Investing in mutual funds is a popular way to diversify your portfolio and benefit from the stock market's high average annual returns. Mutual funds are an investment vehicle that pools money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. They are managed by professional fund managers and provide investors with access to a wide range of assets. When deciding which type of fund to invest in, it is important to consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. There are several types of mutual funds available, including stock funds, bond funds, money market funds, and target-date funds, each with its own investment strategy, risk level, and fee structure. It is crucial to understand the fees associated with mutual funds, such as expense ratios, sales charges, and redemption fees, as they can significantly impact your investment returns. Additionally, mutual funds can be actively or passively managed, with passive funds typically having lower fees and aiming to replicate the performance of a market index. When choosing a mutual fund, it is important to research the fund's past performance, fees, and investment strategy to ensure it aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Risk tolerance | Can you accept dramatic swings in portfolio value? |
| Investment goals | Long-term capital gains or current income |
| Time horizon | How long do you want to hold the investment? |
| Liquidity | High, medium, or low |
| Investment types | Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), money market funds, target-date funds |
| Investment styles | Active or passive |
| Fees | Sales fee/load, expense ratio, 12b-1 fees, redemption fees, other account fees |
| Diversification | Yes or no |
What You'll Learn

Mutual funds
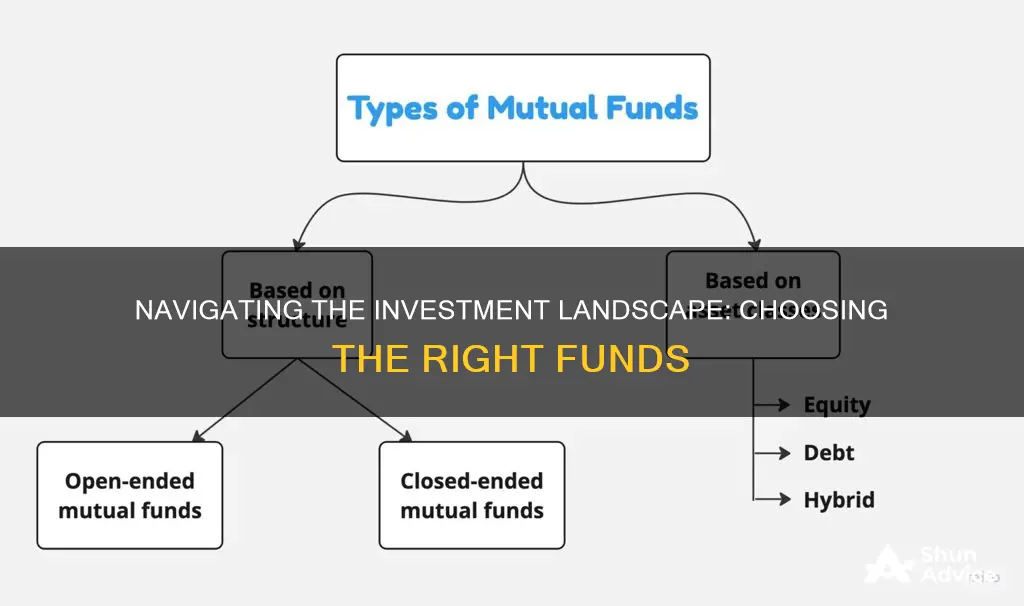
There are several types of mutual funds, including stock, money market, bond, and target-date funds, each with its own investment profile, risk level, performance results, and fees.
- Diversification: Mutual funds offer instant diversification, as they invest in a collection of companies rather than a single stock. This helps to spread risk across multiple investments.
- Professional management: Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers who make decisions about which securities and assets to include in the fund. This provides individual investors with access to full-time, skilled money management at a relatively low cost.
- Accessibility: Mutual funds have minimal investment requirements, making them accessible to a wide range of investors. They are also traded on major stock exchanges, making them relatively easy to buy and sell.
- Variety: There are thousands of mutual funds available through brokerage platforms or the funds themselves, offering investors a wide range of choices to match their investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Fees: Mutual funds charge various fees, including annual fees, expense ratios, and commissions, which can impact overall returns. It is important to carefully review and understand the fee structure before investing.
- Performance: The performance of mutual funds varies, and past performance does not guarantee future results. When evaluating mutual funds, it is essential to consider factors such as the fund's investment strategy, the track record of the fund manager, and the fund's returns over different time horizons.
In summary, mutual funds offer a relatively accessible and diversified investment option for those seeking exposure to a wide range of assets. They are suitable for investors with different risk tolerances and investment goals, providing a balanced approach to investing. However, it is crucial to carefully research and understand the fees, risks, and potential returns associated with mutual funds before investing.
Skills for Investment Fund Managers: Expertise for Success
You may want to see also

Index funds
When investing in index funds, it is important to consider the fund's expense ratio, which represents the annual fee charged by the fund manager. Lower expense ratios result in higher returns for investors. It is also crucial to understand the fund's investment strategy, performance track record, and the level of risk involved.
Some of the best index funds in the market include the Fidelity ZERO Large Cap Index, Vanguard S&P 500 ETF, and SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust. These funds offer broad diversification, low expense ratios, and have delivered attractive long-term returns.
Overall, index funds are an excellent option for investors seeking a simple, cost-effective way to invest in the stock market and benefit from its long-term growth potential. They provide instant diversification, low fees, and the potential for solid returns, making them a popular choice for both beginner and experienced investors.
Key Factors for Investors to Consider in Mutual Funds
You may want to see also

Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
ETFs are also generally cheaper than mutual funds. They are usually sold without a commission, or "load", and have lower expense ratios. Actively managed funds, where a fund manager makes decisions about which securities to include, tend to be more expensive than passively managed funds, which aim to replicate the performance of a particular market index, industry or sector. However, actively managed funds do not necessarily perform better than passively managed funds. In fact, passively managed funds may have an advantage due to their lower costs.
When choosing an ETF, it's important to consider the fund's fees and tax implications, as well as its investment strategy and whether it aligns with your goals and risk tolerance. It's also worth noting that ETFs are subject to the same risks as trading individual stocks, including market and interest rate risk.
Bond Fund Investment: What Percentage is Smart to Invest?
You may want to see also

Stocks
When investing in stocks, it's important to consider the company's performance, financial health, and prospects for growth. It's also crucial to keep in mind that stock prices can be influenced by various factors, such as market conditions, industry trends, and global events.
Investing in stocks can be done through purchasing individual stocks directly or by investing in stock mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that provide exposure to a diversified portfolio of stocks.
- Risk and return: Stocks generally offer higher potential returns compared to more conservative investments like bonds or savings accounts. However, they also carry a higher risk of losing money. It's important to assess your risk tolerance and investment goals before investing in stocks.
- Diversification: Diversifying your stock portfolio across different industries, sectors, and geographic regions can help reduce risk. By investing in multiple stocks or stock funds, you lower the impact of any single stock's performance on your overall portfolio.
- Research and due diligence: Conduct thorough research before investing in a particular stock. Analyze the company's financial health, competitive advantage, management team, and future growth prospects. Look at the company's financial statements, news, and industry trends to make an informed decision.
- Costs and fees: Be mindful of the costs associated with investing in stocks, such as brokerage fees, transaction fees, and management fees. These fees can eat into your investment returns over time.
- Long-term perspective: Investing in stocks is typically a long-term strategy. Stock prices can fluctuate in the short term, but over the long term, they tend to follow the overall growth of the economy and corporate profits.
- Volatility and market timing: Stock prices can be volatile, and it's challenging to time the market perfectly. Instead of trying to predict market highs and lows, focus on a consistent investment strategy and consider dollar-cost averaging to smooth out the impact of market fluctuations.
Mutual Fund Investment: Key Factors to Consider
You may want to see also

Bonds
There are several types of bond funds, including government, corporate, and municipal bond funds. Government bond funds invest in debt issued by governments, while corporate bond funds invest in debt issued by corporations. Municipal bond funds invest in debt issued by municipalities, such as cities or states.
Bond funds can be actively or passively managed. Actively managed funds have portfolio managers who make decisions about which securities and assets to include in the fund, while passively managed funds, or index funds, seek to track and duplicate the performance of a benchmark index. Passively managed funds generally have lower fees than actively managed funds.
When investing in bond funds, it is important to consider the fees associated with the fund, such as expense ratios and sales charges. It is also important to understand the risks involved, such as interest rate risk, credit risk, and default risk.
Overall, bond funds can be a good investment choice for those looking for a more stable rate of return and a way to reduce their overall portfolio risk.
Mutual Fund Investment Strategies: Where to Invest?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are several types of funds you can invest in, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), index funds, and money market funds. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it's important to understand the differences before making a decision.
When choosing a fund to invest in, it's important to consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. You should also pay close attention to the fees associated with the fund, as these can significantly impact your returns. It's also a good idea to research the fund's past performance and the reputation of the fund manager.
Investing in funds offers several benefits, such as diversification, professional management, and access to a wide range of assets. However, there are also some drawbacks, including high fees and the potential for poor performance if the fund is not well-managed. It's important to carefully consider your options before investing.







