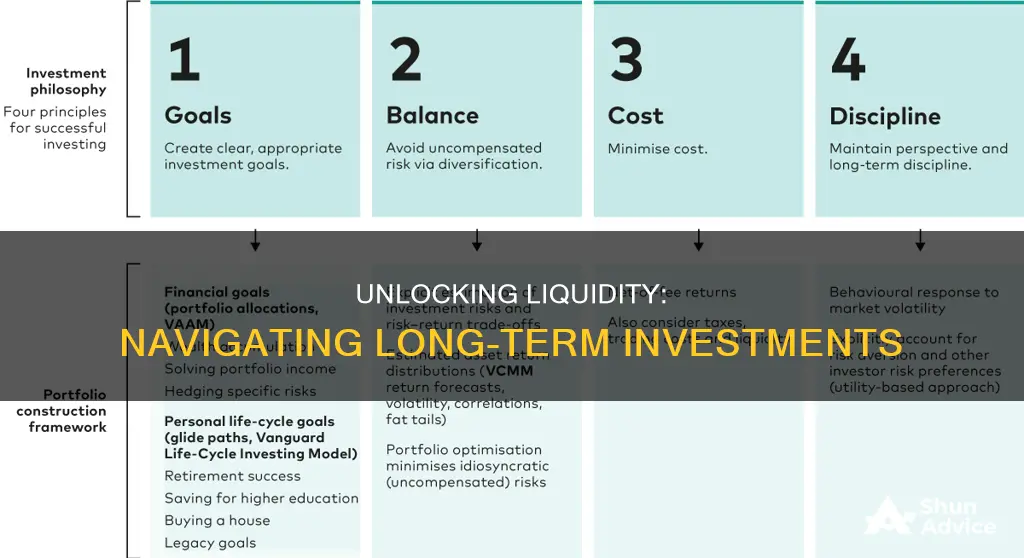
Long-term investments are a crucial component of financial planning, but they often come with a trade-off between potential returns and liquidity. Liquidity refers to how easily an investment can be converted into cash without significant loss of value. While long-term investments like real estate, stocks, or certain types of bonds can offer substantial returns over time, they are generally less liquid compared to short-term investments. This means that selling these assets quickly may result in a lower price than their intrinsic value, making them less suitable for those who need immediate access to their funds. Understanding the liquidity of long-term investments is essential for investors to manage their portfolios effectively and ensure they have the financial flexibility they need.
What You'll Learn
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in asset prices impact liquidity and long-term investment strategies
- Liquidity Preferences: Investors' willingness to convert assets into cash affects long-term investment choices
- Asset Classes: Different investment types have varying liquidity, e.g., stocks vs. real estate
- Risk Management: Liquidity is crucial for managing risks in long-term investment portfolios
- Tax Implications: Tax efficiency is a key consideration when assessing the liquidity of long-term investments

Market Volatility: Fluctuations in asset prices impact liquidity and long-term investment strategies
Market volatility, the rapid and significant fluctuations in asset prices, has a profound impact on the liquidity of long-term investments. Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be converted into cash without significantly affecting its price. In the context of long-term investments, such as real estate, private equity, or venture capital funds, liquidity is often limited due to the illiquid nature of these assets. When market volatility strikes, it can disrupt this delicate balance and present both challenges and opportunities for investors.
During periods of high market volatility, asset prices can experience extreme swings, often driven by panic selling or speculative behavior. This volatility can lead to a decrease in the perceived value of long-term investments, making them less attractive to investors seeking immediate liquidity. For instance, a real estate investor might find it challenging to sell a property at a favorable price during a market downturn, as buyers may be hesitant to enter a volatile market. Similarly, private equity firms may struggle to exit their investments quickly, as potential buyers are wary of the risks associated with volatile market conditions.
On the other hand, market volatility can also create opportunities for long-term investors. When asset prices drop sharply, it can present a buying opportunity for those with a long-term perspective. Investors who remain committed to their strategy can benefit from the discounted prices of quality assets. For example, a venture capitalist might see a downturn as an opportunity to invest in promising startups at lower valuations, with the potential for significant returns over time. This strategic approach requires discipline and a strong conviction in the long-term prospects of the investment.
Managing liquidity risk during market volatility is crucial for long-term investors. Diversification is a key strategy to mitigate this risk. By spreading investments across various asset classes and sectors, investors can reduce the impact of any single asset's performance on their overall portfolio. Additionally, maintaining a robust financial cushion, such as holding a portion of assets in highly liquid forms, can provide a safety net during volatile markets. This ensures that investors can meet their financial obligations and take advantage of potential opportunities without being forced to sell their long-term investments prematurely.
In summary, market volatility significantly influences the liquidity of long-term investments. While it can present challenges in terms of selling assets quickly, it also offers opportunities for strategic investors. Understanding the dynamics of market volatility and implementing appropriate risk management strategies, such as diversification and maintaining liquidity reserves, are essential for long-term investors to navigate these fluctuations successfully. This approach allows investors to stay committed to their long-term investment goals while adapting to the ever-changing market conditions.
Maximize Your Short-Term Cash: Top Investment Strategies
You may want to see also

Liquidity Preferences: Investors' willingness to convert assets into cash affects long-term investment choices
Liquidity preferences play a crucial role in the realm of long-term investments, as they directly influence the decisions made by investors regarding their asset allocation. This concept refers to the degree of ease with which an asset can be converted into cash without significantly impacting its value. In simpler terms, it's about an investor's willingness to exchange their investments for cash when needed.
Investors often have varying levels of liquidity preferences, which can be influenced by several factors. One key factor is the time horizon of the investment. For short-term goals, investors might prefer highly liquid assets, such as cash or money market funds, as they can quickly access their funds without incurring substantial losses. In contrast, for long-term investments, such as real estate or certain stocks, investors are often willing to sacrifice some liquidity to benefit from potential capital appreciation and income generation over an extended period.
The concept of liquidity preference is closely tied to the risk and return associated with different investment vehicles. Generally, more liquid assets provide investors with greater flexibility and are considered lower-risk investments. This is because liquid assets can be sold relatively quickly without a significant drop in price, ensuring that investors can access their funds when required. On the other hand, less liquid investments may offer higher potential returns but could be more challenging to convert into cash without incurring losses.
Understanding liquidity preferences is essential for investors as it helps them make informed decisions about their investment strategies. Investors with a higher liquidity preference might opt for a more diversified portfolio, including a mix of liquid and illiquid assets, to balance their need for quick access to cash with the potential for long-term growth. Conversely, those with a lower preference for liquidity may focus on long-term investments that align with their financial goals, even if they require a longer commitment.
In summary, liquidity preferences are a critical aspect of long-term investment choices. Investors' willingness to convert assets into cash is a driving force behind their investment decisions, impacting the types of assets they choose and the overall composition of their portfolios. By considering their liquidity needs and preferences, investors can navigate the complex world of long-term investments with a more strategic and tailored approach.
Understanding Long-Term Investment: A Guide to Current Asset Classification
You may want to see also

Asset Classes: Different investment types have varying liquidity, e.g., stocks vs. real estate
When considering long-term investments, understanding the liquidity of different asset classes is crucial. Liquidity refers to how easily an asset can be converted into cash without significantly impacting its value. In the context of long-term investments, this becomes even more important as investors may need to access their funds during unforeseen circumstances or when opportunities arise.
Stocks, for instance, are considered highly liquid assets. They represent ownership in a company and can be easily bought or sold on stock exchanges. Investors can quickly convert their stock holdings into cash by placing an order with a broker, often within a matter of seconds. This liquidity is particularly advantageous for long-term investors who may need to access their funds for various reasons, such as taking advantage of other investment opportunities or addressing personal financial needs.
On the other hand, real estate investments generally offer lower liquidity compared to stocks. Purchasing a property involves a complex process, including finding a buyer, negotiating the sale, and completing the transaction, which can take months or even years. Real estate is a tangible asset, and its value can be influenced by various factors, such as location, market conditions, and the overall health of the economy. While real estate can be a valuable long-term investment, it is not as readily convertible into cash as stocks.
Other asset classes, such as commodities and certain types of derivatives, also have varying levels of liquidity. For example, commodities like gold or oil can be traded on exchanges, providing a certain level of liquidity. However, the trading volumes and market dynamics of these commodities may not always be as active as those of stocks, which can impact the ease of conversion into cash.
Understanding the liquidity of different investment types is essential for long-term investors to make informed decisions. It allows investors to assess the accessibility of their funds and the potential impact on their investment strategies. By considering the liquidity of various asset classes, investors can better manage their portfolios and ensure they have the flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions or personal circumstances.
Unlocking the Power of Long-Term Investments: Are They Assets?
You may want to see also

Risk Management: Liquidity is crucial for managing risks in long-term investment portfolios
Liquidity is a critical aspect of risk management in long-term investment portfolios, as it directly impacts an investor's ability to manage risks effectively. In the context of long-term investments, liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be converted into cash without significant loss of value. This is particularly important when considering the potential risks associated with holding investments for extended periods.
One of the primary risks in long-term investments is the need for liquidity to address unforeseen financial obligations or opportunities. Investors often require access to their funds for various reasons, such as unexpected expenses, business expansion, or taking advantage of other investment prospects. For instance, if an investor holds a long-term real estate investment, selling it quickly might be challenging, and the process could result in a substantial loss of potential returns. Similarly, in the stock market, selling stocks promptly can be difficult during volatile periods, leading to potential losses if the investor needs to liquidate their holdings.
To mitigate these risks, investors should aim to maintain a certain level of liquidity in their portfolios. This can be achieved by diversifying investments across various asset classes, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments. Diversification ensures that investors are not overly exposed to any single asset or market, reducing the impact of potential liquidity issues. For example, holding a mix of liquid assets like stocks and bonds can provide quick access to cash when needed, while also offering the potential for long-term growth.
Additionally, investors can consider implementing strategies such as regular portfolio reviews and rebalancing. By periodically assessing the liquidity of their investments, investors can identify any potential issues early on. Rebalancing the portfolio involves adjusting the allocation of assets to maintain the desired level of liquidity and risk exposure. This proactive approach allows investors to manage their risk exposure and ensure that their portfolio remains aligned with their investment goals.
In summary, liquidity is a vital component of risk management in long-term investment strategies. Investors should focus on maintaining a balanced portfolio with a mix of liquid and illiquid assets to address potential risks. By understanding the liquidity characteristics of different investments and implementing appropriate strategies, investors can better manage their risks and make informed decisions to protect their long-term financial objectives.
The Long-Term Value of Real Estate: A Smart Investment Strategy
You may want to see also

Tax Implications: Tax efficiency is a key consideration when assessing the liquidity of long-term investments
When evaluating the liquidity of long-term investments, tax efficiency is a critical factor that investors should consider. The tax implications of selling these investments can significantly impact the overall return and the effectiveness of the investment strategy. Understanding the tax rules and regulations related to long-term investments is essential for making informed decisions.
Long-term capital gains, which are realized from the sale of assets held for more than a year, are typically taxed at a lower rate compared to ordinary income. This tax advantage encourages investors to hold investments for the long term, as it can result in significant tax savings. However, the liquidity of these investments is crucial, as it determines when and how investors can access their funds without incurring excessive tax costs.
One important consideration is the holding period. To qualify for the reduced long-term capital gains tax rate, the investment must be held for at least one year. If an investor sells the investment before this period, they may be subject to higher ordinary income tax rates. Therefore, the liquidity of the investment is vital, as it allows investors to take advantage of the tax benefits without being forced to sell prematurely.
Additionally, the tax treatment of short-term capital gains is more favorable in some jurisdictions. Short-term gains, typically those realized from assets held for less than a year, are often taxed at the investor's ordinary income tax rate. This means that frequent trading or short-term investments might be more tax-efficient in certain markets. However, this strategy also carries higher risks and may not be suitable for all investors.
In summary, tax efficiency is a critical aspect of assessing the liquidity of long-term investments. Investors should carefully consider the tax implications of selling these investments to ensure they maximize their returns while minimizing tax liabilities. Understanding the tax rules, holding periods, and potential tax benefits associated with long-term investments can help investors make more informed decisions and optimize their investment strategies.
Understanding NAV: The Key to Investment Clarity
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Liquidity refers to how quickly an asset can be converted into cash without significant loss of value. In the case of long-term investments, it means the ability to sell or convert these investments into cash relatively easily and without incurring substantial costs or delays.
Long-term investments are generally considered less liquid compared to short-term or highly liquid assets. Stocks, for example, can be sold quickly on the stock market, but the process may take a few days to settle. Real estate investments often require time and effort to find a buyer, and the sale process can be lengthy and complex.
To evaluate liquidity, consider the investment's marketability, transaction costs, and the time it takes to convert it into cash. For instance, if you own a piece of property, you can assess its liquidity by researching recent sales in the area, understanding the local market conditions, and considering any potential holding costs or taxes.
Liquid investments provide flexibility and the ability to quickly access funds when needed. They can serve as a safety net or a source of emergency funds. Additionally, liquid assets can be easily rebalanced or adjusted to align with changing financial goals or market conditions.
Diversification is essential for long-term investment strategies, and it can be achieved while still maintaining a certain level of liquidity. Consider a mix of assets such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These investments offer a range of options, allowing you to balance risk and return while keeping some assets liquid for quick access to funds.