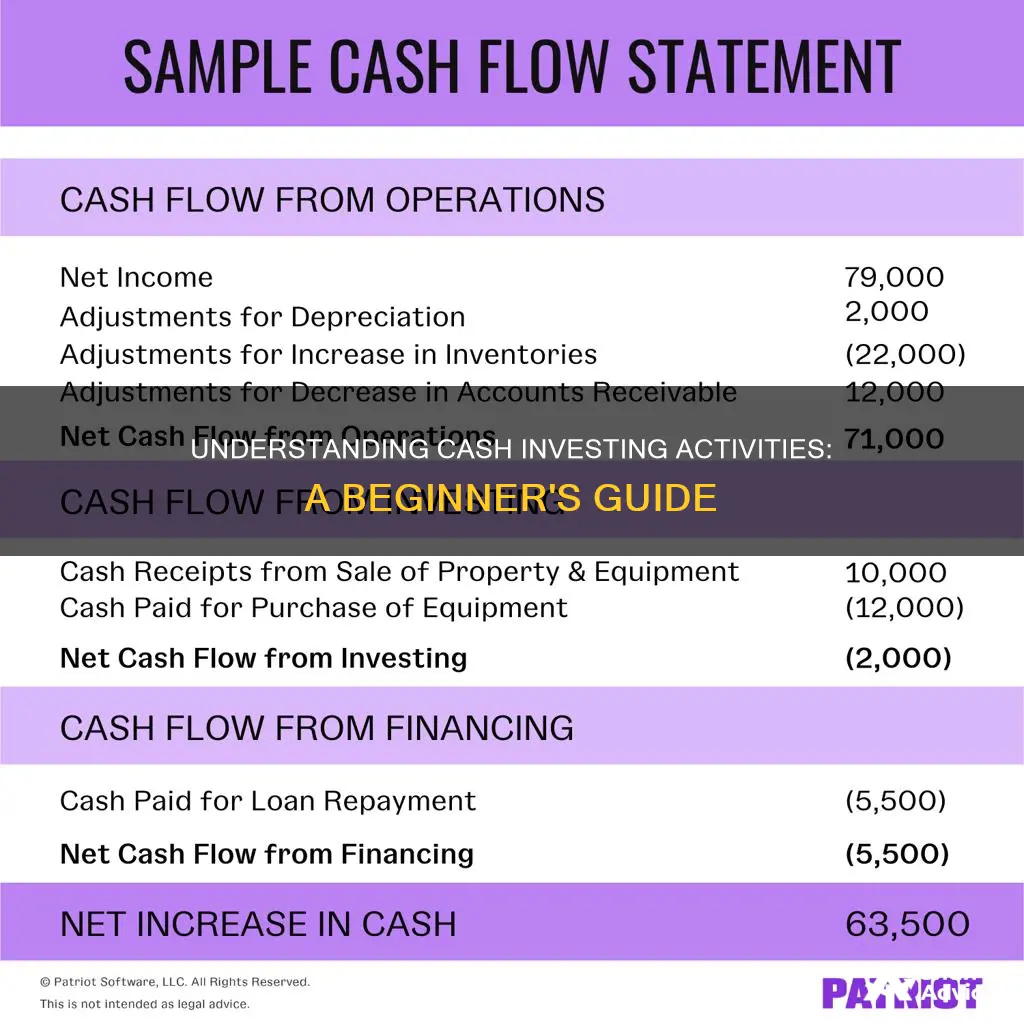
Cash flow from investing activities (CFI) is a section of a company's cash flow statement that shows the cash generated by or spent on investment activities over a specific period. It includes any cash inflows or outflows from a company's long-term investments, such as the purchase or sale of physical assets, investments in securities, or the acquisition of other businesses. CFI is an important indicator of a company's financial health and growth strategy, providing insights into how effectively a company manages its cash and investments.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Section of company's cash flow statement | Cash Flow from Investing Activities (CFI) |
| Purpose | To display how much money has been used in or generated from making investments during a specific time period |
| Types of activities | Purchases of long-term assets, acquisitions of other businesses, investments in marketable securities, proceeds from the sale of assets or investments, loans, debt instruments, equity instruments, investment pools |
| Cash inflows | Proceeds from sales of equity instruments, returns from investments, cash receipts from interest and dividends, cash receipts from investment pools |
| Cash outflows | Cash payments for loans, acquisition of debt instruments, cash payments to acquire equity instruments, cash payments into investment pools |
| Formula | Cash Flow from Investing Activities = (Capital Expenditures) + (Purchase of Long-Term Investments) + (Business Acquisitions) – Divestitures |
| Interpretation | Positive CFI indicates divestment of assets, while negative CFI suggests heavy investment in fixed assets for future growth |
What You'll Learn

Long-term assets and investments
Long-term assets can be tangible, such as property, plant, and equipment, or intangible, such as trademarks, patents, and goodwill. They are expected to benefit the company for many years and are not easily liquidated into cash. This makes long-term assets less liquid than current assets, which can be converted into cash within a year. Examples of long-term assets include:
- Fixed assets: Land, machinery, buildings, fixtures, and vehicles.
- Long-term investments: Stocks, bonds, real estate, and investments in other companies.
- Intangible assets: Trademarks, patents, copyrights, franchises, and goodwill.
Long-term investments are not subject to adjustments due to temporary market fluctuations but may be written down to reflect declining market value. They can provide meaningful wealth creation over time, and investors can benefit from lower transaction fees and the power of compounding. However, long-term assets can be expensive and may require large amounts of capital, impacting a company's cash flow.
When analysing long-term assets, investors should consider the management team's ability to allocate capital effectively and understand that the benefits of these investments may not be realised for many years. Changes in long-term assets can indicate capital investment or liquidation. For example, a company investing in its long-term growth may use revenues to purchase more assets, while a company facing financial difficulties may sell long-term assets to raise cash for short-term operational costs.
Understanding Your Cash Available to Invest
You may want to see also

Capital expenditures
CapEx is important for companies to grow and maintain their business by investing in new property, plant, equipment, products, and technology. Financial analysts and investors pay close attention to a company’s capital expenditures as they can have a significant impact on cash flow.
There are two forms of capital expenditures: maintenance capex and growth capex. Maintenance capex refers to expenditures to maintain the current level of a company's operations, while growth capex refers to expenditures that will enable future growth.
The decision to capitalize or expense an expenditure depends on how long the benefit of that spending is expected to last. If the benefit is less than one year, it is expensed directly on the income statement. If the benefit is greater than one year, it is capitalized as an asset on the balance sheet. For example, the purchase of a building would be deemed a capital expenditure, whereas the purchase of office supplies like printer ink and paper would be an operating expense.
To calculate net capital expenditure, an analyst can use either a direct or indirect approach. The direct approach involves adding up all the individual items that make up the total expenditures, while the indirect approach involves looking at the value of assets on the balance sheet in conjunction with depreciation expense.
Easy Ways to Earn Paytm Cash Without Investment
You may want to see also

Business acquisitions
Cash flow from investing activities (CFI) is a section of a company's cash flow statement that details the cash inflows and outflows from investment activities over a specific period. This includes the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, as well as investments in securities. Business acquisitions are a key part of this, and these can be broken down as follows:
Acquisition of Another Company
The acquisition of another company is a significant investing activity. This involves a cash outflow, as the acquiring company purchases the assets, operations, or ownership of another company. This type of investment can be a strategic decision to expand operations, gain a competitive edge, or increase market share. It is often a long-term investment in the health and growth of the acquiring company.
Proceeds from Sales of Other Business Units
When a company sells a division or a subsidiary, it can generate cash inflows. This may be a strategic decision to focus on core competencies, restructure operations, or gain capital for other investments. The proceeds from such sales are considered investing activities and can positively impact the company's cash position.
Cash Flow Impact
The acquisition of another company typically results in a negative cash flow from investing activities in the short term. However, this does not necessarily indicate poor financial health. It showcases a company's commitment to investing in its future operations and potential for growth. Well-managed acquisitions can lead to significant long-term gains and improved financial performance.
Analysis of Business Acquisitions
Analysing business acquisitions is crucial for assessing a company's financial health and efficiency. Investors and analysts examine the cash flow statement to understand how a company allocates its resources for future growth. A company's ability to invest in acquisitions while maintaining a positive cash flow can be a positive sign, indicating effective capital allocation and strategic decision-making.
In summary, business acquisitions are a significant aspect of cash investing activities, involving the purchase or sale of entire companies or business units. These activities impact a company's cash flow and are carefully scrutinised by investors and analysts to gauge the company's financial health and strategic direction.
Understanding Owner Cash Investments: Reporting and Strategies
You may want to see also

Sale of fixed assets
The sale of fixed assets is a critical component of a company's cash flow statement, specifically within the investing activities section. Fixed assets are typically long-term assets that are expected to deliver value to the company in the future. Examples of fixed assets include property, plant, and equipment (PP&E).
When a company sells a fixed asset, it results in a positive cash flow, as cash is received in exchange for the sale. This is true even if the sale price is lower than the original purchase price, resulting in a loss for the company. The positive cash flow from the sale of fixed assets is reflected in the investing activities section of the cash flow statement.
For example, if a company sells a used vehicle or a computer, the proceeds from this sale will lead to an increase in cash flow, which is recorded as a positive investing activity. This positive cash flow is essential for understanding the overall financial health and profitability of the company.
It's important to note that the sale of fixed assets can also be classified as an investing activity in financial statements. This classification distinguishes it from other types of activities, such as operating activities and financing activities.
The cash flow statement is a crucial tool for analysts and investors to assess the financial health and growth prospects of a company. By reviewing the investing activities section, they can gain insights into the company's capital expenditures and long-term investments.
In summary, the sale of fixed assets is a key component of the cash flow statement, contributing to positive cash flow and providing valuable information about the company's investment strategies and financial performance.
Maximizing Cash Value Life Insurance: A Smart Investment Guide
You may want to see also

Loans and debt instruments
Debt instruments, a type of financial asset, play a significant role in raising capital and generating investment income. They are commonly used by individuals, companies, and governments. Debt instruments can be in the form of fixed-income assets, such as bonds or debentures, or they can take the shape of credit facilities offered by financial institutions, like mortgages, loans, lines of credit, or credit cards. When an entity issues a debt instrument, it essentially functions as an IOU, with the purchaser providing a lump-sum payment and becoming the lender. In return, the issuer or borrower guarantees full repayment, often with interest, at a specified future date.
The acquisition and disposition of debt instruments by agencies or governmental enterprises are also considered cash investing activities. This includes the purchase and sale of debt instruments, such as bonds, debentures, or other types of securities. These transactions can result in cash inflows or outflows, depending on whether the agency is buying or selling these debt instruments. It's important to note that debt instruments can vary in terms of their backing or collateral. For instance, bonds are typically backed by the assets of the issuing entity, while debentures rely solely on the creditworthiness of the issuer.
Overall, loans and debt instruments are integral components of cash investing activities, encompassing a range of financial transactions that involve lending, borrowing, and the management of debt obligations. These activities are reflected in a company's cash flow statement and can have a significant impact on their long-term financial health and growth prospects.
Understanding Cash Flows from Ordinary Investing Activities
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Cash investing activities refer to the amount of cash that has been generated or spent on various investment-related business activities. This includes the purchase or sale of non-current assets, investments in securities, or acquisitions of other businesses.
Cash investing activities include making and collecting loans (except for program loans) and the acquisition and disposition of debt or equity instruments. It also includes proceeds from the sale of fixed assets or marketable securities.
Cash investing activities are important because they show how a company is allocating cash for the long term. It also provides insight into the company's financial health and investment strategy.
The formula for calculating cash flow from investing activities is: Cash Flow from Investing Activities = (Capital Expenditures) + (Purchase of Long-Term Investments) + (Business Acquisitions) – Divestitures.