Negative interest rates are an unconventional monetary policy tool used to stimulate economic activity and stave off inflation. They occur when interest rates dip below 0%, usually during periods of deflation when the value of a nation's currency rises due to a drop in prices. During these periods, central banks may set interest rates into negative territory, meaning borrowers may be credited interest rather than having to pay it. While negative interest rates can provide opportunities for certain investors, they also carry risks and can impact assets like mortgages and bonds.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| When do negative interest rates occur? | During periods of deflation |
| What happens during deflation? | The value of a nation's currency rises because of a drop in prices |
| What does this mean for borrowers? | They may be credited interest rather than having to pay it |
| What is an example of this? | A -2% interest rate means the bank pays the borrower $2 after a year of using the $100 loan, instead of the other way around |
| What are negative interest rates intended to do? | Stimulate economic activity and stave off inflation |
| What are some policymakers concerned about? | There are several ways negative interest rates could backfire, for example, with certain assets like mortgages |
| What are the opportunities for investors? | People who already own bonds will benefit because existing bonds rise in value when interest rates decline |
| What about retirees who have relied on fixed income investing? | They will learn the meaning of "interest rate risk" when their bonds mature during a time of negative interest rates |
| What is interest rate risk? | The inability to reinvest your principal in a way that yields the same fixed return |
| What is the alternative? | Dividend-paying stocks, which can further push up the price of dividend-paying stocks |
What You'll Learn

How negative interest rates work
Negative interest rates are an unusual monetary policy tool, which can be used to stimulate economic activity and stave off inflation. They are usually employed during periods of deflation, when the value of a nation's currency rises because of a drop in prices.
During deflationary periods, people tend to hoard money rather than spend or invest it, which causes aggregate demand to collapse. This leads to a slowdown or halt in real production and output, and an increase in unemployment.
Negative interest rates are a way to encourage people to spend and invest their money, rather than keeping it in a bank account. This is because, with negative interest rates, borrowers may be credited interest rather than having to pay it. For example, a 2% interest rate means that a bank would pay a borrower $2 after a year of using a $100 loan, instead of the borrower paying the bank.
However, negative interest rates can also have a negative impact on certain assets, such as mortgages. They can also affect retirees who have relied on fixed income investing to provide a steady flow of cash. When their bonds mature during a time of negative interest rates, they may find that they are unable to reinvest their principal in a way that yields the same fixed return.
Investment Interest: AMT Adjustments Explained
You may want to see also

The impact on bond holders
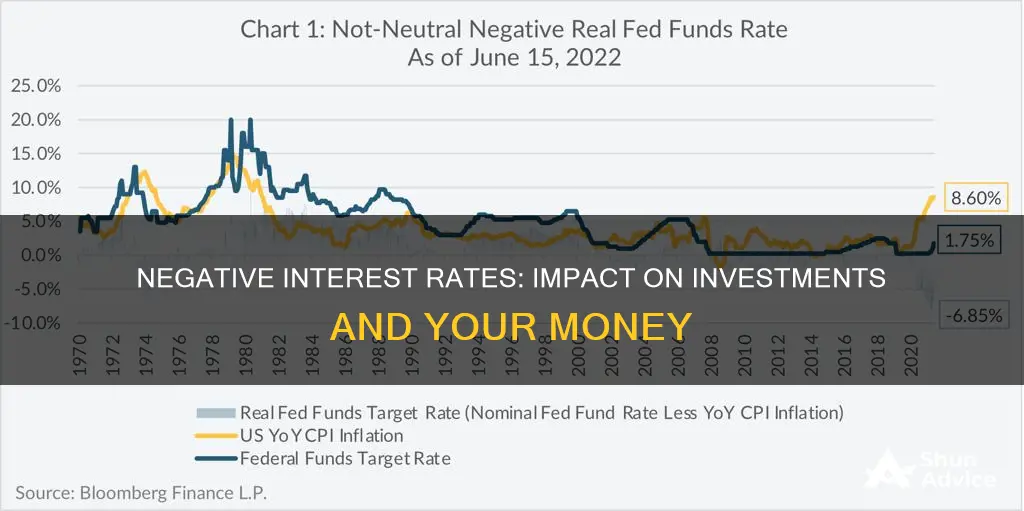
Negative interest rates occur when interest rates dip below 0%. This happens during periods of deflation, when the value of a nation's currency rises because of a drop in prices. Central banks may have to set interest rates into negative territory to stimulate economic activity and stave off inflation.
When interest rates are negative, people who already own bonds will benefit. This is because existing bonds rise in value when interest rates decline. However, retirees who have relied on fixed income investing to provide a steady flow of cash will learn the meaning of "interest rate risk" when their bonds mature during a time of negative interest rates. Interest rate risk refers to the inability to reinvest your principal in a way that yields the same fixed return. Dividend-paying stocks will, as a result, represent a more attractive alternative. This demand can then further push up the price of dividend-paying stocks.
Send Home Investment Interest: Worthwhile or Wasteful?
You may want to see also

Interest rate risk
Negative interest rates occur when interest rates dip below 0%. This happens during periods of deflation, when the value of a nation's currency rises because of a drop in prices. Central banks may then have to set interest rates into negative territory. This means that borrowers may be credited interest rather than having to pay it. For example, a -2% interest rate means the bank pays the borrower $2 after a year of using a $100 loan, instead of the other way around.
Negative interest rates are an unconventional monetary policy tool. They are used to stimulate economic activity and stave off inflation. However, there are several ways they could backfire. For example, consider what happens with certain assets like mortgages.
Despite the risks, astute investors can find uncommon opportunities in such situations. The most obvious case is the same advantage all bondholders experience during periods of falling interest rates. People who already own bonds will benefit because currently existing bonds rise in value when interest rates decline.
Dollar Interest Rate Changes: Impact on Your Investments
You may want to see also

The role of central banks
Negative interest rates are an unusual monetary policy tool used by central banks to stimulate economic activity and stave off deflation. During deflationary periods, the value of a nation's currency rises because of a drop in prices. This can lead to a collapse in aggregate demand, a further fall in prices, a slowdown or halt in real production and output, and an increase in unemployment.
Central banks may have to set interest rates into negative territory to encourage borrowing and lending. This means that borrowers may be credited interest rather than having to pay it. For example, a 2% interest rate means the bank pays the borrower $2 after a year of using a $100 loan, instead of the other way around.
Negative interest rates can also affect certain assets like mortgages, and retirees who have relied on fixed-income investing. However, astute investors can find uncommon opportunities in such situations. For example, people who already own bonds will benefit because existing bonds rise in value when interest rates decline. This demand can then further push up the price of dividend-paying stocks.
Understanding the Power of Compounding: Doubling Investments
You may want to see also

The effect on retirees
Negative interest rates occur when interest rates dip below 0%. This happens during periods of deflation, when the value of a nation's currency rises because of a drop in prices. During these periods, central banks may have to set interest rates into negative territory. This means that borrowers may be credited interest rather than having to pay it. For example, a 2% interest rate means that a bank would pay the borrower $2 after a year of using a $100 loan, instead of the other way around.
Negative interest rates are intended to stimulate economic activity and stave off inflation. However, they can have a significant impact on retirees. Those who have relied on fixed-income investing to provide a steady flow of cash will learn the meaning of "interest rate risk" when their bonds mature during a time of negative interest rates. Interest rate risk refers to the inability to reinvest your principal in a way that yields the same fixed return.
Retirees may need to consider alternative investment options to maintain their income. Dividend-paying stocks can represent an attractive alternative to fixed-income investing during periods of negative interest rates. The demand for these stocks can push up their price. However, it is important to carefully consider the risks associated with any investment, especially during times of economic uncertainty.
Negative interest rates can also impact other assets, such as mortgages. It is important for retirees to stay informed about the potential implications of negative interest rates on their investments and seek professional advice if necessary.
Calculating Total Investment: Understanding Annual Interest Accrual
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Negative interest rates are when interest rates dip below 0%. This happens during periods of deflation, when the value of a nation's currency rises because of a drop in prices.
Negative interest rates can cause interest rate risk, which is the inability to reinvest your principal in a way that yields the same fixed return. However, people who already own bonds will benefit, because existing bonds rise in value when interest rates decline.
Negative interest rates should help to stimulate economic activity and stave off inflation. They can also be used to deal with economic stagnation, when people hoard money rather than spend or invest it.