additionally, Chinese investors have made significant purchases in the US, such as the Bank of China's acquisition of a Manhattan office building for $600 million and Anbang Insurance Group's purchase of the Hilton Waldorf Astoria New York for $1.95 billion, the largest US real estate purchase by a Chinese firm.
Chinese private equity investors are also investing in real estate in other parts of the world, including the UK, Canada, and Australia. For instance, the SinoFortone Group has announced investments of up to $328 million in the UK tourism sector, including the Lakeview Country Club purchase. In Canada, Chinese investors from the Zhong Ya Group Hebei acquired an entire ghost town, Bradian, in British Columbia, for $850,000. Chinese property investors have also been acquiring properties in Manly, Australia.
Savings vs. Investments: Understanding the Key Differences
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Chinese private equity investors like to invest in a variety of industries, including technology (especially IT, internet, and semiconductors), healthcare, manufacturing, cleantech, consumer, energy, real estate, and financial services.
Some examples of Chinese private equity firms include Blackstone, Boyu Capital, BPEA EQT, Carlyle, CDH Investments, CITIC Capital, FountainVest, General Atlantic, GLP China, and Hillhouse.
Chinese private equity investors consider factors such as long-term growth potential, sustainable competitive advantages, and the caliber of the management team. They also prefer local firms and local funds due to the hyper-local nature of the Chinese market.







