Investment demand is a key component of aggregate demand, which is a macroeconomic term for the total demand for goods and services in an economy at a given price point. An increase in investment demand can lead to a shift in the aggregate demand curve, resulting in higher economic growth and potentially inflation. Various factors influence investment spending, including expected demand for goods and services, anticipated profits, interest rates, availability of finance, and business confidence. Lower interest rates, for example, can reduce borrowing costs and encourage businesses to invest in capital spending. Additionally, government policies, such as lowering corporation tax, can stimulate investment and have a positive impact on aggregate demand. Understanding the factors that drive investment demand is crucial for policymakers and businesses to make informed decisions that promote economic growth and stability.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Interest rates | Lower interest rates can lead to an increase in investment demand as borrowing costs are reduced. |
| Consumer wealth | An increase in household wealth typically leads to higher aggregate demand. |
| Inflation expectations | Consumers who anticipate higher inflation will tend to make immediate purchases, leading to rises in aggregate demand. |
| Currency exchange rates | A decrease in the value of the domestic currency will make foreign goods more expensive, increasing aggregate demand. |
| Economic conditions | Positive economic conditions, such as increased business investment spending, can positively impact aggregate demand. |
| Investment spending | Investment spending represents businesses' investment to support current output and increase production capability. |
| Government spending | Government spending on infrastructure and public goods can increase aggregate demand. |
| Net exports | A positive net export value, where exports exceed imports, can increase aggregate demand. |
What You'll Learn

Lower interest rates
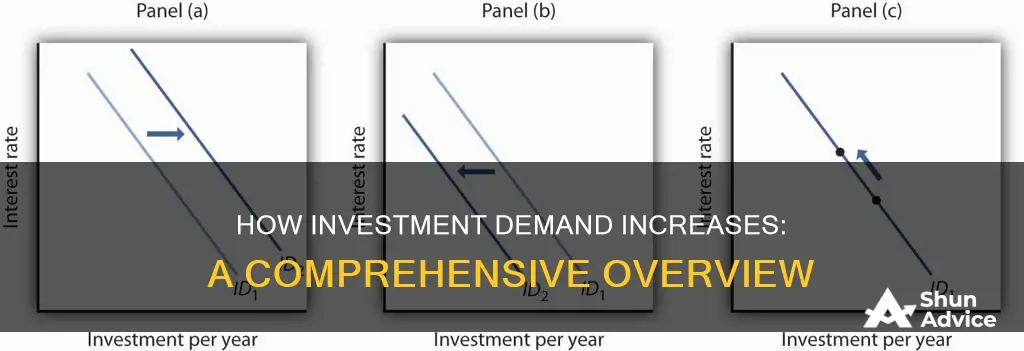
The relationship between interest rates and investment demand is closely linked to the concept of "animal spirits," a term coined by John Maynard Keynes. Animal spirits refer to a mix of confidence, trust, mood, and expectations in the economy. When interest rates are low, businesses and individuals tend to have higher confidence in the economy, which can lead to increased investment and spending. This can create a positive feedback loop, further stimulating investment demand.
Furthermore, lower interest rates can have a direct impact on investment demand by making investments in financial assets more attractive. When interest rates are low, the opportunity cost of investing in riskier assets, such as stocks or business ventures, decreases. This is because the returns offered by safe investments, such as government bonds or savings accounts, are relatively lower, making riskier investments more appealing. As a result, investors may be more inclined to allocate their capital towards investments with higher potential returns, thereby increasing investment demand.
It is worth noting that while lower interest rates can stimulate investment demand, they may also have potential drawbacks. For example, in times of very low-interest rates, individuals may become discouraged from saving, as the returns on savings accounts are diminished. This can lead to reduced financial stability for individuals and a potential increase in household debt. Additionally, prolonged periods of low-interest rates can lead to the formation of asset bubbles, as investors seek higher returns in riskier assets, potentially destabilizing the financial system. Therefore, while lower interest rates can be a powerful tool to stimulate investment demand, they must be used judiciously and complemented with other economic policies to ensure a stable and sustainable economy.
Smart Strategies to Turn $2K into $4K
You may want to see also

Increased business confidence
Business confidence is a critical factor in increasing investment demand. When businesses are confident about the future, they are more likely to invest in capital expenditures, such as purchasing new equipment or expanding their operations. This increase in investment then has a positive impact on the economy, creating a ripple effect of benefits.
Firstly, increased business confidence can lead to higher investment spending. Businesses with a positive outlook are more willing to invest in their operations and future growth. This could involve investing in new technology, research and development, or expanding their physical presence, such as building bigger factories or opening new stores. Such investments can increase a company's production capacity and efficiency, enabling them to meet rising demand and expand their operations.
Secondly, higher business confidence can lead to increased output and economic growth. As businesses invest more, they can produce more goods and services, leading to an increase in aggregate supply. This increased supply can then meet rising consumer demand, driving economic growth and potentially reducing unemployment as more workers are needed to support the expanded operations.
Additionally, increased business confidence and investment can have a positive impact on consumer spending. When businesses are confident and investing, it sends a positive signal to consumers, who may feel more secure about their own financial prospects. As a result, consumers may spend more, further boosting aggregate demand and creating a virtuous cycle of economic growth.
Moreover, business confidence can influence investment decisions regarding new products and services. When businesses are confident, they are more likely to invest in innovation and bring new offerings to market. This can stimulate consumer demand, as people are often willing to spend on the latest technologies, services, or experiences. This dynamic can be particularly impactful in sectors such as technology, entertainment, and fashion, where consumer demand is driven by a desire for novelty and the latest trends.
Lastly, government policies can play a role in boosting business confidence and, by extension, investment demand. Governments can implement fiscal policies, such as lowering corporate tax rates or offering tax incentives, to encourage businesses to invest. These policies signal to businesses that the government is supportive of their growth and development, which can increase their confidence and willingness to invest in new projects and initiatives.
Do Investment Managers Beat the S&P Performance?
You may want to see also

Higher consumer spending
Consumer spending is the largest component of a country's gross domestic product (GDP). In the United States, for example, consumer spending accounts for over two-thirds of the nation's GDP. As consumers spend more on everyday goods and services, as well as large one-time purchases, businesses see a direct increase in their revenue. This rise in revenue provides businesses with the financial means and incentive to invest in their operations.
A strong job market, low unemployment rates, and wage increases are significant contributors to higher consumer spending. When individuals have stable and well-paying jobs, they tend to spend more, which boosts the economy and encourages businesses to invest in growth. Additionally, consumer confidence and sentiment play a crucial role in driving consumer spending. Optimistic consumers are more likely to make purchases and contribute to higher aggregate demand.
The wealth effect also influences consumer spending. When consumers have higher purchasing power, they tend to spend more. Conversely, during periods of economic uncertainty or high inflation, consumers may become more cautious and reduce their spending, which can lead to decreased investment demand.
It's important to note that the relationship between consumer spending and investment demand is complex and subject to various economic factors. While higher consumer spending generally stimulates investment demand, businesses also consider other factors when making investment decisions, such as expected demand, spare capacity, and business confidence. Nonetheless, higher consumer spending remains a critical factor in increasing investment demand and promoting economic growth.
Equities Investment Guide for Indians: Getting Started
You may want to see also

Increased government spending
Investment demand is a component of aggregate demand (AD), which is the total amount of demand for all finished goods and services in an economy. AD is calculated using the formula: Consumer Spending (C) + Investment Spending (I) + Government Spending (G) + Net Exports (NX).
For example, government investment in improving the road network can reduce congestion and contribute to long-term economic growth. Additionally, governments can encourage investment by lowering corporation tax and offering tax incentives, making it more attractive for businesses to invest.
However, it is important to note that government spending on services such as Medicare or social security is not included in the calculation of AD, as these programs only transfer demand from one group to another without creating new demand.
Futures and Equity: Two Sides of Investment Strategy
You may want to see also

Higher business investment
Business investment is a key component of aggregate demand, and an increase in investment can lead to a rise in aggregate demand and economic growth. Investment spending includes businesses investing in new capital assets, such as equipment and facilities, to support current output and increase production capacity.
There are several factors that influence business investment spending. Firstly, businesses tend to invest more when they expect rising demand for their goods and services, and when they have limited spare capacity to meet that demand. Secondly, lower interest rates can encourage businesses to borrow more for capital spending, while higher interest rates may lead to reduced investment. Thirdly, government policies can impact business investment. For example, lowering corporation tax or offering tax incentives can increase investment, while contractionary fiscal policies, such as raising taxes or decreasing government spending, may lead to reduced investment.
Business confidence also plays a crucial role in investment decisions. When confidence is high, businesses are more likely to invest in new projects and expand their operations. Conversely, when confidence is low, businesses may postpone or cancel investment plans, leading to reduced investment and potentially causing an economic contraction.
The effectiveness of business investment in boosting aggregate demand and economic growth depends on various factors, including the type of investment and the economic circumstances. For instance, during a period of falling house prices and lower consumer spending, increased business investment may not be sufficient to increase aggregate demand. Additionally, the opportunity cost of investment should be considered, as a higher share of GDP devoted to investment in the short term could mean lower consumption.
Fidelity Investments: Branch Deposits and You
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Lower interest rates will lower the borrowing costs for big-ticket items such as appliances, vehicles, and homes. Companies will be able to borrow at lower rates, often leading to capital spending increases. Conversely, higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for consumers and companies, and spending tends to decline or grow at a slower pace.
As household wealth increases, aggregate demand typically increases. Conversely, a decline in wealth usually leads to lower aggregate demand. When consumers are feeling good about the economic outlook, they tend to spend more and save less.
The government can lift investment by lowering corporation tax or offering other tax incentives as part of their fiscal policy.