The average stock market return is about 10% per year, as measured by the S&P 500 index. However, this 10% average rate is reduced by inflation, and investors can expect to lose purchasing power by 2% to 3% annually due to inflation. The average hourly earnings in the US measure the change in the price businesses pay for labour, excluding the agricultural sector.
What You'll Learn

Average stock market return
The average stock market return is about 10% per year, as measured by the S&P 500 index. However, this 10% average rate is reduced by inflation, which causes investors to lose purchasing power of 2% to 3% every year.
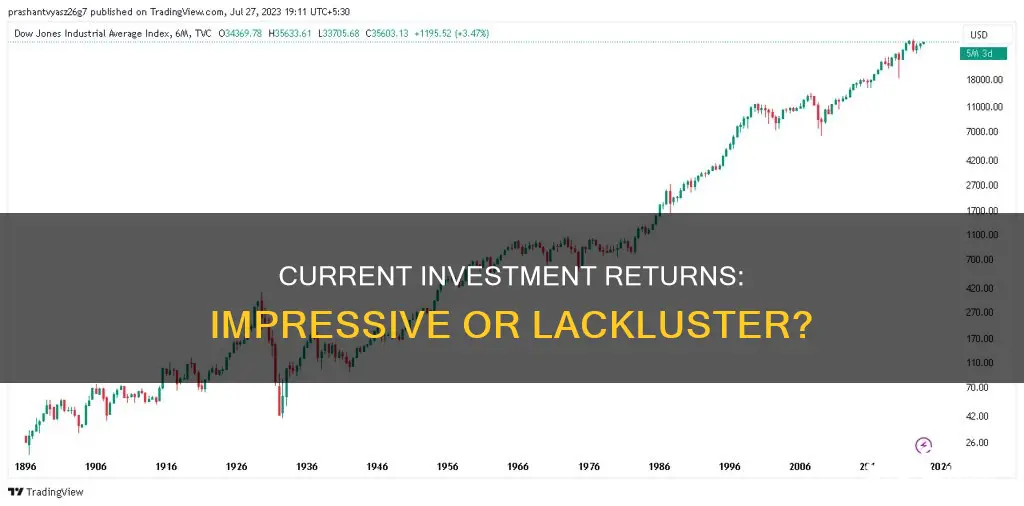
The average stock market return is not always average. While 10% might be the average, the returns in any given year can vary significantly. In fact, between 1926 and 2024, returns were in the "average" band of 8% to 12% only eight times. The rest of the time they were much lower or, usually, much higher.
The S&P 500 has returned a median compound annual growth rate of 9.3% during Democratic presidencies and 10.2% during Republican presidencies since its inception in 1957. However, the stock market's performance cannot be attributed to the political party in power, as macroeconomic fundamentals control the stock market.
The stock market is most effective for long-term investments—money you don't need for at least five years. For shorter time frames, lower-risk options such as a high-yield online savings account are more suitable, with the trade-off being a lower return.
If you're estimating how much your stock-market investment will return over time, it's suggested to use an average annual return of 6%, with the understanding that there will be down years as well as up years.
- Temper your enthusiasm during good times: When stocks are running high, remember that the future is likely to be less positive than the past.
- Become more optimistic when things look bad: A down market should cause you to celebrate as you can buy stocks when they're essentially on sale and anticipate higher future returns.
- You get the average return only if you buy and hold: If you trade in and out of the market frequently, you can expect to earn less due to commissions and taxes eating up your returns.
Investing During Depressions: Strategies for Success
You may want to see also

Average hourly earnings
In the US, the average hourly wage rose by 10 cents, or 0.3%, to $35 in June 2024. This was an increase of 3.9% over the previous 12 months. The average workweek for all employees on private nonfarm payrolls remained unchanged at 34.3 hours in June. However, the average workweek for manufacturing employees was 40.3 hours, with 2.9 hours of overtime. For production and non-supervisory employees, the average workweek increased to 34.1 hours, up from 33.6 hours the previous month.
Shark Tank: Payback Time?
You may want to see also

ROI calculation
Return on Investment (ROI) is a profitability ratio that compares the net profits received from an investment to the original cost of that investment, expressed as a percentage. ROI is calculated by dividing the net profit (or return) of an investment by the cost of the investment. The formula for calculating ROI is as follows:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100
Alternatively, the ROI formula can be rearranged to the following:
ROI = (Final Value of Investment - Initial Value of Investment) / Initial Value of Investment x 100
ROI is a useful metric for evaluating the efficiency and profitability of an investment. It is often used to compare the performance of different investments or to assess the potential return of an investment. However, it is important to note that ROI does not take into account the holding period, opportunity costs, or the impact of inflation on investment returns. As such, it may not always provide a complete picture of an investment's performance.
When calculating ROI, it is important to consider all relevant costs and returns associated with the investment. For example, in the context of a real estate investment, potential costs could include maintenance, repairs, insurance, and lost rental income. By accurately accounting for all costs and returns, investors can make more informed decisions and comparisons between different investment opportunities.
Additionally, it is worth noting that the average stock market return, as measured by the S&P 500 index, has been approximately 10% per year over the long term. However, individual years can vary significantly, and this average return is reduced by inflation. Therefore, investors should consider their investment horizons, risk tolerance, industry norms, and personal goals when evaluating the potential ROI of an investment.
Blackberry: Invest or Avoid?
You may want to see also

Risk and return
Different types of risks include project-specific, industry-specific, competitive, international, and market risk. The return on an investment is usually expressed as a percentage and is considered a random variable that can take any value within a given range.
The appropriate risk-return tradeoff depends on factors such as an investor's risk tolerance, years to retirement, and the potential to replace lost funds. Time also plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate levels of risk and reward. For instance, if an investor can invest in equities over the long term, they have the potential to recover from bear markets and benefit from bull markets. Conversely, if an investor can only invest for a short time, the same equities present a higher risk.
When considering high-risk, high-return investments, investors can apply the risk-return tradeoff to a single investment and within the context of their portfolio as a whole. Examples of high-risk, high-return investments include options, penny stocks, and leveraged exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Diversifying a portfolio can reduce the risks presented by individual investment positions.
To calculate an appropriate risk-return tradeoff, investors can use the alpha, beta, or Sharpe ratio. The alpha ratio measures excess returns on an investment, while the beta ratio shows the correlation between a stock and the benchmark that determines the overall market (usually the S&P 500). The Sharpe ratio helps determine whether the investment risk is worth the reward.
It is important for investors to understand their risk profile and appetite before investing. This means knowing their level of comfort with risk and the types of investments suitable for them. While some investors are willing to take on more risk for potentially higher returns, others are more cautious.
Hydrogen's Future: Invest Now
You may want to see also

Rate of return
The rate of return is the profit or loss made on an investment, expressed as a percentage of the amount invested. For example, if you bought a stock for $10 and it's now worth $11, that's a 10% return.
The average stock market return is about 10% per year, as measured by the S&P 500 index. However, this average rate of return is reduced by inflation, which causes investors to lose purchasing power by 2-3% every year.
The rate of return on investments can vary significantly from year to year. For example, between 1926 and 2024, the average annual return of 10% was only achieved in eight years. In other years, the return was much lower or higher.
When considering the rate of return on investments, it's important to take a long-term view. While the market can be volatile in the short term, with positive and negative returns in different years, over time the market has gone up just over 70% of the years.
Additionally, the expected rate of return depends on what has happened in the recent past. If returns have been high recently, future returns are likely to be lower, and vice versa. It's also important to remember that frequent trading in and out of the market will reduce returns, as commissions and taxes eat up profits.
For those looking to invest, it's recommended to utilise long-term investments for money that won't be needed for at least five years. For shorter time frames, lower-risk options such as high-yield savings accounts are more suitable, although they offer lower returns.
Retirement Investments: Safe Options for the Elderly
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The average stock market return is about 10% per year, as measured by the S&P 500 index, but that 10% average rate is reduced by inflation. Investors can expect to lose purchasing power by 2% to 3% every year due to inflation.
Inflation reduces the average rate of return on investments. For example, an investment with a 10% return may only have a 7% to 8% effective return after accounting for inflation.
The average stock market return has been about 10% per year for nearly the last century. While the returns in any given year vary, the market has gone up just over 70% of the years.