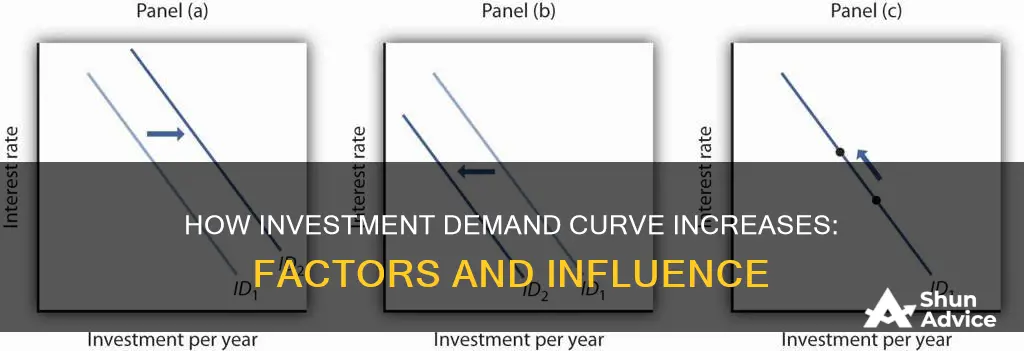
The investment demand curve illustrates the relationship between business spending on investment goods and interest rates. The curve is downward-sloping, indicating that businesses are more inclined to invest when interest rates are low. A change in the money supply leads to a change in interest rates, which, in turn, affects investment demand. When interest rates decline, the amount of investment increases, shifting the aggregate demand curve to the right. Conversely, when interest rates increase, investment demand decreases, causing a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
Other factors also influence the investment demand curve, including expectations of future profitability, the level of economic activity, the stock of capital, capacity utilization, the cost of capital goods, and technological advancements. Public policy decisions, such as tax rates and regulatory policies, can also play a significant role in shaping investment demand.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Interest rates | Lower interest rates increase the demand for investment, while higher interest rates decrease it |
| Expectations | Expectations of higher future sales or favourable economic conditions increase investment demand |
| Level of economic activity | A higher GDP boosts investment demand |
| Stock of capital | A larger stock of capital increases investment demand |
| Capacity utilization | A higher capacity utilization rate increases investment demand |
| Cost of capital goods | A lower cost of capital goods increases investment demand |
| Other factor costs | Lower labour costs and higher energy costs increase investment demand |
| Technological change | The implementation of new technology requiring new capital increases investment demand |
| Public policy | Fiscal policies that reduce the cost of capital for firms, such as accelerated depreciation, investment tax credits, lower taxes on corporate profits, and favourable capital gains tax rates, increase investment demand |
What You'll Learn

Low interest rates
Firstly, low interest rates make borrowing more affordable for both businesses and consumers. This incentivizes businesses to invest in capital goods, such as machinery or technology, as the cost of financing projects decreases. As a result, businesses are able to undertake more projects with the same amount of funds, leading to an increase in investment demand. Lower interest rates also encourage consumers to borrow and spend more, creating further opportunities for business expansion.
Secondly, the investment demand curve, which represents the relationship between business spending and interest rates, is downward-sloping. This means that as interest rates decrease, the quantity of investment demanded increases. This inverse relationship highlights the sensitivity of business investment decisions to changes in interest rates. When interest rates are low, businesses find it more profitable to invest, as they can maximize their returns while minimizing the cost of financing.
Additionally, low interest rates can have a positive impact on bank balance sheets. They help improve banks' capacity to lend by increasing their net interest margin (NIM), which boosts their retained earnings and capital. This, in turn, can lead to a more robust banking system that is better equipped to support economic growth.
Moreover, low interest rates can contribute to raising asset prices. When interest rates decrease, people tend to use their excess funds to increase their purchases of goods, services, and assets. This increased demand leads to higher prices for these assets, which can boost household wealth and lower the cost of financing for businesses.
However, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks of maintaining low interest rates for an extended period. While they can stimulate economic activity in the short term, they may also encourage excess borrowing and higher debt levels. Additionally, low interest rates can disincentivize saving, negatively impacting those who rely on interest income.
In summary, low interest rates play a crucial role in increasing investment demand by making borrowing more affordable, influencing the investment demand curve, improving bank lending capacity, and raising asset prices. However, it is essential to carefully manage these rates to avoid potential drawbacks and maintain a healthy economy.
Strategies to Optimize Your Investment Portfolio Performance
You may want to see also

Positive economic indicators
Interest Rates
Interest rates are a critical factor in the investment demand curve. Lower interest rates encourage businesses to invest more in capital goods, such as machinery or technology, as the cost of financing projects decreases. This, in turn, leads to an increase in investment demand. Conversely, higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, potentially discouraging business investments. The relationship between interest rates and investment demand is inverse, with lower interest rates stimulating more investment.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
An increase in GDP indicates a strong and growing economy, which can boost business confidence and investment demand. As firms experience higher levels of production, their demand for capital goods tends to increase, leading to greater investment. This creates a positive feedback loop, as the increase in investment further enhances the multiplier effect on GDP growth.
Economic Growth and Activity
Positive economic growth and increased economic activity can stimulate investment demand. When the economy is expanding, firms are more likely to invest in capital goods to meet the rising demand for their products or services. This additional investment can further fuel economic growth, creating a virtuous cycle.
Government Policies
Government policies, such as tax incentives, regulatory changes, and investment subsidies, can significantly impact investment demand. For example, policies that offer tax breaks or accelerated depreciation on capital investments can make investing more attractive to businesses. Additionally, government spending on infrastructure and public goods can directly contribute to investment demand.
Business Confidence and Expectations
Firms' expectations about future economic conditions and the potential return on investments can influence investment demand. When businesses anticipate higher future sales, favourable economic conditions, or positive regulatory changes, they are more likely to increase their investment spending. This positive sentiment can lead to a rightward shift in the investment demand curve.
In summary, positive economic indicators, such as low-interest rates, increasing GDP, economic growth, supportive government policies, and optimistic business expectations, can contribute to an increase in the investment demand curve. These indicators play a crucial role in shaping businesses' investment decisions and the overall economic landscape.
Convince and Persuade: Get Investors to Back Your Idea
You may want to see also

Increased GDP
Firstly, it's important to understand the concept of real GDP, which measures the total value of all goods and services produced in an economy while adjusting for inflation. When real GDP increases, it means there are more goods and services available in the economy. This increase in production and economic activity leads to a positive impact on investment demand.
As businesses expand their operations to meet the growing demand for goods and services, they require additional capital goods, such as machinery, technology, or construction of new facilities. This increased demand for investment goods shifts the investment demand curve to the right, indicating a higher quantity of investment demanded at any given interest rate.
Moreover, increased real GDP often leads to higher consumer spending and economic growth. Consumers demand more goods and services, which, in turn, encourages businesses to invest in capital projects to meet this increased demand. This positive economic outlook further fuels business confidence, leading to a higher demand for investment goods.
Additionally, a rise in real GDP can be indicative of favourable economic conditions, prompting businesses to invest in expansionary projects. Businesses may take advantage of the positive economic climate to invest in research and development, innovate, or diversify their product offerings. This strategic investment approach can help them gain a competitive edge and capture a larger market share.
It's worth noting that the relationship between increased GDP and investment demand is complex and influenced by various factors. Businesses also consider interest rates, forecasts about future demand, expectations about the economic climate, and government policies when making investment decisions.
In summary, increased GDP can lead to a rightward shift in the investment demand curve as businesses demand more investment goods to expand their operations and meet the growing demand for goods and services. This relationship underscores the importance of economic growth in driving investment and vice versa.
Diversifying Investments: Managing Financial Risk Strategically
You may want to see also

Expectations of high future sales
Firms' expectations of high future sales are shaped by various factors, including government policies, technological advancements, and shifts in consumer preferences. For instance, government announcements of favourable economic conditions or new regulations that reduce production costs can boost expectations and encourage firms to increase their supply. Similarly, advancements in technology that enhance production efficiency or reduce costs can lead to increased expectations and supply.
Consumer behaviour also plays a crucial role in shaping expectations of high future sales. When consumers expect a product to be in high demand, they may choose to purchase it earlier to avoid potential stockouts. This behaviour can create an immediate increase in demand, reinforcing firms' expectations and prompting them to produce more. Conversely, if consumers anticipate a decrease in demand or expect lower prices in the future, they may delay their purchases, leading to a decline in demand and a shift in the supply curve.
The relationship between expectations of high future sales and the supply curve is dynamic and complex. While firms may adjust their production and pricing strategies based on these expectations, they must also consider the potential for inaccurate assumptions about future market conditions. Accurate prediction of supply expectations is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about production, pricing, and distribution strategies.
In summary, expectations of high future sales can drive firms to increase production and supply, adjust pricing strategies, and manage inventory levels accordingly. However, it is important for businesses to continuously analyse market trends and consumer behaviour to align their expectations with actual demand and make strategic decisions that maximize profits and maintain competitiveness in the market.
Equity Investments: Fair Value Reporting Requirements
You may want to see also

Low opportunity cost of investing
The opportunity cost of investing is a crucial factor in the investment demand curve. It refers to the potential return that could be earned by choosing an alternative investment option, such as investing in bonds instead of a solar energy system. When the opportunity cost of investing is low, the investment demand curve increases.
For example, suppose a company is considering investing in a solar energy collection system that costs $10,000 and is expected to reduce energy bills by $1,000 per year indefinitely. The effective income from this investment is $1,000 per year, resulting in a 10% annual return. Now, suppose the company has the option to invest in bonds that offer an 8% interest rate. In this case, the solar energy system becomes a more attractive investment option, as it provides a higher return. As a result, the company is more likely to invest in the solar energy system, increasing the investment demand.
On the other hand, if the company could invest in bonds with a 12% interest rate, the opportunity cost of investing in the solar energy system would be higher, as the bonds offer a higher return. In this case, the company is more likely to choose the bonds, reducing the investment demand for the solar energy system.
The relationship between the opportunity cost of investing and the investment demand curve is inverse. When the opportunity cost is low, investment demand increases, and when the opportunity cost is high, investment demand decreases. This is because a lower opportunity cost makes a particular investment option more attractive relative to its alternatives.
Additionally, the interest rate plays a significant role in the opportunity cost of investing. A lower interest rate reduces the opportunity cost of investing, making it more attractive to invest in projects with potential returns that exceed the interest rate. Conversely, a higher interest rate increases the opportunity cost, making alternative investment options, such as bonds, more appealing. Therefore, the interaction between interest rates and the opportunity cost of investing has a substantial impact on the investment demand curve.
Creating Compelling Characters: Strategies for Reader Investment
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There is an inverse relationship between interest rates and the investment demand curve. When interest rates are low, businesses are more likely to invest as the cost of financing projects is lower. This leads to an increase in investment demand. Conversely, high-interest rates make borrowing more expensive, potentially discouraging business investments.
Expectations about future profitability can shift the investment demand curve. If expectations of increased profitability rise, the investment demand curve shifts to the right. On the other hand, if expectations of reduced profitability increase, the curve shifts to the left.
An increase in the level of economic activity, such as a rise in GDP, is likely to boost demand for capital and lead to greater investment. This, in turn, shifts the investment demand curve to the right.