The base of the investment risk pyramid is made up of low-risk assets, which form the foundation of an investor's portfolio. These investments are generally considered safe and include government bonds, cash, and money market securities. By allocating a larger proportion of their portfolio to these low-risk assets, investors can reduce the overall risk of their investments. This strategy is particularly suitable for those with a lower risk tolerance or those approaching retirement, as it provides a more stable foundation for their financial goals.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Risk level | Low |
| Proportion of portfolio | Largest |
| Types of investments | Cash, money markets, savings and checking accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), short-term government bonds, US government securities, federal agency securities, AAA-rated corporate bonds, treasuries |
What You'll Learn
- Low-risk assets like cash, money markets, and government bonds
- Medium-risk investments with stable returns and potential for capital appreciation
- High-risk, speculative investments with potential for above-average returns
- Risk-reward trade-off: higher risk, higher potential returns
- Customising the pyramid: adjusting levels of risk and return to individual preferences

Low-risk assets like cash, money markets, and government bonds
Cash is considered the safest asset, as it carries virtually no risk of loss unless it is lost or stolen. It is ideal for short-term financial needs due to its liquidity and universal acceptance. However, its safety comes at a cost, as it generally yields minimal returns, especially during high inflation periods.
Money market funds are mutual funds that invest in short-term, low-risk securities such as treasury bills and commercial paper. They are considered cash equivalents and offer slightly higher returns than cash. Money market funds are suitable for investors seeking yield and safety.
Government bonds, particularly those issued by developed economies, are considered among the safest investments. They are sometimes referred to as "risk-free" since governments can, in theory, print more money to cover their debts. However, government bonds often provide lower returns compared to other riskier investments.
While these low-risk assets provide stability and safety, investors should be mindful of their limitations. For example, holding too much cash can expose investors to inflation risk, where the purchasing power of their cash decreases over time. Additionally, the returns on low-risk assets may not keep up with inflation, resulting in a decrease in their value.
When constructing an investment portfolio, it is essential to diversify and balance risk and reward. The investment risk pyramid is a useful tool for allocating assets according to their risk levels. By placing low-risk assets at the base of the pyramid, investors ensure that the majority of their portfolio is stable and secure. This strategy provides a strong foundation for investing, allowing investors to take on calculated risks with a smaller portion of their capital.
Investment Banking vs Asset Management: Who Earns More?
You may want to see also

Medium-risk investments with stable returns and potential for capital appreciation
Medium-risk investments are a crucial component of any investment portfolio, offering stable returns while also providing the potential for capital appreciation. These investments form the middle portion of the investment risk pyramid, representing a balance between risk and reward. Here are some detailed examples of medium-risk investments with stable returns and the potential for capital growth:
Corporate Bonds and Blue-Chip Stocks
The middle section of the investment pyramid typically includes moderately risky assets like corporate bonds and blue-chip stocks. Corporate bonds offer a stable income stream through regular interest payments, while blue-chip stocks are issued by well-established, financially sound companies with a strong track record of performance. These stocks may provide both capital appreciation and dividend income.
Real Estate
Real estate is often considered a medium-risk investment, especially in a stable economic environment with low unemployment and steady growth. This sector benefits from the necessity of shelter, making it a relatively safe bet. Real estate investments can be made through various avenues, such as real estate investment trusts (REITs) or real estate crowdfunding platforms.
Dividend Mutual Funds and Corporate Bond Funds
Dividend mutual funds and corporate bond funds are another example of medium-risk investments. Dividend mutual funds invest in companies that pay regular dividends, providing a steady income stream. Corporate bond funds, on the other hand, offer exposure to a diversified portfolio of corporate bonds, reducing the overall risk.
Low Volatility Small-Cap Stocks
Small-cap stocks with low volatility can be a good option for medium-risk investors. These stocks exhibit lower price fluctuations compared to larger-cap stocks, providing a more stable investment opportunity. The Invesco S&P SmallCap Low Volatility ETF (XSLV) is an example of a low-volatility small-cap ETF with a decent yield and a low management fee.
Convertible Bonds
Convertible bonds are a type of hybrid debt security that offers both interest payments and the potential for capital appreciation. They are more secure than equity as they receive priority in payments over common stockholders if the issuing company faces financial difficulties. Convertible bonds are often issued by disruptive growth companies and those involved in mergers and acquisitions.
India's Economy: Invest or Avoid?
You may want to see also

High-risk, speculative investments with potential for above-average returns
High-risk, speculative investments are located at the top of the investment risk pyramid. This is the smallest part of the pyramid and is reserved for investments that carry a greater chance of losing value or failing to provide expected returns. These investments are typically characterised by significant volatility, meaning their prices can fluctuate dramatically over a short period. While they offer the potential for substantial returns, these are not guaranteed.
Some examples of high-risk investments include:
- Penny stocks: Shares of small companies that typically trade for less than $5 per share. These stocks are highly speculative, often illiquid, and prone to manipulation and fraud due to a lack of regulation and transparency.
- Junk bonds: Also known as high-yield bonds, these are issued by companies with poor credit ratings. While they offer higher interest rates, the chance of default is much higher than with investment-grade bonds.
- Binary options: A type of options contract that allows investors to wager a fixed amount with the possibility of winning a fixed amount or losing the entire investment. Binary options are often likened to gambling due to their simplicity and high likelihood of loss.
- Venture capital in startups: This involves investing in early-stage companies with high growth potential, but it is inherently risky due to the high failure rate of new businesses. Many startups do not survive beyond the first few years, resulting in potential losses for investors.
- Derivatives: These are complex financial instruments that can be used to speculate on the success of a new company or product. However, they are inherently uncertain and can lead to significant losses.
- Collectibles: Such as artwork or wine, which can be challenging to accurately value due to infrequent pricing. They may also go through fad periods and boom-and-bust cycles, adding to the overall risk.
- Cryptocurrency and non-fungible tokens (NFTs): These are highly speculative and volatile investments with a high risk of loss.
It is important to approach these types of investments with caution and to ensure limited exposure within an investment portfolio. Diversification across various investment types with different risk levels can help mitigate potential losses and achieve a more balanced portfolio.
India's Bilateral Investment Treaty: Benefits and Challenges
You may want to see also

Risk-reward trade-off: higher risk, higher potential returns
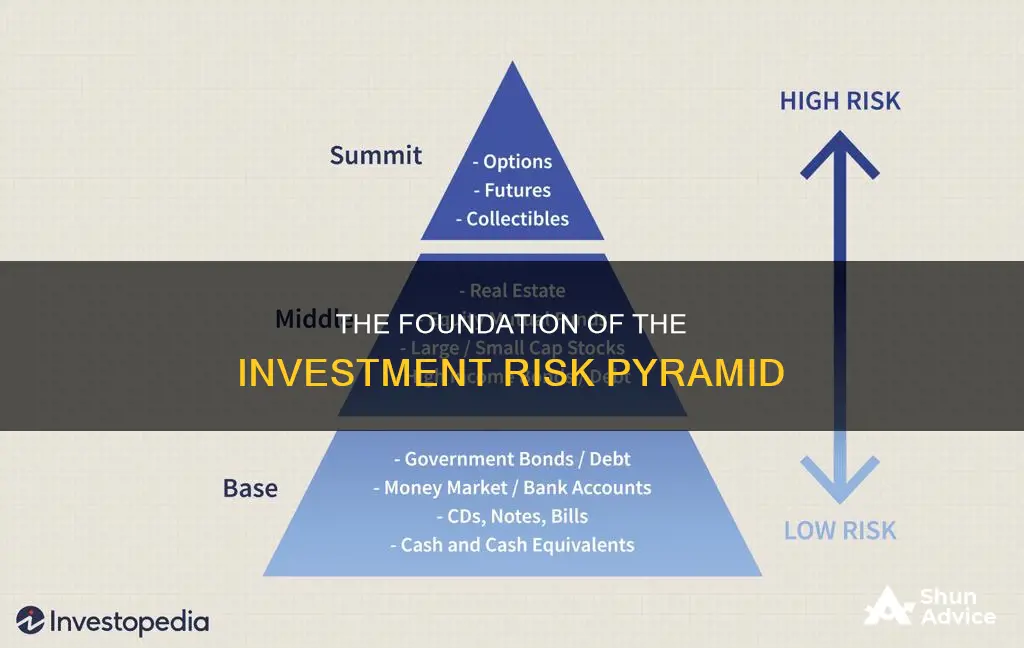
The investment risk pyramid is a strategy that helps investors understand the risk/reward profile of various assets. It is a useful tool for investors to determine their risk tolerance and return goals when building a portfolio. The pyramid is divided into three levels, with the least-risky securities at the base, growth and moderately risky assets in the middle, and the most speculative strategies at the top.
The base of the pyramid is made up of low-risk investments, which typically constitute the bulk of an investor's portfolio. These include cash and cash equivalents, such as government bonds, AAA-rated bonds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and savings and checking accounts. These investments have set rates of return and are considered safe, with a low possibility of losing money.
As we move up the pyramid to the middle portion, we find medium-risk investments. These assets offer a stable return while still allowing for capital appreciation. Investments in this tier include growth and income stocks, capital appreciation funds, real estate, dividend stock mutual funds, and higher-risk bond funds. While these investments have some growth potential, they also carry a higher risk of losing money compared to the low-risk assets at the base of the pyramid.
At the top of the investment risk pyramid are the most speculative and high-risk investments. This includes stock options, futures, commodities, cryptocurrencies, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and even collectibles such as artwork or wine. These investments offer the potential for large returns but also come with a high chance of significant losses. Only a small portion of an investor's portfolio should be allocated to this high-risk, high-reward niche.
The risk-reward trade-off is a fundamental concept underlying the investment risk pyramid. The higher the risk of an investment, the higher the potential return. When investing in high-risk assets, it is crucial to ensure that you can afford to lose that money without life-changing repercussions. On the other hand, low-risk investments may provide moderate profits but offer a lower chance of substantial losses.
By understanding the risk-reward trade-off and utilising the investment risk pyramid, investors can make informed decisions about their portfolios. The pyramid provides a basic framework for analysing portfolio construction and helps individuals determine the percentage of their assets that should be allocated to different types of investments based on their risk tolerance and return objectives.
India's Wealthy: Where They Invest Their Money
You may want to see also

Customising the pyramid: adjusting levels of risk and return to individual preferences
The investment risk pyramid is a useful tool for investors to understand the risk/reward profile of various assets. It is a general framework that can be used to assess an individual's personal level of risk and how this relates to different potential investments. The pyramid is structured with low-risk assets at the base, moderately risky assets in the middle, and high-risk, speculative assets at the top. This structure should balance risk and reward based on an individual's time horizon, assets, and risk tolerance.
It is important to note that not all investors have the same willingness or ability to take on risk. Therefore, the pyramid should be customised to an individual's particular risk preference and financial situation. For example, those who want more risk in their portfolios can increase the size of the summit (high-risk investments) by decreasing the size of the base (low-risk investments) and the middle portion (moderate-risk investments). On the other hand, those who want less risk can increase the size of the base.
When deciding on an investment strategy, it is crucial to consider your risk tolerance, which refers to how much risk you are willing to accept, and your risk capacity, which is the amount of financial risk you can take on given your current financial situation. Two important factors to consider when determining your risk tolerance are your time horizon (how long you can keep your money invested) and your bankroll (how much money you can afford to lose).
The investment pyramid approach provides a guideline for investors to balance their assets. The base of the pyramid should consist of low-risk investments with foreseeable returns and comprise the bulk of your assets. The middle portion should be made up of medium-risk investments that offer a stable return while still allowing for capital appreciation. The summit, or the top of the pyramid, is reserved for high-risk investments and should consist of money you can lose without serious repercussions.
In summary, the investment risk pyramid is a useful tool for investors to understand and customise their risk tolerance and return preferences. By adjusting the levels of risk and return, individuals can make informed investment decisions that align with their financial goals and risk preferences.
India's Investment in Chabahar: Exploring Strategic Interests
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Low-risk investments are located at the base of the investment risk pyramid. These include cash and cash equivalents with set rates of return, such as government bonds, AAA-rated bonds, and certificates of deposit (CDs).
The base of the pyramid represents the strongest portion, which supports everything above it. Low-risk investments are generally the largest area of the pyramid and comprise the bulk of an investor's assets.
Low-risk investments are generally suitable for those with a low-risk tolerance or those approaching retirement age. Additionally, young people often have time to take on more risk.







