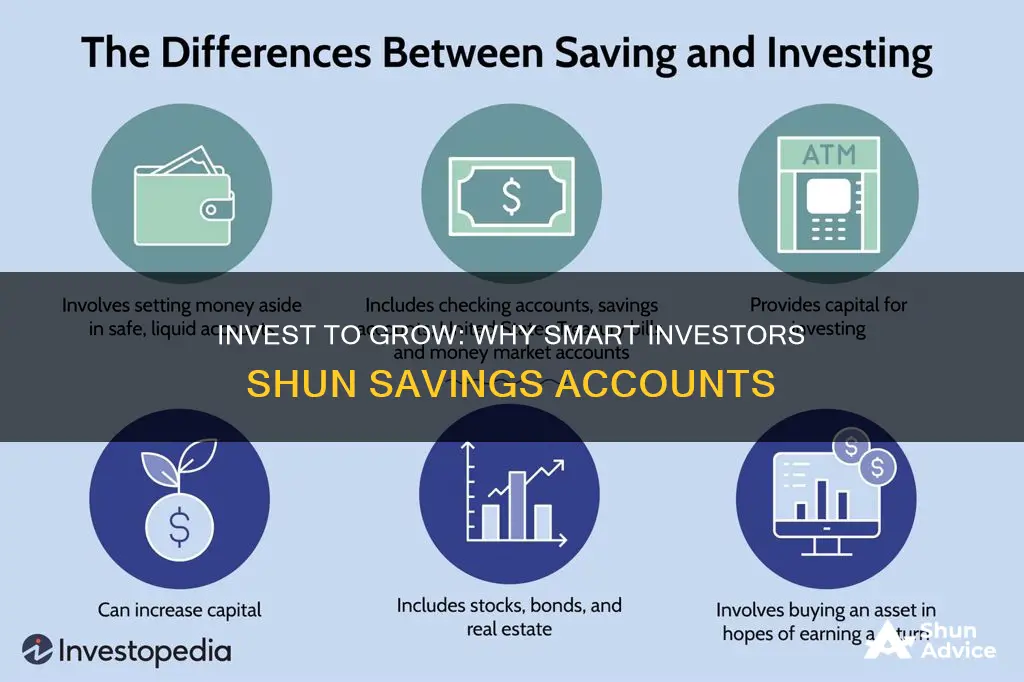
Saving and investing are both important concepts for building a sound financial foundation. While both can help you achieve a more comfortable financial future, it's essential to understand their differences and when it's best to save or invest. The biggest distinction between the two is the level of risk involved. Saving typically offers lower returns but carries little to no risk, while investing provides the opportunity for higher returns, but you take on the risk of potential loss.
Saving is ideal for preserving your money and achieving short-term financial goals. It entails setting aside cash in a low-risk, low-return environment, such as a savings account, money market account, or certificate of deposit (CD). These options provide easy access to your funds and are generally safe from loss, making them suitable for emergency funds or short-term goals like buying a new gadget or going on vacation. However, savings accounts may fail to keep up with inflation, resulting in a loss of purchasing power over time.
On the other hand, investing is geared towards growing your money and is suitable for long-term financial goals. It involves buying assets such as stocks, bonds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), real estate, or commodities, which carry a higher risk but offer the potential for higher returns. Investing is ideal for funding retirement, building generational wealth, or achieving long-term goals like saving for college or a down payment on a house. However, investing comes with the risk of losing money, and some investments may be less liquid, making it challenging to access your funds quickly.
To summarise, saving is suitable for short-term goals and provides security and quick access to funds, while investing offers the potential for higher returns and wealth growth but carries a higher risk of loss. Determining whether to save or invest depends on factors such as your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. It's recommended to have an adequate emergency fund in a savings account before considering investing.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Risk | Saving: Low |
| Investing: High | |
| Returns | Saving: Low |
| Investing: High | |
| Time horizon | Saving: Short-term |
| Investing: Long-term | |
| Liquidity | Saving: High |
| Investing: Low | |
| Accessibility | Saving: Easy |
| Investing: Difficult | |
| Goals | Saving: Short-term |
| Investing: Long-term |
What You'll Learn
- Investing can help you achieve long-term financial goals, such as saving for retirement
- You can invest in a variety of assets, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and more
- Investing provides the potential for higher returns than saving
- There are different types of investment accounts, such as brokerage, retirement, and education accounts
- You can start investing with a small amount of money and take advantage of compound interest

Investing can help you achieve long-term financial goals, such as saving for retirement
Investing is a crucial tool to achieve long-term financial goals, such as saving for retirement. While saving is important, it is typically used for short-term goals and emergency funds. Investing, on the other hand, allows your money to grow over time and achieve higher returns. Here are some ways investing can help you achieve your long-term financial goals:
Higher Returns
One of the main advantages of investing over saving is the potential for higher returns. While saving provides low and often negative inflation-adjusted returns, investing offers the opportunity for much greater growth. For example, the average annual growth of the stock market is about 7% after inflation, allowing your assets to double in value roughly every 10 years.
Long-Term Goals
Investing is particularly well-suited for long-term goals, such as saving for retirement, children's college funds, or buying a house. The longer time horizon allows you to take advantage of compound interest and ride out any short-term downturns in the market.
Diversification
By investing across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate, you can reduce the overall risk of your portfolio while still achieving solid returns. Diversification ensures that your portfolio is not overly exposed to any one particular investment or industry.
Tax Benefits
Certain investment vehicles, such as a 401(k) or an IRA, offer significant tax benefits. Contributions to these accounts may be tax-deductible, and the investments can grow tax-free until you withdraw the funds during retirement.
Professional Guidance
If you are unsure where to start or how to build a portfolio that aligns with your goals, you can seek guidance from financial advisors or robo-advisors. These professionals can help you navigate the complexities of investing and ensure your investments are well-suited to your long-term goals.
In summary, investing is a powerful tool to achieve long-term financial goals due to its potential for higher returns, ability to diversify, and tax advantages. However, it is important to remember that investing also carries risks, and it is crucial to understand those risks and ensure they align with your risk tolerance and time horizon.
Roth Accounts: Savings or Investment?
You may want to see also

You can invest in a variety of assets, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and more
There are several types of assets that you can invest in, each with its own pros and cons. Here are some of the most common ones:
Stocks
Investing in stocks means buying shares of ownership in a company. Stocks are typically traded on a stock exchange, and the value of stocks can fluctuate based on market demand and the company's performance. Investing in stocks can provide the potential for higher returns, but it also comes with the risk of losing money. It's important to diversify your portfolio by investing in different companies and industries to reduce risk.
Bonds
Bonds are a type of fixed-income investment where you lend money to a government or company, and they pay you a fixed interest rate until the maturity date. Government bonds are generally considered lower risk but offer lower returns, while corporate bonds may offer higher returns but come with a higher risk of default.
Real Estate
Real estate investing involves purchasing property and generating income through rental income or capital gains. It can be a great way to build wealth over time and expand your investment portfolio. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) are a popular way to invest in real estate without the upfront costs and management involved in owning properties directly.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds allow you to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other securities. They provide less risk compared to investing in individual stocks but may offer potentially lower returns. Mutual funds are a good option for investors who want a more hands-off approach to investing.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
ETFs are similar to mutual funds but are traded on an exchange like stocks. They typically track an index or sector and can include a variety of investments, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities. ETFs offer more flexibility and liquidity than mutual funds but may have higher fees.
Commodities
Commodities are basic goods such as metals, energy resources, and agricultural products. Investing in commodities can be risky due to volatile price fluctuations, but they can also provide a hedge against inflation. Many investors choose to invest in commodities indirectly by buying shares in companies that produce them or through futures contracts.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is a relatively new asset class that has gained popularity in recent years. It involves investing in decentralized digital currencies that are secured by cryptography. Cryptocurrency can be highly volatile but offers the potential for high returns. However, it's important to note that cryptocurrency is not subject to the same regulations as traditional investments, so investors should be cautious.
Other Alternative Investments
In addition to the traditional asset classes, there are also alternative investments such as hedge funds, private equity, collectibles, and more. These investments may have higher minimum investment requirements and are typically suited for more sophisticated investors.
Investment Opportunities in Pakistan: Where to Invest Your Savings
You may want to see also

Investing provides the potential for higher returns than saving
While saving is a great way to meet short-term financial goals and prepare for unexpected situations, investing provides the potential for higher returns and can help achieve long-term financial goals. Here are some reasons why investing provides the potential for higher returns than saving:
- Potential for higher returns: Investing offers the potential for higher returns than savings accounts. Over the long term, the average annual growth of the stock market is about 7% after inflation. At this growth rate, invested assets double in value roughly every 10.5 years.
- Compounding wealth: Investing allows you to take advantage of compounding returns, where your earnings start generating more earnings. This can dramatically expedite wealth creation.
- Beating inflation: Savings accounts often provide returns that are lower than the inflation rate, causing your savings to lose purchasing power over time. Investing, on the other hand, offers the potential to beat inflation and grow your wealth in real terms.
- Long-term goals: Investing is ideal for long-term goals such as retirement planning or saving for college. With a longer time horizon, you can take on more risk and have the potential to earn higher returns.
- Diversification: By investing across different asset classes, sectors, and industries, you can reduce the overall risk of your portfolio while still aiming for higher returns.
- Tax benefits: Certain investment accounts, such as retirement accounts (e.g., 401(k) or IRA), offer tax advantages. Contributions to these accounts may be tax-deductible, and the investments can grow tax-free until withdrawal.
Savings vs Investments: Where Should Your Money Go?
You may want to see also

There are different types of investment accounts, such as brokerage, retirement, and education accounts
There are several types of investment accounts, each with its own unique features, eligibility criteria, and investment options. Here are some of the most common types:
Brokerage Accounts:
Brokerage accounts, also known as taxable investment accounts, are suitable for individuals who want to invest on their own. They are often chosen by those who want more flexibility and access to a broad range of investments, such as stocks, mutual funds, bonds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These accounts do not have the tax benefits offered by certain retirement accounts but provide the advantage of no restrictions on withdrawals. Additionally, there are no limits on how much money can be contributed to a taxable brokerage account.
Retirement Accounts:
Retirement accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) and employer-sponsored plans like 401(k)s, are designed to help individuals save for retirement. IRAs come in two main types: traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs, each offering different tax advantages. Traditional IRAs allow tax-deductible contributions and tax-deferred growth, while Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement if specific conditions are met. On the other hand, 401(k) plans are offered by employers and often include matching contributions, providing an opportunity for tax-advantaged savings.
Education Accounts:
Education accounts, such as 529 plans and Coverdell Education Savings Accounts (ESAs), are designed to help save for education expenses. 529 plans can be used for qualified education expenses, including tuition, fees, and room and board, and offer tax-free withdrawals. Coverdell ESAs can be used for private elementary, middle, and secondary school expenses, in addition to college tuition, and also offer tax-free withdrawals for qualified expenses.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs):
HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts for individuals enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP). Contributions are made on a pre-tax basis or may be tax-deductible, and earnings grow tax-free. Withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are also tax-free, providing a "triple-advantaged" investment option.
Custodial Accounts for Minors:
These accounts are set up by adults to gift money to minors. Two common types are the Uniform Gift to Minors Act (UGMA) and the Uniform Transfers to Minors Act (UTMA) accounts, which differ mainly in the types of assets that can be contributed. These accounts allow adults to maintain control over the investments until the minor reaches the age of majority, at which point the assets and control are transferred to the child.
Each type of investment account serves a different purpose and caters to varying financial goals, eligibility criteria, and investment options. It is essential to understand the features and requirements of each account type before making a decision.
Savings, Investment, and Their Intricate Balance Sheet Equation
You may want to see also

You can start investing with a small amount of money and take advantage of compound interest
Investing is an excellent way to grow your money over time. Even if you are starting with a small amount of money, you can take advantage of compound interest to build wealth. Compound interest is a powerful tool that allows you to earn interest on your interest. This means that your investment grows at an accelerated rate over time. The key to compound interest is to give your money time to grow. The longer you keep your money invested, the more compound interest can work in your favour.
Here's an example that illustrates the power of compound interest. Let's say you start saving $100 a month at age 20, earning an average of 4% annually, compounded monthly, across 40 years. By the time you reach age 65, you will have earned $151,550, even though your principal investment was just $54,100. On the other hand, if you wait until age 50 to start investing, you would need to invest twice as much principal ($95,000) to end up with less money ($132,147) by age 65.
When it comes to investing with compound interest, you have several options. One option is to invest in dividend-paying stocks or mutual funds. Dividends are payouts that you can choose to reinvest to buy more shares, allowing you to benefit from compound interest. Another option is to invest in zero-coupon bonds, which are purchased at a discount and grow over time until they reach their full value at maturity. You can also take advantage of compound interest by investing in high-yield savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), or money market accounts. These options typically offer higher interest rates than regular savings accounts, allowing you to grow your money faster.
It's important to remember that investing comes with risks. There is always the possibility of losing money, and the value of your investments can fluctuate. However, by investing with a small amount of money and taking advantage of compound interest, you can increase your chances of building a substantial nest egg over time.
Maximizing Small Savings: Smart Strategies for Investing Wisely
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Investing offers the potential for higher returns than saving. While saving is a great way to build an emergency fund or save for short-term goals, investing is better for long-term financial goals. This is because investing has a higher risk/reward profile than saving.
Investing has the potential for much higher returns than saving. Over the long term, the average annual growth of the stock market is about 7% after inflation. At this growth rate, invested assets double in value roughly every 10.5 years.
The main risk of investing is that you could lose money. There is no guarantee that you will make money from investing, and there is always the possibility of losing some or all of your investment.