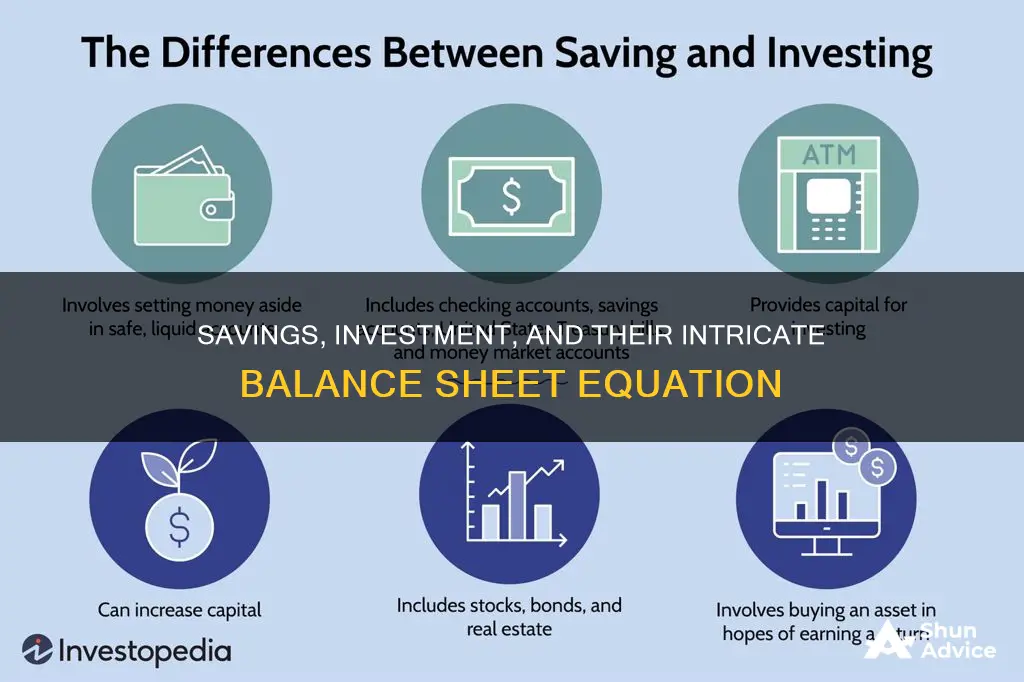
Saving and investing are both essential components of a solid financial plan, but they serve distinct purposes. Saving entails storing money securely for future use, often for short-term goals like purchases or emergencies, and is generally considered low-risk. On the other hand, investing involves using money to buy financial instruments like stocks or mutual funds, with the potential for higher returns but also greater risk. While saving provides a safety net, investing is geared towards long-term financial goals. The question of whether savings equals investment is crucial as it determines an individual's financial stability and security.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Saving means storing money safely so that it is available when needed and has a low risk of losing value |
| Investment comes with risk but also the potential for higher returns | |
| Time horizon | Saving is for the short-term |
| Investment is for the long-term | |
| Reasons | People save for purchases and emergencies |
| People invest for children's college funds or retirement | |
| Risk | Saving is low-risk |
| Investment is high-risk | |
| Returns | Saving has low returns |
| Investment has high returns |
What You'll Learn

Saving for a new phone, laptop, or vacation
Saving for a big purchase like a phone, laptop, or vacation can be challenging, but with a solid plan and some dedication, it's definitely achievable. Here are some strategies to help you save for these specific goals:
Saving for a New Phone or Laptop
The cost of smartphones and laptops can vary widely, so it's important to define your needs and budget accordingly. Here are some tips to help you save for that new device:
- Buy online: Online retailers often offer phones and laptops at lower prices compared to physical stores or major carriers. Shop around on websites like Amazon, Flipkart, or eBay, and take advantage of their convenient search filters to find the best deals.
- Pay in installments: Many retailers offer the option to pay off your device in monthly installments, helping to make the cost more manageable over time.
- Unlocked phones: Consider buying an unlocked phone, which gives you the freedom to choose your service provider and avoid being locked into a contract. This can save you money on phone service and allow you to upgrade your device whenever you want.
- Last-generation or mid-range devices: Instead of buying the latest and greatest model, opt for a last-generation or mid-range phone or laptop. These devices often have very similar features to their newer counterparts but come at a more affordable price.
- Trade-in or sell your old device: Many retailers offer financial incentives for trading in your old phone, or you can sell it to a third party to offset the cost of your new purchase.
- Refurbished devices: Refurbished smartphones and laptops are often like new but come at a fraction of the cost.
Saving for a Vacation
Vacations can be expensive, but with proper planning and saving strategies, you can make that dream trip a reality without breaking the bank. Here's how:
- Open a dedicated vacation savings account: Consider opening a high-yield savings account specifically for your vacation fund. This way, your money can grow while you plan your trip. Choose an online bank to make it less tempting to withdraw the funds.
- Set a savings goal: Research the costs of your expected expenditures, including airfare, accommodation, transportation, meals, and activities. Then, work backward to set a monthly savings goal. For example, if your trip will cost $2,400, aim to save $200 a month for a year to reach your goal.
- Boost your income: Pick up a side gig or a part-time job to boost your income. This could be something as simple as tutoring, waiting tables, or reselling items online.
- Cut back on expenses: Look for areas where you can cut back on spending, such as dining out or subscription services. Consider using budgeting apps or money-saving challenges to help you stay on track.
- Make your credit card work for you: Use a credit card that accumulates airline miles or travel rewards, and put all your regular expenses on it. By the time your vacation comes around, you might have earned enough points for a free flight or other travel perks.
Remember, saving for these goals is a marathon, not a sprint. Be patient, stay dedicated to your plan, and you'll be well on your way to achieving your financial goals and enjoying the fruits of your labor.
Hong Kong Savings: Best Places to Invest Your Money
You may want to see also

Pros and cons of saving
Saving money is an important habit to build for a more secure financial future. While saving is generally a positive step towards financial stability, there are some drawbacks to be aware of. Here is a detailed look at the pros and cons of saving.
Pros of Saving
Safety Net
Building an emergency fund is a crucial savings goal. Life is unpredictable, and an emergency fund ensures that you have financial support during hardships. This fund can cover unexpected costs, such as medical emergencies, unemployment, natural disasters, home repairs, or family emergencies. It provides peace of mind and helps you avoid accumulating debt during challenging times.
Meeting Life Goals
Many of our aspirations, from education to homeownership, require financial backing. Saving proactively allows you to achieve both short-term and long-term goals. Whether it's taking a dream vacation, pursuing higher education, or starting a business, saving gives you the financial freedom to turn your aspirations into reality.
Reduced Tax Liability
Saving in a retirement plan offers tax advantages. For example, contributing to a traditional 401(k) plan can reduce your taxable income. Alternatively, a Roth 401(k) or Roth IRA allows your savings to grow tax-free, and you won't have to pay taxes when withdrawing the funds.
Travel Opportunities
Saving for travel enables you to explore the world and gain new experiences without accumulating long-term credit card debt. Setting aside a specific amount each month for a vacation fund can help you achieve your travel goals while maintaining financial stability.
Relieve Financial Stress
Financial uncertainty can take a toll on your mental well-being. Saving consistently gives you a sense of control over your future and reduces financial stress. It provides options and the ability to manage unexpected expenses without falling into debt.
Supporting Causes
Once you've built a comfortable savings cushion, you can also contribute to causes beyond your personal goals. This could mean helping family or friends in need or donating to charities and supporting initiatives that resonate with you.
Cons of Saving
Variable Interest Rates
One drawback of saving is the variability of interest rates. Interest rates can fluctuate, affecting the growth of your savings. If the federal funds rate drops, your annual percentage yield (APY) may also decrease, impacting the overall returns on your savings.
Minimum Balance Requirements and Fees
Some savings accounts have minimum balance requirements. Failing to maintain the minimum balance may result in account maintenance fees. Additionally, banks may charge various other fees, including overdraft fees, wire transfer fees, ATM fees, and inactivity fees, which can eat into your savings.
Tax on Interest Earnings
While saving in certain accounts may provide tax benefits, it's important to remember that you'll typically have to pay income tax on any interest earned. This can reduce the overall returns on your savings.
Savings Investment Strategies: Accessibility and Growth
You may want to see also

Pros and cons of investing
Investing in the stock market can be a great way to build wealth over time and take advantage of short-term opportunities. However, it's essential to understand the pros and cons before diving in.
Pros of Investing in the Stock Market
- Potential for high returns: Historically, the stock market has delivered generous returns over time, with the S&P 500—a stock index tracking the 500 largest US companies—averaging an annualized return of around 10% since 1957.
- Staying ahead of inflation: Over the long term, stocks have typically outperformed the average annualized inflation rate, making them a good hedge against inflation.
- Liquidity: Stocks are liquid assets, meaning you can easily convert them into cash with low transaction costs. This flexibility is advantageous if you need quick access to your money.
- Diversification: Investing in different stocks across various sectors and geographies can help diversify your portfolio, reducing risk. If one stock or sector underperforms, other investments may offset those losses.
- Low barrier to entry: You don't need a substantial sum to start investing in stocks. Many brokers offer commission-free trades and fractional shares, allowing you to buy a portion of a share.
- Income from price appreciation and dividends: Investing in stocks offers the potential for capital gains as companies grow and share prices rise. Additionally, many stocks pay dividends, providing a regular income stream.
Cons of Investing in the Stock Market
- Risk of loss: Investing in stocks comes with the risk of losing your entire investment. Stock prices fluctuate, and poor company performance or market downturns can lead to significant losses.
- Time-consuming: Investing in stocks requires diligent research and monitoring. You need to analyze financial statements, annual reports, and market trends to make informed investment decisions.
- Tax implications: Profits from stock sales are subject to capital gains taxes. While holding stocks for the long term can reduce the tax rate, taxes still eat into your returns.
- Emotional rollercoaster: The volatility of stock prices can lead to emotional decisions. Investors often buy out of greed during highs and sell out of fear during lows, which can be detrimental to their portfolios.
- Competition: Professional and institutional investors have more time, knowledge, and sophisticated tools at their disposal. Competing against them can be challenging for individual investors.
In conclusion, investing in the stock market offers the potential for substantial returns but also carries significant risks. It is crucial to carefully consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon before deciding whether to invest in stocks. Diversification and a long-term perspective can help mitigate some of the risks associated with stock market investing.
Maximizing Your Savings: Safe Investment Strategies for Beginners
You may want to see also

When to save and when to invest
Saving and investing are two distinct strategies for storing and growing your money. While saving means keeping your money secure for future use, investing means purchasing assets that you expect to increase in value over time, resulting in higher returns than savings accounts.
When to Save
- Short-term goals: If you have a specific financial goal that you need to achieve within a short time frame, saving is often the better option. This could include saving for a security deposit on an apartment, purchasing a vehicle, or any other goal where you need to access the funds within the next five years.
- Emergency fund: It is recommended to have an emergency fund that can cover your living expenses for at least three to six months. This fund should be easily accessible, such as in a savings account, to provide quick access to cash in case of unexpected events like job loss, medical emergencies, or car repairs.
- Debt repayment: Before investing, it is generally advisable to pay off any high-interest debt. Focus on clearing debt with interest rates of 10% or higher.
When to Invest
- Long-term goals: Investing is suitable for long-term financial goals, such as retirement planning, saving for college, or a down payment on a home. These investments are intended to grow your money over time, and you should be prepared to keep the funds invested for an extended period.
- Employer-matched retirement plans: If your employer offers a retirement plan, such as a 401(k), and matches your contributions, it is generally a good idea to invest enough to take full advantage of this benefit. This way, you maximize the amount of "free money" you receive from your employer.
- Tax advantages: Certain investment accounts, like Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or Roth IRAs, offer tax advantages. Contributing to these accounts can help reduce your taxable income while also investing for the future.
Remember, the decision to save or invest depends on your unique financial situation and goals. Consult a fiduciary financial advisor if you need personalized advice.
Kids' Guide to Saving and Investing Wisely
You may want to see also

Savings and investments for teens
Why Teens Should Invest
There are many advantages to investing early. The most significant is that the sooner you begin investing, the more time your money has to grow. This is magnified by the power of compounding, which means that the value of your account can snowball over time. For example, if you start investing $100 per month from age 22 and earn a 10% return, you would have $710,810.83 by age 65. However, if you had started at age 15, you would have $1,396,690.23 – almost double the amount.
Another reason is that teens have their own unique perspectives and interests that can inform their investment decisions. For example, younger generations have played a significant role in driving environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing.
How Teens Can Invest
While it is generally not possible for minors to open their own brokerage account, there are several options for teens who want to start investing with adult supervision:
- Custodial accounts: An adult controls the investments on behalf of a minor until they reach 18 or 21, depending on the state. Custodial accounts can be opened under the Uniform Gifts to Minors Act (UGMA) or the Uniform Transfers to Minors Act (UTMA).
- Joint brokerage accounts: Minors can share legal ownership of assets with an adult. The adult co-owner will typically have the final say on investment decisions.
- Roth individual retirement accounts (Roth IRAs): Teens can get an early start on retirement savings with a Roth IRA, but they will need earned income from a job.
What Teens Can Invest In
Teens should be aware of the risks involved in investing. It is possible to lose some or all of your money. Generally, the riskier the investment, the greater the potential returns. However, since younger investors have a longer time frame, they can afford to take more risks.
- Stocks: Buying stocks gives you a small share of ownership in a company. Stocks can be risky due to their volatility, but they offer higher potential returns, making them suitable for younger investors.
- Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs): These funds invest in multiple stocks and other assets, providing built-in diversification. ETFs are designed to track a specific market index or sector and are available to trade on the stock market.
- Bonds: Bonds are a type of debt instrument, where you are essentially making a loan to the bond issuer. They are considered less risky than stocks but offer lower returns.
- Certificates of deposit (CDs): CDs are similar to savings accounts, but you agree to leave the money untouched for a specific time frame in exchange for a higher interest rate.
- High-yield savings accounts: These accounts offer much higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts, with minimal risk.
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs): ETFs hold a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other investments, and they trade on stock market exchanges during regular trading hours.
Where to Start
- Educate yourself about investing.
- Set clear investment goals.
- Research potential investments.
- Open a custodial or joint brokerage account with the help of an adult.
- Buy your selected investments.
Additional Considerations
It is important for teens to be aware of investment scams. If someone promises very high returns, it is likely a scam. Remember that higher returns always come with higher risk.
It is also recommended that teens gain basic stock knowledge, learn about different companies, and experiment with dummy or mock portfolios before investing real money.
Lastly, while cryptocurrency may be tempting, it is extremely volatile and is more like gambling unless you know what you are doing.
Invest Less, Save More: Strategies for Financial Success
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Saving means storing money safely with low risk, while investing involves taking on some risk with the potential for higher returns.
Both saving and investing are critical elements of personal finance, and understanding the difference is essential to ensure financial security and a bright future.
Examples of saving include setting aside a portion of your allowance or paycheck into a savings account, using automatic transfers, or saving for a specific purchase like a laptop or a vacation.
Saving provides financial security and a safety net for unexpected expenses, but it may also result in missing out on potential higher returns from riskier investments.







