Equity investment is a traditional form of investment that enables investors to obtain a stake in companies by purchasing shares. This makes them partial owners of the company, with voting rights and entitling them to a portion of the assets and profits. The return on investment can vary depending on the company, sector and market, but equity investments are usually one of many types of investments in a diverse investment portfolio.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | An equity investment is money that is invested in a company by purchasing shares of that company in the stock market. |
| Purpose | Investors purchase a company's shares, expecting them to accrue value over time and generate capital gains at the point of divestment or dividends. |
| Benefits | Equity investment is a traditional form of investment that many people are familiar with. The equity stake of shareholders often yields returns that are greater than more conservative or safer investments. |
| Notable benefits of equity investment include gains, liquidity, participation in decisions, limited liability, bonus share issues and stock splits, and the ability to manage multiple investments. | |
| Types | Common stocks, preferred stocks, stock warrants, equity line of credit, convertible debt, restricted stock |
| Risks | Market risk, credit risk, foreign currency risk, liquidity risk, political risk, economic concentration risk, inflation risk |
What You'll Learn

Equity investment funds
Equity funds are often categorised based on the size of the companies they invest in. Some funds focus on large-cap companies, which are typically well-established businesses with a history of stable growth and consistent dividends. Mid-cap funds invest in companies that are in the growth phase of their life cycle and may offer higher growth potential but carry more risk. Small-cap funds, on the other hand, focus on younger, less established businesses with high growth potential but tend to be more volatile and less liquid.
Actively managed equity funds have portfolio managers who actively research, analyse and select stocks with the goal of outperforming a benchmark index. The success of these funds depends largely on the fund manager's skill and decision-making ability. Passively managed funds, on the other hand, include index funds, which aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index. Passive fund managers do not attempt to outperform the market but instead track the index as closely as possible.
Equity funds provide investors with several benefits, including diversification, professional management, and the potential for superior returns. However, investing in equity funds also carries risks, mainly due to the volatility of the stock market. Market downturns, geopolitical events, or changes in investor sentiment can cause stock prices to decline, leading to potential short-term losses for investors.
When considering investing in equity funds, it is essential to assess your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and time horizon. These factors will help determine the type of equity fund that best aligns with your goals and risk profile.
Debenture Investment Guide for Indians: A Secure Option
You may want to see also

Equity and shareholder value
Equity is a term used in finance to describe the ownership interest in property that may be offset by debts or other liabilities. Equity is calculated by subtracting liabilities from the value of the assets owned. For example, if someone owns a car worth $24,000 and owes $10,000 on the loan used to buy the car, the difference of $14,000 is equity. Equity can apply to a single asset, such as a car or house, or to an entire business.
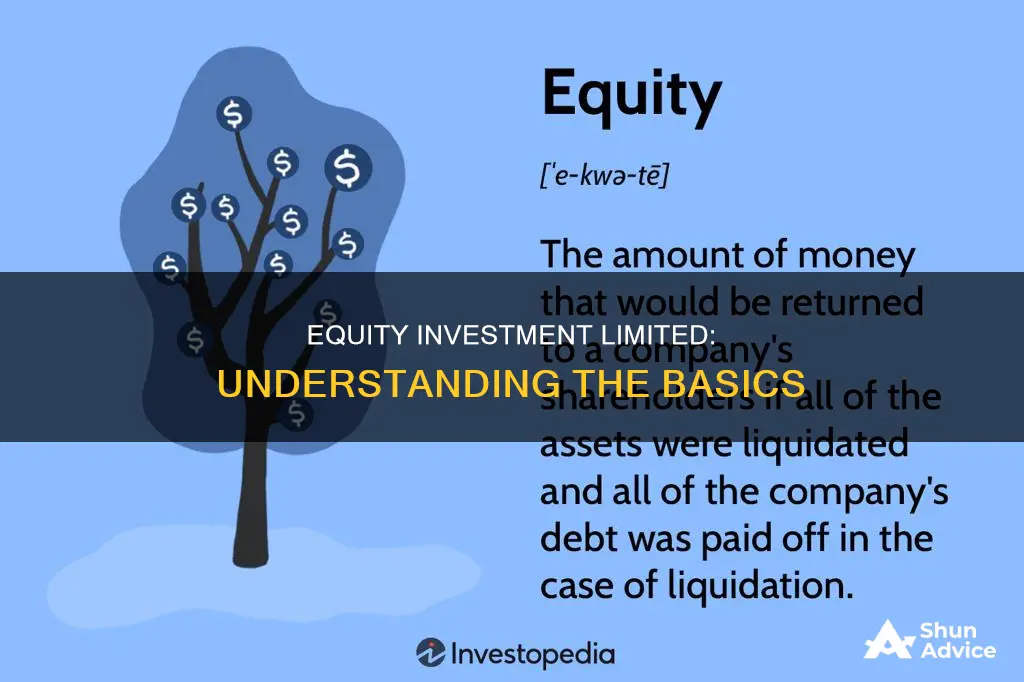
Shareholder equity, also known as stockholders' equity, represents the amount of money that would be returned to a company's shareholders if all of the assets were liquidated and all of the company's debt was paid off in the case of liquidation. It is the value of company sales minus any liabilities owed by the company not transferred with the sale. Shareholder equity can be either negative or positive. If positive, the company has enough assets to cover its liabilities. If negative, the company's liabilities exceed its assets; if prolonged, this is considered balance sheet insolvency.
Equity investment enables investors to obtain a stake in companies by purchasing shares. Equity investors purchase shares of a company with the expectation that they will accrue value over time and generate capital gains at the point of divestment or dividends. The primary incentive of equity investment is the potential to increase the value of the original investment. Investors receive the gains on the principal amount as capital gains and dividends. Equity investment is a traditional form of investment that many people are familiar with and often yields returns greater than more conservative or safer investments.
There are several types of equity investments, including common stocks, preferred stocks, stock warrants, equity lines of credit, convertible debt, and restricted stock. Common stocks confer a share of company profits and the right to take part in votes on corporate policy and the composition of the executive board. Preferred stocks entitle the holder to a higher claim on dividends and other asset distributions compared to common stockholders. Stock warrants provide the right to buy common stock at a specific time for a pre-arranged price. Equity lines of credit are used by companies to raise capital for use as needed, without the expense of debt. Convertible debt is a type of equity-based bond that a holder can cash in or convert into shares from the issuing company. Restricted stock is a special type of stock that carries specific restrictions on its transfer.
Equity funds are a type of investment fund that pools money from investors to trade primarily in a portfolio of stocks, also known as equity securities. Equity funds offer investors a professionally managed, diversified approach to investing in stocks, with the potential for attractive long-term returns. Equity funds are often categorized by investment style, portfolio focus, and level of diversification. Actively managed funds have portfolio managers who actively research, analyze, and select stocks with the goal of outperforming a benchmark index. Passively managed funds, including index funds, aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index. Equity funds can be further categorized by market capitalization, investment strategy, and sector and geographic specialization.
Understanding what equity investments are enables investors to evaluate the options, benefits, and risks of becoming a shareholder. Equity represents the shareholders' stake in the company and is a key indicator of the financial health of a business. Equity investments provide shareholders with the right to vote on corporate actions and elections for the board of directors.
Valuing Equity Growth Investments: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

Equity as security
A business that needs to start up or expand its operations can sell its equity to raise cash that does not have to be repaid on a set schedule. The equity of an asset can also be used to secure additional liabilities, such as home equity loans and home equity lines of credit.
The term "security" refers to a multitude of different investments, such as stocks, bonds, investment contracts, notes, and derivatives. An equity security represents ownership interest held by shareholders in an entity (a company, partnership, or trust), realized in the form of shares of capital stock, which includes shares of both common and preferred stock.
Holders of equity securities are typically not entitled to regular payments, but they are able to profit from capital gains when they sell the securities (assuming they've increased in value). Equity securities entitle the holder to some control of the company on a pro rata basis, via voting rights. In the case of bankruptcy, they share only in the residual interest after all obligations have been paid out to creditors. They are sometimes offered as payment-in-kind.
There are several advantages to owning equity securities. These securities give their holders voting rights and, in the case of liquidation, the right to a proportion of the earnings of the issuing organization. A sufficiently large amount of ownership of equity securities will give the owner voting control over a business.
Strategizing Your Investment Portfolio: A Smart Division Guide
You may want to see also

Equity in private companies
The most common awards include interest in the partnership or LLC (e.g., a profits interest), restricted stock (RS)/restricted stock units (RSU), and stock options (both non-qualified and incentive). These awards are similar to those offered by public companies but have unique complexities. For example, certain types of equity compensation require employees to remain with the company for a specific period before they earn full ownership of the equity.
Private company equity holders usually have very limited liquidity compared to public company equity, which is traded daily through public market exchanges. Private company equity is not listed on a stock exchange, and resales are restricted by regulations, making it generally illiquid.
Valuation is another important consideration for private company equity. It may include independent third-party appraisals, and the process can be complex. Additionally, private companies often retain certain rights upon granting equity, such as a right of first refusal, stock buyback, and/or repurchase rights.
Overall, private company equity presents a unique set of opportunities and challenges that require careful evaluation and sometimes professional guidance. It offers the potential for significant growth and upside but also carries inherent risks that should be carefully considered.
Taxable Investment Portfolio: Diversification Strategies for Long-Term Growth
You may want to see also

Equity in mature companies
Mature companies are valued based on forecasts of earnings and cash flows, which are built on assumptions about how the company will be run. The value of a firm is a function of five key inputs, and changes in three of them can increase operating asset value. These are:
- Cash flow from assets in place or investments already made
- Expected growth rate in the cash flows during a period of high growth and excess returns
- Length of time before the firm becomes a stable growth firm
There are two aspects of financing that affect the cost of capital and, therefore, the value of a firm. Firstly, the mix of debt and equity used to fund operations. Secondly, the choices of financing in terms of seniority, maturity, currency, and other features.
While debt is often cheaper than equity, equity has advantages. For instance, cash flow to equity investors, such as dividends, are generally not tax-deductible, whereas interest paid on debt financing is. This gives equity a tax advantage.
Equity investors also have more upside from risky investments than lenders, and they can influence management decisions. Equity investors will tend to take more risk in investments than lenders, and they can alter financing and dividend policies to serve their interests.
In terms of investing in mature companies, Permanent Equity, for example, invests in mature businesses with $3-25+ million in net profits.
Portfolio Investments: Global Politics' Impact
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Equity investment is when investors buy shares in a company, becoming partial owners and entitling them to a portion of the company's assets and profits.
Equity investment offers the potential for high returns, with gains made through capital gains and dividends. It is also a liquid asset, allowing investors to buy and sell shares with ease.
The main risk is market risk, where economic downturns or changes in investor sentiment can cause share prices to decline. Other types of risk include credit risk, foreign currency risk, liquidity risk, political risk, and economic concentration risk.
You can invest in equity by purchasing shares on a stock exchange, either directly or through an investment fund. It is important to research the company and consider your financial goals and risk tolerance before investing.
Equity is the value of a company's shares, calculated by subtracting its total liabilities from its total assets. It represents the amount of money that would be returned to shareholders if the company's assets were liquidated and all debts were paid off.